11 18. Qualitative data collection
Chapter Outline
- Ethical responsibility and cultural respect (5 minute read)
- Critical considerations (3 minute read)
- Preparations for the data gathering process (6 minute read)
- Interviews (20 minute read)
- Focus groups (15 minute read)
- Observations (6 minute read)
- Documents and other artifacts (13 minute read)
Content warning: examples in this chapter contain references to multiple demands on students’ time, loss of employment, sexual assault, trauma-informed care, inpatient psychiatric services, immigration, and the Holocaust.
In this chapter we will explore information to help you plan for and organize your strategy to gather your qualitative data. You will face a number of decisions as you plan this section of your proposal. Gathering qualitative data comes with important ethical and cultural responsibilities. Furthermore, qualitative research can be a powerful tool, but we need to be thoughtful as to how it will be used, as it can as easily become a tool of oppression as one of empowerment. Below are some considerations to help you reflect on some of these dynamics as you plan your study. The first sections apply to every type of qualitative research. Then, we discuss specific strategies to choose from as you plan your qualitative study.
18.1 Ethical responsibility and cultural respect
Learning Objectives
Learners will be able to…
- Explain the special considerations researchers should keep in mind as they design qualitative studies and collect qualitative data
- Determine steps that can be taken to protect participants and exhibit cultural respect during qualitative data collection
Because qualitative data collection so often involves direct contact with human participants and requesting them to share detailed and potentially personally sensitive information with us as researchers, we need to be especially sensitive to ethical considerations. It is a process that requires forethought, planning, and mindful attention throughout. Below are some ethical considerations to help guide you in this activity.
Special limitations to anonymity, confidentiality and ability to remove or withdraw data
Because with qualitative research we are often meeting with people in person to gather data, either from interviews, focus groups, or observations, we clearly can’t guarantee them anonymity. This makes it all the more important to consider what you will do to protect the confidentiality of your participants. This may involve using steps like:
- Using pseudonyms or assigned study identification codes rather than names on study materials
- Stripping all potentially identifying information from transcripts
- Keeping signed informed consent forms separate from other data so the two can’t be linked
- Ensuring that when data is not being used it is appropriately stored and locked so that others outside the research team don’t have access to it
- Ensuring that when data is being used it is not in a space (in person or virtual) where people outside the research team can view it
- Making sure that all members of your research team have been approved by your IRB
- Being very clear in your informed consent who will have access to data and for what purposes
Additionally, at times we will write into our informed consent that participants may withdraw from a study at any time. When a person expresses a desire to withdraw, we remove their data from the study. However, let’s say we conducted interviews and identified a theme that was present in their interview, but was also in a number of other interviews. Their ideas would still be represented in our findings, but we would make sure not to use any quotes or unique contributions from that individual. Also, if a person participates in a focus group, they are part of an interactive dialogue and the discussion is often connected to ideas shared by others as the conversation evolves, making it very hard to completely remove their data. Again, we would respect their wishes by not using any of their direct words, but their presence and contributions shaped the discussion in ways that we won’t be able to excise. It is best to be upfront about this as you are seeking informed consent.
Exercises
- What steps will you be taking to protect the qualitative data that is shared with you?
Prepare with competence, enter with humility
When we ask people to share their thoughts, feelings, and experiences with us, we need to do so in a way that demonstrates respect and authenticity. This means that we approach participants in a professional manner that reflects both competence as a researcher and that illustrates we have done some preparation to learn about the population ahead of time (that we are not “coming in cold”). Activities that can help to demonstrate this are:
- Speaking with knowledgeable community members regarding the topic, our research design, and important aspects of the community (contemporary and historical) before beginning our data collection)
- Examining previous research and other sources of information regarding the group/community we are interested in work with, or if not available, groups/communities that may be similar
- Using data from the first two bullet points, we design our data collection in a way that is culturally sensitive (e.g. where we ask people to provide data, what tools we use, our wording)
- Preparing research materials (e.g. informed consent forms, recruitment materials, informational sheets) that are accessible and understandable for participants
- Providing information and education about research in general and our research topic specifically
This needs to be tempered with humility. Participants grant us the privilege of allowing us to witness some piece of their life. We need to have humility in knowing that we can never fully understand their experiences because we are not them. In a real sense, we are the learners and they are the teachers. Despite us doing the pre-work discussed above to become more competent in our approach, humility means we will ask the participant directly what is acceptable in respect to our data collection. I believe that when taking a culturally humble approach that we should take at least a little bit of time to understand what research means to the participant and what this particular topic means to the them, again, by asking them directly.
Key Takeaways
- Qualitative data collection involves special considerations to help ensure the privacy, confidentiality, or anonymity of participants because of the the often intimate and detailed information that we are collecting as qualitative researchers.
- Preparing for qualitative data collection requires that we educate ourselves as researchers in advance about the population we will be working with to guide and develop our data collection plan. Furthermore, from the standpoint of cultural humility, we don’t assume that these preparations are adequate. We need to verify with participants what is culturally acceptable to them as individuals.
Exercises
- As you prepare for data collection planning, what actions do you plan to take to demonstrate preparations for cultural sensitivity and cultural humility?
18.2 Critical considerations
Learning Objectives
Learners will be able to…
- Assess factors that may impact community members’ perceptions of researchers and their intentions
- Identify opportunities to support greater reciprocity in researcher-participant relationships (especially as it relates to your proposal)
What/whose interests are represented?
Data is a resource that participants own that they choose to share with us. Think about it: When a smartphone app or computer program wants your personal data, you’re usually asked to read a privacy statement and agree to certain terms. Companies are legally required to notify you about their intentions to use the data you may share. And many companies certainly recognize that your data is a valuable resource and seek it out. As researchers, we have similar responsibilities, but with higher ethical standards.
If we are going to ask participants to share this resource, we need to consider why we need it. Clearly, we are invested in this research for some reason, otherwise we wouldn’t be spending our time doing it. Being upfront and genuine with our participants about why this topic is important to us and what we hope comes out of this research is a good first step. We also need to describe to other stakeholders (such as funders or sponsors) who might be involved why we are interested in it. In addition, it is helpful to consider what this research might represent to our participants.
- They may be unsure what to think about the research—This especially may be true if they have had limited exposure to research and/or academia.
- They might be nervous or apprehensive that it could have consequences, either for them individually or for their community
- They might be excited to share their story and may feel as though they are contributing to something larger or some beneficial change
Considering these factors can help us to be more sensitive as we prepare to enter the field for data collection.
Exercises
Think about your study. Put yourself in the role of research participant.
What information would you want to know?
- About research in general
- About the researcher
- About the research topic
How reciprocal is the arrangement?
Building off the preceding discussion about what research might mean to participants, it is also important to consider the reciprocity in the researcher – participant relationship. We know that we are benefiting from the exchange – we are getting data, research findings, research products and any other advantages or opportunities that might be attached to these. However, the benefits are not always as clear on the participant side of this relationship. Sometimes we are able to provide incentives to honor a participant’s time and contribution to a project, but these are often relatively limited. Participants may also intrinsically value making a contribution to a research project that can eventually help to change or build awareness around something that is important to them, but these are often distant and intangible benefits. While we may not be able to change the fact that we may benefit more from this exchange than our participants, it is important for us to acknowledge this and to consider how this can affect the power differential. We may be asking for a lot, with relatively little to offer in return. This is in contrast to participatory research approaches (which have been discussed elsewhere), in which there is much more of an intentional effort to more equally distribute the benefits of these relationships.
Key Takeaways
- As a means of developing empathy as a researcher, it is worth considering what the significance or meaning of research is to the populations we are interested in working with. What do we (as researchers) and our projects represent to community members?
- As critical researchers, we need to be considered with the power differences that often exist as we conduct research, especially in the act of asking for data from participants. The request is often lop-sided, with us benefiting considerably more than the participant.
18.3 Preparations for the data gathering process
Learning Objectives
Learners will be able to…
- Explain important influences to account for in qualitative data gathering
- Organize and document preparatory steps to plan data gathering activities for your qualitative proposal

As you may have guessed from our discussion regarding qualitative research planning and sampling, you have a number of options available for qualitative data gathering, and consequently, a number of choices to make. Your decisions should be driven by your research question and research design, including the resources that are at your disposal for conducting your study. Remember, qualitative research is a labor-intensive venture. While it may not require lots of fancy equipment, it requires a significant investment of people’s time and potentially other resources (e.g. space, incentives for participants, transportation). Each source of data (interviews, focus groups, observations, other artifacts), will require separate planning as you approach data gathering.
Our impact on the data gathering process
In the last chapter, you were introduced to the tool of reflexive journaling as a means of encouraging you to reflect on and document your role in the research process. Since qualitative researchers generally play a very active and involved role in the data gathering process (e.g. conducting interviews, facilitating focus groups, selecting artifacts), we need to consider ways to capture our influence on this part of the qualitative process. Let’s say you are conducting interviews. As you head into the interview, you might be bringing in thoughts about a previous interview, a conversation you just had with your research professor, or worries about finishing all your assignments by the end of the semester! During the interview, you are likely to be surprised by some things that are said or some parts may evoke strong emotions. These responses may lead you to consider pursuing a slightly different line of questioning, and potentially highlighting or de-emphasizing certain aspects. Understanding and being aware of your personal reactions during the data collection process is very important. As part of your design and planning, you may specify that you will reflexively journal before and after each interview in an attempt to capture pre- and post-interview thoughts and feelings. This can help us to consider how we influence and are influenced by the research process. Towards the end of this chapter, after we have had a chance to talk about some of these data gathering strategies, there is a reflexive journal prompt to help you consider how to begin to reflect on the way you as a researcher might impact your work and how you work might impact you.
Exercises
Decision Point
How will you account for your role in the research process?
- What strategies will you employ to demonstrate transparency in your research process?
- This may be your reflexive journal or you may have other thoughts about how you can account for this.
- Whatever you choose, how will you develop a routine/habit around this to ensure that you are regularly implementing this?
Exercises
Reflexive Journal Entry Prompt
This is going to be a bit meta, but for this prompt, I want you reflect on the reflecting you are doing for your reflexive journaling.
- What are your thoughts about reflexive journaling?
- Do you see this as a potentially helpful tool for tracking your influence and reactions? What appeals to you? What puts you off?
- Are you used to thinking reflexively like this—stepping back and thinking about what you are doing and why? Does this come easily/naturally to you?
- If so, how did you develop this mindset?
- If not, how can you strengthen this skill?
When are we done
Finally, as you plan for your data collection you need to consider when to stop. As suggested previously in our discussion on sampling, the concept of saturation is important here. As a reminder, saturation is the point at which no new ideas or concepts are being presented as you continue to collect new pieces of data. Again, as qualitative researchers, we are often collecting and analyzing our data simultaneously. This is what enables us to continue screening for the point of saturation. Of course, not all studies utilize the point of saturation as their determining factor for the amount of data they will collect. This may be predetermined by other factors, such as restricted access or other limitations to the scope of the investigation. While there is no hard and fast rule for the quantity of data you gather, the quality is important; you want to be comprehensive, consistent, and systematic in your approach.

Next, we will discuss some of the different approaches to gathering qualitative data. I’m going to start out with Table 18.1 that allows us to compare these different approaches, providing you with a general framework that will allow us to dive a bit deeper into each one. After you finish reading this chapter, it might be helpful to come back to this table as you continue with your proposal planning.
| Data Gathering Strategy | Strengths | Challenges |
| Interviews | Strengths
|
Challenges
|
| Focus Groups | Strengths
|
Challenges
|
| Observations | Strengths
|
Challenges
|
| Documents & Other Artifacts | Strengths
|
Challenges
|
Key Takeaways
- As you are preparing to initiate data collection, make sure that you have a plan for how you will capture and document your influence on the process. Reflexive journaling can be a useful tool to accomplish this.
- Be sure to take some time to think about when you will end your data collection. Make this an intentional, justified decisions, rather than a haphazard one.
18.4 Interviews
Learning Objectives
Learners will be able to…
- Identify key considerations when planning to use interviewing as a strategy for qualitative data gathering, including preparations, tools, and skills to support it
- Assess whether interviewing is an effective approach to gather data for your qualitative research proposal
A common form of qualitative data gathering involves conducting interviews. Interviews offer researchers a way to gather data directly from participants by asking them to share their thoughts on a range of questions related to a research topic. Interviews are generally conducted individually, although occasionally couples (or other dyads, which consist of a combination of two people) may be interviewed. Interviews are a particularly good strategy for capturing unique perspectives and exploring experiences in detail. People may have a host of responses to the request to be interviewed, ranging from flat out rejection to excitement at the opportunity to share their story. As you plan to conduct your interviews you will need to decide on your delivery method, how you will capture the data, you will construct your interview guide, and hone your research interviewing skills.
Delivery method
As technology has advanced, so too have our options for conducting interviews. While in-person interviews are generally still the mainstay of the qualitative researcher, phone or video-based interviews have expanded the reach of many studies, allowing us to gain access to participants across vast distances with relatively few resources. Interviewing in-person allows you to capture important non-verbal and contextual information that will likely be limited if you choose to conduct your interview via phone or video. For instance, if we conduct an interview by phone, we miss the opportunity to see how our participant interacts with their surroundings and we can’t see if their arms are crossed or their foot is fidgety. This may indicate that a certain topic might make them particularly uncomfortable. Alternatively, we may pose a question that makes a smile come across their face. If we are interviewing in person, we can ask a follow-up question noting the smile as a change in their expression, however, it’s hard to hear a smile over the phone! Additionally, there is something to be said for the ability to make a personal connection with your interviewee that may help them to engage more easily in the interview process. This personal connection can be challenging over the phone or mediated by technology. As an example, I often offer to my students that we can meet for “virtual” office hours using Zoom if it is hard for them to get to campus. However, they will often prefer to come to campus, despite the inconvenience because they would prefer to avoid the technology.
Regardless of which method you select, make sure you are well prepared. If you are meeting in person, know where you are going and allow plenty of time to get there. Remember, you are asking someone to give up their time to speak with you, and time is precious! When determining where you will meet for your interview, you may choose to meet at your office, their home, or a neutral setting in the community. If meeting somewhere in the community, do consider that you want to choose a place where you can reasonably assure the participant’s privacy and confidentiality as they are speaking with you. In most instances, I try to ask participants where they would feel most comfortable meeting. If you are speaking over phone or video, make sure to test your equipment ahead of time so that you are comfortable using it, and make sure that both you and the participant have access to a private space as you are speaking. If participants have minor children, plan ahead for whether the children should stay in the same space as the interview. If not, you may need to arrange child care or at least discuss child care with participants in advance. We also want to be mindful of how we are situated during an interview, ideally minimizing any power imbalances. This may be especially important when meeting in an office, making sure to sit across from our participants rather than behind a desk.
Capturing the data
You will also need to consider how you plan to physically capture your data. Some researchers record their interviews, using either a smartphone or a digital recording device. Recording the exchange allows you to have a verbatim record, which can allow the researcher to more fully participate in the interview, instead of worrying about capturing everything in writing. However, if there is a problem with recording – either the quality of the recording or some other equipment malfunction, the researcher can be up the proverbial creek without a paddle. Additionally, using a recording device may be perceived as a barrier between the researcher and the participant, as the participant may not feel comfortable being recorded. If you do plan to record, you should always ask permission first and announce clearly when you are starting and stopping the recording. If you will use recording equipment, be sure to test it carefully in advance, and bring backup batteries/phone charger with you.

The alternative to recording is taking field notes. Field notes consist of a written record of the interview, completed during the interview. You may elect to take field notes even if you are recording the interview, and most people do. This allows us to capture main ideas that stand out to us as researchers, nonverbal information that won’t show up in a recording, and some of our own reactions as the interview is being conducted. These field notes become invaluable if you have a problem with your recording. Even if you don’t, they provide helpful information as you interpret the data you do have in your transcript (the typed version of your recording).
If you are not recording and are relying completely on your notes, it is important to know that you are not going to capture every word and that you shouldn’t try. You want to plan in advance how you will structure your notes so that they make sense to you and are easy to follow. Try to capture all main ideas, important quotes that stand out, and whenever possible, use the participant’s own words. We need to recognize that when we paraphrase what the person is stating, we are introducing our ‘spin’ on it – their ideas go through our filter. We likely can’t avoid some of this, but we do want to minimize it as much as possible. Part of how we do this when we are relying on field notes is to take our interview notes and create expanded field notes, ideally within 24 hours of the interview. The longer you wait to expand your field notes, the less reliable they become, as our memory fades quickly! Much like they sound, expanded field notes take our jottings from the interview and expand them, providing more detail regarding the context or meaning of the statements that were captured. Expanded field notes may also contain questions, comments, or reactions that we, as the researcher, may have had to the data, which are usually kept in the margins, rather than in the body of the notes.
| Field Notes | Expanded Field Notes |
| Q 4
[Long pause] [Soft] “I was scared” (wow—fear 1st emotion) -provider -no purpose -feel lost/empty -losing house -losing family |
After asking question #4 about the participant’s reaction after he lost his job, there was a long pause in our conversation.
When he started speaking again his tone change dramatically. He was joking around a lot before this, but afterward, he became more subdued and spoke softly, breaking direct eye contact with me to stare at the floor during this part fo the conversation. He stated, “I was scared”. (I was really surprised that this was the first thing he mentioned. Previously when we had touched on job loss, he mostly expressed anger or laughed it off, but this felt very different. I’m glad this question was a bit later in the interview.) When I followed up by asking what he was scared of, he mentioned a number of things, including that he would not be able to provide for his family, that he wouldn’t have a sense of purpose and that his work was an important part of who he is. He also described feeling lost and “empty”. Additionally, he feared if this went on that he might lose his house and even his family. He feared this would change how his family saw him. |
Below are a few resources to learn more about taking quality field notes. Along with the reading, practice, practice, practice!
Resources to learn more about capturing your Field Notes:
Deggs, D., & Hernandez, F. (2018). Enhancing the value of qualitative field notes through purposeful reflection.
Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (2008). Qualitative guidelines project: Fieldnotes.
University of Southern California Libraries. (2019). Research guides: Organizing your social sciences research paper, writing field notes.
Wolfinger, N. (2002). On writing fieldnotes: Collection strategies and background expectancies.
Interview guide
The questions that you ask during your interview will be outlined in a tool called an interview guide. Along with your interview questions, your interview guide will also often contain a brief introduction reminding the participant of the topics that will be covered in the interview and any other instructions you want to provide them (note: much of this will simply serve as a reminder of what you already went over in your informed consent, but it is good practice to remind them right before you get started as well). In addition, the guide often ends with a debriefing statement that thanks the participant for their contribution, inquires whether they have any questions or concerns, and provides contact and resource information as appropriate. Below is a brief interview guide for a study that I was involved with, in which we were interviewing alumni regarding their perceptions of advanced educational needs in the field of social work and specifically their thoughts about practice doctorate of social work (DSW) degrees/programs.
|
Introduction Thank you for taking the time to speak with me today. As a reminder, we are conducting a study to examine your thoughts and perceptions about advanced educational needs in our field and specifically about social work practice doctorate degrees (DSW). We can stop at any time and your participation is completely voluntary. If you need anything explained more clearly as we are going through the questions, please don’t hesitate to ask. Before we get started, I will ask you to complete a brief demographic survey. [pause while participant completes demographic survey] Do you have any questions before we get started?
Interview Guide Questions
Debriefing We are so grateful that you shared your thoughts with us. We will analyze what you shared with us, along with other participants to look for themes and commonalities to help us better understand advanced educational needs in our field and also to help us as we consider developing our own DSW degree at this institution As a reminder, if you have any questions, concerns or you would like to receive copy of the results of our findings, you can contact us at XXX. |
Some interviews are prescribed or structured, with a rigid set of questions that are asked consistently each time, with little to no deviation. This is called a structured interview. More often however, we are dealing with semi-structured interviews, which provide a general framework for the questions that will be asked, but- contain more flexibility to pursue related topics that are brought up by participants. This often leads to researchers asking unplanned follow-up questions to help explore new ideas that are introduced by participants. Sometimes we also use unstructured interviews. These interview guides usually just contain a very open-ended talking prompt that we want participants to respond to. If we are using a highly structured interview guide, this suggests we are leaning toward deductive reasoning apporach—we have a pretty good idea based on existing evidence what we are looking for and what questions we want to ask to help us test our existing understanding. If we are using an unstructured guide, this suggests we are leaning toward an inductive reasoning approach—we start by trying to get people to elaborate extensively on open-ended questions to provide us with data that we will use to develop our understanding of this topic.
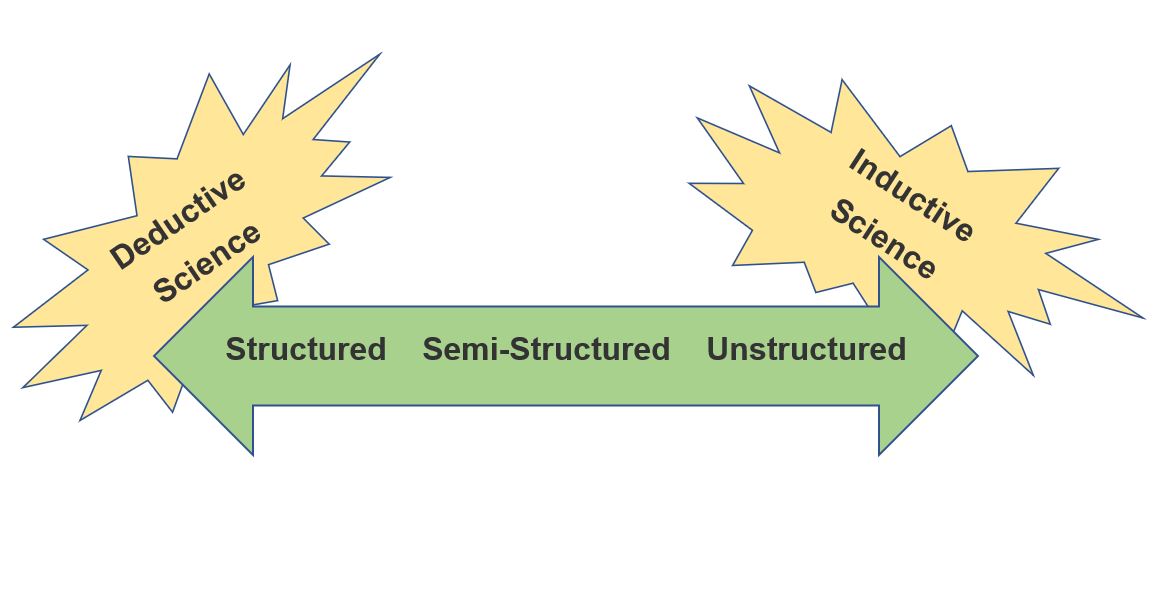
An important concept related to the contents of your interview guide is the idea of emergent design. With qualitative research we often treat our interview guide as dynamic, meaning that as new ideas are brought up, we may integrate these new questions into our interview guide for future interviews. This reflects emergent design, as our interview guide shifts to accommodate our emerging understanding of the research topic as we are gathering data. If you do plan to use an emergent design approach in your interviews, it is important to acknowledge this in your IRB application. When you submit your application, you will need to provide the IRB with your interview guide so that they have an idea of the questions you will be discussing with participants. While using an emergent approach to some of your questions is generally acceptable (and even expected), these questions still should be clearly relevant and related to what was presented in your IRB application. If you find that you begin diverging into new areas that are substantively different from this, you should consider submitting an IRB addendum that reflects the changes, and it may be a good idea to consult with your IRB to see if this is necessary.
Designing interview questions and probes
Making up questions, it sounds easy right? Little kids are running around asking questions all the time! However, what you quickly find when conducting research is that it takes skills, ingenuity and practice to craft good interview questions. If you are conducting an unstructured interview, you will generally have fewer questions and they will be quite broad. Depending on your topic, you might ask questions like:
- Tell me about a time…
- What was it like to…
- What should people understand about…
- What does it mean to…
If your interview is more structured, your questions will be a bit more focused, but with qualitative interviewing, we are still generally trying to get people to open up about their experiences with something, so you will want to design questions that will help them to do this. Probes can be important tools to help us accomplish this. You can think of probes as brief follow-ups that are attached to a particular question that will help you explore a topic a bit further. We usually develop probes either through existing literature or knowledge on a topic, or we might add probes to our interview guide as we begin data collection based on what previous participants tell us. As an example, I’m very interested in research on the concept of wellness. I know that the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) has adopted a heuristic tool, The Wheel of Wellness, that outlines eight dimensions of wellness based on research by Swarbrick (2006).[1] When interviewing participants with the broad, unstructured question “What does wellness mean in your life?”, I might use these eight dimensions that are spokes of this wheel (i.e. emotional, spiritual, intellectual, physical, environmental, financial, occupational, and social) as probes to explore if/how these dimensions might be relevant in the lives of these participants. Probes suggest that we are anticipating that certain areas may be relevant to our question.
Here are a few general guidelines to consider when crafting your interview questions.
Make them approachable
We are usually relatively unfamiliar with our participants, at least on a personal level. This can make sitting down for an interview where we might be asking some deep questions a bit awkward and uncomfortable, at least at first. Because of this, we want to craft our questions in such a way that they are not off-putting, inadvertently accusatory or judgmental, or culturally insensitive. To accomplish this, we want to make sure we phrase questions in a neutral tone (e.g. “Tell me what that was like”, as opposed to, “That sounds horrible, what was that like”). To accomplish this, we can shift perspectives and think about what it would be like for us to be asked these questions (especially by a stranger). Pilot testing is especially important here. You should plan in time for this, both conducting pilot testing and incorporating feedback on questions. Pilot testing involves you taking your questions on a dry-run with a few people outside of your sample. You might consider testing these out with peers, colleagues, or friends to get their perspective. You might want to get feedback on:
- Did the question make sense to them?
- Did they know what information you were looking for and how to respond?
- What was it like to be asked that question?
- What suggestions do they have for rephrasing the question (if it wasn’t clear)?
Also, if we are conducting interviews on topics that may be particularly hard for people to talk about, we will likely want to start out with some questions that are easier to address prior to getting into the heavier topics.
Make them relatable
Unlike surveys, where researchers may not be able to explain the meaning of a question, with interviews, we are present to help clarify questions if needed. However, ideally, our questions are as clear as possible from the beginning. This means that we avoid jargon or technical terms, we anticipate areas that might be hard to explain and try to provide some examples or a metaphor that might help get the point across, and we do our homework to relay our questions in an appropriate cultural context. Like the discussion above, pilot testing our questions can be very helpful for ensuring the relatability of our questions, especially with community representatives. When pilot testing, do your best to test questions with a person/people from the same culture and educational level as the future participants. What sounds good in our heads might make little sense to our intended audience.
Make them individually distinct, but collectively comprehensive
Just like when we are developing survey questions, you don’t want to ask more than one question at the same time. This is confusing and hard to respond to for the participant, so make sure you are only asking about one idea in each question. However, when you are thinking about your list of questions, or about your interview guide collectively, ensure that you have comprehensively included all the ideas related to your topic. It’s extremely disheartening for a qualitative researcher that has concluded their interviews to realize there was a really important area that was not included in the guide. To avoid this, make sure to know the literature in your area well and talk to other people who study this area to get their perspective on what topics need to be included. Additional topics may come up when you pilot test your interview questions.
Interview skills
As social workers, we receive much training regarding interviewing and related interpersonal skills. Many of these skills certainly transfer to interviewing for research purposes, such as attending to both verbal and non-verbal communication, active listening, and clarification. However, it is also important to understand how a practice-related interview differs from a research interview.
The most important difference has to do with providing clarity around the purpose of the interview. For a practice-related interview, we are gathering information to help understand our client’s situation and better meet their needs. The interview is a means to provide quality services to our clients, and the emphasis is on the client and resources flowing to them. However, the research interview is ideologically much different. The interview is the means and the end. The purpose of the interview is to help answer the research question, but most often, there is little or limited direct benefit to the participant. The researcher is largely the beneficiary of the exchange, as the participant provides us with data. If the participant does become upset or is negatively affected by their participation, we may help facilitate their connection with appropriate support services to address this, such as counseling or crisis numbers (and indeed, this is our ethical obligation as a competent researcher). However, counseling and treatment is not our responsibility when conducting research interviews and we should be very careful not to confuse it as such. If we do act in this way, it creates the potential for a dual relationship with the interviewee (participant and client) and puts them in a vulnerable situation. Make sure you are clear what your role is in this encounter.
Along with recognizing the focus of your role, here is a checklist of general tips for qualitative interviewing skills:
- Approach the interview in a relaxed, but professional manner
- Be observant of verbal, nonverbal, and contextual information
- Exhibit a non-judgmental stance
- Explain information clearly and check for comprehension
- Demonstrate respect for your participants and be polite
- Utilize much more listening and much less talking
- Check for understanding when you are unclear, rather than making assumptions
- Know your materials and technology (e.g. informed consent, interview guide, recording equipment)
- Be concise, clear and organized as you are taking notes
- Have a structured approach for what you need to cover and redirect if the conversation is losing focus
- Be flexible enough so that the interview does not become impersonal and disengaging due to rigidity of your agenda
Key Takeaways
- Data collection through interviewing requires careful planning for both how we will conduct our interviews (e.g. in person, over the phone, online) and the nature of the interview questions themselves. An interview guide is an important document to develop in planning this.
- Qualitative interviewing uses similar skills to clinical interviewing, but is markedly different. This difference is due in large part to the very different purpose of these two activities.
Exercises
Let’s get some practice!
Thinking about your topic, if you were to use interviewing as an approach for data collection, identify 4 interview questions that you would consider asking about your topic. Make sure these are open-ended questions so that your participants can elaborate on them.
- Interview question 1:
- Interview question 2:
- Interview question 3:
- Interview question 4:
Now pilot these. Ask a peer to read these questions and think about trying to answer them. You aren’t interested in their actual answers, you want feedback about how these questions were.
- Were they understandable and clear?
- Were they potentially culturally insensitive or offensive in any way?
- Are they something that it seems reasonable that someone could answer (especially with a researcher they likely don’t know previously)?
- Are they asked in a way that are likely to get people to elaborate (rather than just give a one-word answer)?
- What suggestions do they have to address all/any of these areas?
Based on your peer feedback, re-write your four questions incorporating their suggestions.
- Revised interview question 1:
- Revised interview question 2:
- Revised interview question 3:
- Revised interview question 4:
Resources for learning more about conducting Qualitative Interviews.
Baker, S. E., & Edwards, R. (2012) National Centre for Research Methods review paper: How many qualitative interviews is enough?
Clifford, S. Duke University Initiative on Survey Methodology at the Social Science Research Institute (n.d.). Tipsheet: Qualitative interviews.
Harvard University Sociology Dept. (n.d.). Strategies for qualitative interviews.
McGrath et al., (2018). Twelve tips for conducting qualitative research interviews.
Oltmann, S. M. (2016). Qualitative interviews: A methodological discussion of the interviewer and respondent contexts.
A few exemplars of studies employing Interview Data:
Ewart‐Boyle, S., Manktelow, R., & McColgan, M. (2015). Social work and the shadow father: Lessons for engaging fathers in Northern Ireland.
Flashman, S. H. (2015). Exploration into pre-clinicians’ views of the use of role-play games in group therapy with adolescents.
Irvin, K. (2016). Maintaining community roots: understanding gentrification through the eyes of long-standing African American residents in West Oakland.
18.5 Focus groups
Learning Objectives
Learners will be able to…
- Identify key considerations when planning to use focus groups as a strategy for qualitative data gathering, including preparations, tools, and skills to support it
- Assess whether focus groups are an effective approach to gather data for your qualitative research proposal
Focus groups offer the opportunity to gather data from multiple participants at once. As you have likely learned in some of your practice coursework, groups can help facilitate an environment where people feel (more) comfortable sharing common experiences which can often allow them to delve deeper into topics than they may have individually. As people relate to what others in the group say, they often go on to share their responses to these new ideas – offering a collaborative synergy. Of course, similar to the research vs. clinical interview described above, the purpose of the focus group is much different than that of the therapeutic, psychoeducational, or support group. While other elements (e.g. information sharing, encouragement) may take place, the aim of the focus group must remain anchored in the collection of data and that should be made explicitly clear so participants have accurate expectations. As a cautionary note, the advantages discussed above should be the reason you choose to use a focus group to collect data. You should not choose to conduct a focus group solely out of convenience. Focus groups require a considerable amount of planning and skill to execute well, so it is not reasonable to think that just because a focus group allows you to collect data from multiple participants at once that it is an easier option for data gathering.
Group assembly
Assembling your focus group is an important part of your planning process. Generally speaking, focus groups shouldn’t exceed 10-12 participants. When thinking about size, there are a couple things to consider. On the lower end, you do want enough participants so that they don’t feel pressure to be constantly speaking. If you only have a couple of focus group members, it loses most of the collective benefit of the focus group approach, as there are few people to generate and share ideas. On the higher end, you want to avoid having so many participants that not everyone gets to be heard and the group conversation becomes unwieldy and hard to manage.
As you are forming your group, you want to strike up a balance between heterogeneity (difference) and homogeneity (sameness) between your group members. If the group is too heterogeneous, then opinions may be so polarized that it is hard to have a productive conversation about the topic. People may not feel comfortable sharing their opinion or it may be difficult to gain a common understanding across the data. If the group is too homogeneous, then it may be hard to get much depth from the data. People may see the topic so similarly that we don’t gain much information about how differing perspectives think about the issue. You generally want your group composition to be different enough to be interesting and produce good conversation, but similar enough that members can relate to each other and have a cohesive conversation. Along these lines, you also need to consider whether or not your participants know each other. Do they have existing relationships? If they do know each other, we need to anticipate that there may be existing group dynamics. This may influence how people engage in discussion with us. On one hand, they may find it easy to share more freely. However, these dynamics may inhibit them from speaking their mind, as they might be concerned about repercussions for sharing within their social network.
As a final note on group composition, sometimes we make decisions on group members’ characteristics based on our topic. For instance, if we are asking questions about help-seeking and common experiences after (heterosexual) sexual assault, it may be challenging to host a mixed-gender group, where participants may feel triggered or guarded having members of the opposite gender present and therefore potentially less open to sharing. It is important to consider the population you are working with and the types of questions you are asking, as this can help you to be sensitive to their perceptions and facilitate the creation of a safe space. Other issues, such as race, age, levels of education, may require consideration as you think about your group composition.

Related to feelings of safety, the setting you select for your focus group is an important decision. Much like with interviews, we want participants to feel as comfortable and at-ease as possible, however, it is perhaps less common to use someone’s home for the purpose of a focus group because we are often bringing together people who may not know one another. As such, try to select a place that feels neutral (e.g. some people may not feel comfortable in a church or a courthouse), accessible, convenient, and that offers privacy for participants. If you are working with a particular group or community, there may be a space that is especially relevant or familiar for people that may work well for this purpose. A community gatekeeper or other knowledgeable community member can be an excellent resource in helping to identify where a good space might be. Seating in a circle will help participants to share more easily. Focus group organizers often provide refreshments as an incentive and to make participants feel more comfortable. If you decide to provide refreshments, be sensitive to issues like common dietary restrictions and cultural preferences.
Roles of the researcher(s)
Ideally, you are conducting your focus group with a co-researcher. This is important because it allows you to divide up the tasks and makes the process more manageable. Most often, one of you will take on the main facilitator role, with responsibilities for providing information and instructions, introducing topics, asking follow-up questions and generally structuring the encounter. The other person takes on a note-taking/processing role. While not necessarily silent, they likely say very little during the focus group. Instead, they are focused on capturing the context of the encounter. This may include taking notes about what is said, how people respond or react, other details about the space and the overall exchange as a whole. They will also often be especially attentive to group dynamics and capturing these whenever possible. Along with this, if they see that certain group members are dominating or being left out of the conversation, they may help the facilitator to address or shift these dynamics so that the sharing is more equitable. Finally, if something arises where a participant becomes upset or there is an emergency where they need to leave the room, having a co-researcher allows one of you to remain with the group, while the other can attend to the person in distress. For consistency sake, you may want to maintain roles throughout data collection. If you do decide to alternate roles as you conduct multiple focus groups, it is important that you both conduct the respective roles as similarly as possible. Remember, research is about the systematic collection of data, so you want your data collection to follow a consistent process. Below is a chart that offers some tips for each of these roles.
| Main Facilitator | Observer |
|
|
Focus group guide and preparations
As in your preparation for an interview, you will want to spend considerable time developing your focus group guide and the questions it contains. Be sure the language you use in your questions is appropriate for the educational level of your participants; you will need to use vocabulary that is clear and not “jargon”. At the same time, you also want to avoid talking down to your participants. You will probably want to start with some easier, non-threatening questions to help break the ice for the group and help get folks comfortable talking and sharing their input. Be prepared to ask questions in a different way or follow up with probes to help prod the conversation along if a question falls flat or fails to elicit a dialogue. In addition, you will want to plan introductions, both to the study and to one another. Usually we stick to first names, and occasionally during introductions, participants will share how they are connected to the topic of the research. Just like in many practice-related groups, facilitators usually take time to review group norms and expectations before getting started with questions. Some common norms to discuss are:
- Not talking over other participants
- Being respectful of other participants’ contributions
- All people are expected to participate in the conversation
- Not pressuring people to respond to a question if they are uncomfortable
- Using respectful language and avoiding derogatory, discriminatory or accusatory language or tone
- Not using electronic devices and silencing cell-phones during the focus group
- Allowing others ample time to contribute to the conversation and not dominating the discussion
Another expectation to address that is especially important to include is confidentiality. It is important to make clear to participants that what is shared in the group should be kept confidential and not discussed outside the context of the focus group. Additionally, it is important to let participants know that while the researchers ask all participants to protect the confidentiality of what is shared, they can’t guarantee that will be honored. Below figure 18.4 offers an example of a focus group guide template to help you think about how to structure this type of document.
|
Welcome & Housekeeping
Guidelines
Focus Group Questions I will introduce each of these questions and allow people to respond with their thoughts, viewpoints, and perspectives. Please allow a person to finish their thought before stating your own. I may invite people directly to contribute to the conversation if we have not heard from you; if you would prefer not to share at that time, feel free to say “pass”. I may ask you clarifying questions or request that you explain an idea further for me and I may ask the larger group their response to something that has been shared. Let’s get started. Question 1 Probe 1A Probe 1B Question 2 Probe 2A Probe 2B Probe 2C Probe 2D Debriefing Thank you so much for joining us today and sharing your thoughts about ___________. If you would like to learn more about our project as it progresses or if you have any questions about the results of today’s discussion, we would love to hear from you! Here is a card with my contact information so you can reach me. Email is the fast way to get through to me. If anything we talked about was upsetting and you feel like you need to speak with someone, as a reminder, you can reach out to _______________. Again, it has been our pleasure to meet with you today. |
Capturing your data
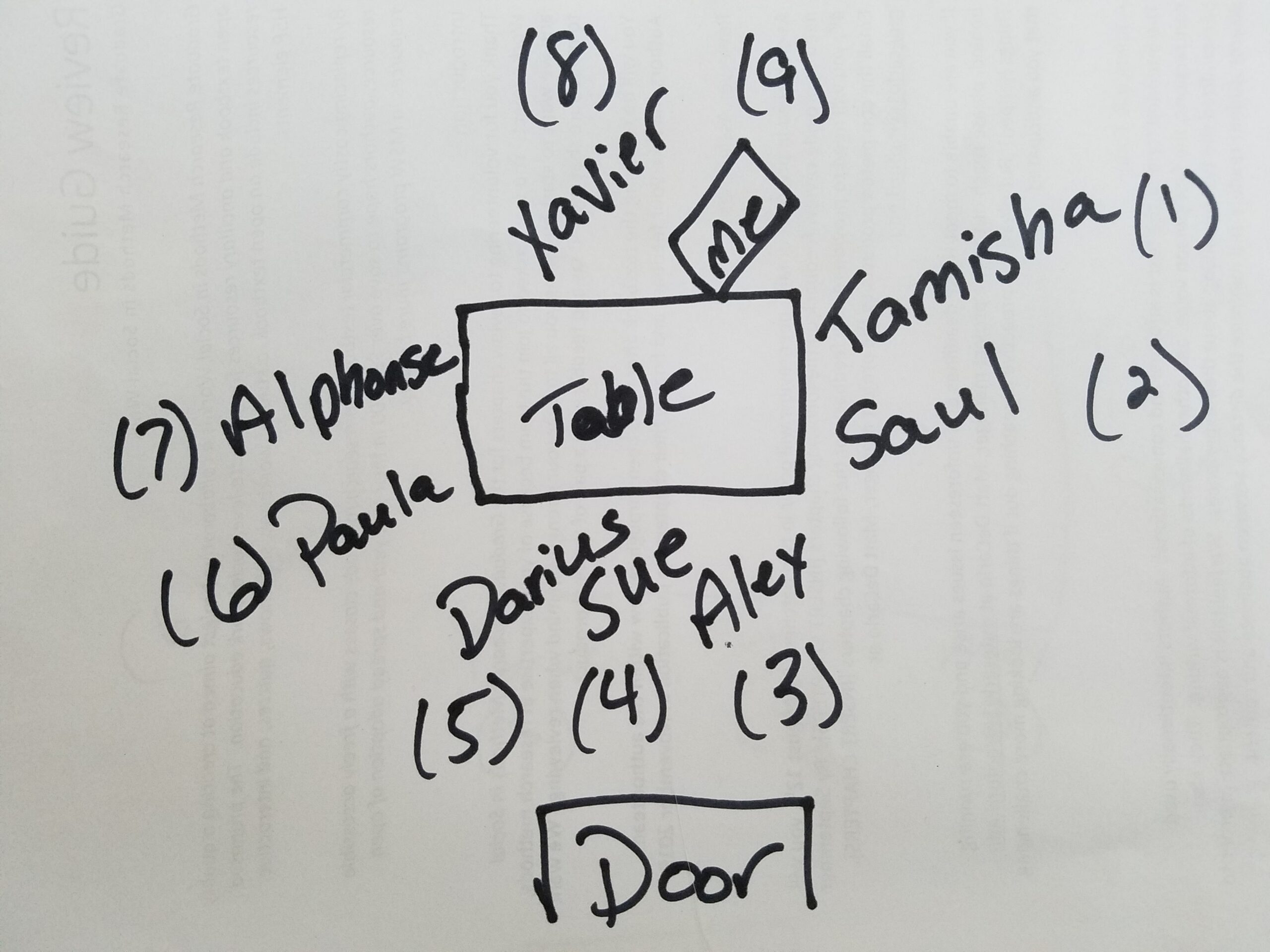
Finally, as with interviews, you will need to plan how you will capture the data from your focus group(s). Again, you may choose to record the focus groups, take field notes, or use a combination of both. There are some special considerations that apply to these choices when using a focus group, however. First, if recording, anticipate that it may be especially challenging when transcribing the recording to determine who said what. In addition, the quality of the recording can become a challenge. Despite requests for individuals to speak one at a time, inevitably there will be spots where there are multiple people talking at once, especially with an animated group. Additionally, do test the recording devices, ideally in the space you will be using them. You want to make sure that it can pick up everyone’s voice, even if they are soft-spoken and seated a distance from the device. If you are relying solely on a recording and there is a problem with it, it can be difficult to surmount the barriers this can pose. If this occurs with an interview, while not ideal, you can re-interview a person to replace the information, but re-creating a focus group can be a logistical nightmare. When taking field notes, it is a good practice to make a quick seating chart at the beginning so you can make quick references for yourself of who is saying what (see Figure 18.5). Regardless of what system you use to stay organized in taking these notes, make sure to have one that works for you. The conversations will likely happen more rapidly and will include multiple voices, so you will want to be prepared in advance.
Key Takeaways
- Focus groups offer a valuable tool for qualitative data collection when the topic we are exploring might best be understood through a group discussion that helps participants verbally process and consider their experiences, thoughts, and opinions with others.
- Details like focus group composition, roles of co-facilitators, and anticipation of group norms or guidelines require our attention as we prepare to host a focus group.
Exercises
Reflexive journal prompt
How do you feel about conducting a focus group?
- What about it is appealing
- What about it seems challenging
- Would you prefer to be the main facilitator or the observer (and why)?
- What might make using a focus group a good choice for your specific research question?
- What might make using a focus group a poor choice for your specific research question?
Resources to learn more about conducting Focus Groups.
Leung, F. H., & Savithiri, R. (2009). Spotlight on focus groups.
Duke, ModU (2016, October 19). Powerful concepts in social science: Preparing for focus groups, qualitative research methods
Onwuegbuzie et al. (2009). A qualitative framework for collecting and analyzing data in focus group research.
Nyumba et al. (2018). The use of focus group discussion methodology: Insights from two decades of application in conservation.
Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (2008). Qualitative Guidelines Project: Focus groups.
A few exemplars of studies employing Focus Groups:
Foote, W. L. (2015). Social work field educators’ views on student specific learning needs.
Hoover, S. M., & Morrow, S. L. (2016). A qualitative study of feminist multicultural trainees’ social justice development.
Kortes-Miller, K., Wilson, K., & Stinchcombe, A. (2019). Care and LGBT aging in Canada: A focus group study on the educational gaps among care workers.
18.6 Observations
Learning Objectives
Learners will be able to…
- Identify key considerations when planning to use observations as a strategy for qualitative data gathering, including preparations, tools, and skills to support it
- Assess whether observations are an effective approach to gather data for your qualitative research proposal

Observational data can also be very important to the qualitative researcher. As discussed in Chapter 17, observations can provide important information about context, reactions, behaviors, exchanges, and expressions. The focus of observations may be individuals, interactions between people or within groups, environments or settings, or events like artistic expressions (e.g. plays, poetry readings, art shows), public forums (e.g. town hall meetings, community festivals), private forums (e.g. board meetings, family reunions), and finally, your reactions or responses as the researcher to any and all of these. We will be discussing a variety of different types of qualitative designs in Chapter 22, including ethnography. Observational data is especially important for ethnographic research designs.
Researcher engagement
Observational data gathering is a more indirect form of data collection when compared with previous methods we have discussed. With both interviews and focus groups, you are gathering data directly from participants. When making observations, we are relying on our interpretation of what is going on. Even though we are often not directly interacting with people, we generally have an ethical responsibility to disclose that we are gathering data by making observations and gain consent to do so. That being said, there are some instances where we are making observations in public spaces, and in these instances disclosure may not be necessary because we are not gathering any identifiable information about specific people. These instances are rare, but if you are in doubt, consult with your IRB.
Even though I just suggested that making observations is often a more indirect form of data gathering, it does exist on a continuum. If utilizing observational data, you will need to consider where you fall on this continuum. Some research designs situate the researcher as an active participant in the community or group that they are studying, while other designs have the researcher as an independent and detached onlooker. In either case, you need to consider how your presence, either involved or detached, may influence the data you are gathering. This requires us to think of this on a more individual or micro level (how do the individuals we are directly observing perceive us) and a more mezzo or even macro level (how does the community or group of people we are studying collectively feel about our presence and our research)? Are people changing their behavior because of your presence? Are people monitoring or censoring what they say? We can’t always know the answers to these questions, but we can try to reduce these concerns by making repeated observations over time, rather than using a one-time, in-and-out data gathering mission. This means actually spending time within the community that is the focus of your observation. Taking the time to make repeated observations will allow you to develop a reasonable framework of understanding, which in turn will empower you to better interpret what you see and help you determine whether your observations and interpretation are consistent.
Observational skills
When gathering observational data, you are often attending to or taking in many different dimensions. You are potentially observing:
- the context of the environment
- the content of what is being said
- behaviors of people
- affective or emotional aspects of interactions
- sequences of events
- your own reactions to what is being observed
To capture this information, you will need to be keenly aware, focused, and organized. Additionally, you need to make sure you are capturing clear descriptions of what is going on. Remember, notes that seem completely logical and easy to understand at the time you are taking them can become vague and confusing with the passage of time and as you gather more and more data. Part of the clarity of your description often involves taking a non-judgmental approach to documenting your observations. While this may seem easy, judgments or biases frequently slip into our thinking and writing (unbeknownst to us). Along with a non-judgmental stance, researchers making observations also attempt to be as unobtrusive as possible. This means being conscious of your behaviors, your dress and overall appearance. If you show up wearing a suit and tie, and carrying a clipboard while everyone else is wearing jeans and t-shirts, you are likely to stick out like a sore thumb. This is also likely to influence how participants respond and interact with you. Know the environment that you are making your observations in, with a goal of blending in as much as possible.
Capturing your data
Observational data is most often captured using field notes. Using recordings for observational data is infrequently used in social work research. This is especially true because of the potential for violations of privacy and threats to confidentiality that recordings (video or audio) may pose to participants. Mirroring our discussion above, when taking field notes, make sure to be organized and have a plan for how you will structure your notes so they are easy to interpret and make sense to you. Creswell (2013)[2] suggests capturing ‘descriptive’ and ‘reflective’ aspects in your observational field notes. Table 18.3 offers some more detailed description of what to include as you capture your data and corresponding examples.
| Areas to capture | Aspects to consider in each area | Example |
| Demographic Info | What details help to frame the logistics of the interaction
|
Date: 7/17/19
Place: Pride Rock Time: 10:30 AM (start); 1:00 PM (stopped) |
| Descriptive Aspects | What you observe externally
|
Simba is sitting across the room from Mufasa
Neither are making eye-contact After two or so minutes, Mufasa shifts in his chair and raises his eyebrow, clearing his throat… |
| Reflective Aspects | What you observe internally
|
I’m uncomfortable watching the exchange—it’s only been a couple of minutes, but it feels like much longer
It seems extremely hard for these two to discuss their feelings |
For the purposes of qualitative research, our observations are generally unstructured or more naturalistic. However, you may also see mention of more systematic or structured observations. This is more common for quantitative data collection, where we may be attempting to capture or count the frequency with which a specific behavior or event occurs.
Key Takeaways
- Observational data collection can be an effective tool for gathering information about settings, interactions, and general human behavior. However, since this is gathered strictly through the researchers own direct observation, it is not a source of data on people’s thoughts, perceptions, values, opinions, beliefs or interpretations.
- There are a range of aspects that we may want to take note of while we are observing (e.g. the setting, interactions, descriptions of people, etc.).
- While we are making our observations, we generally want to do so as inconspicuously and non-judgmentally as possible.
Resources for learning more about conducting Qualitative Observations.
Kawulich, B.B. (2005, May) Participant observation as a data collection method.
Kawulich, B.B. (2012). Collecting data through observation. In C. Wagner, B. Kawulich, & M. Garner (Eds.), Doing social research: A global context (150-160). New York: McGraw Hill.
Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (2008). Qualitative Guidelines Project: Observations.
Sliter, M. (2014, June 30). Observational methods: Research methods.
A few exemplars of studies employing qualitative observations:
Avby et al. (2017). Knowledge use and learning in everyday social work practice: A study in child investigation work.
Wilkins et al. (2018). A golden thread? The relationship between supervision, practice, and family engagement in child and family social work.
Wood et al. (2017). The “gray zone” of police work during mental health encounters: Findings from an observational study in Chicago.
18.7 Documents and other artifacts
Learning Objectives
Learners will be able to…
- Identify key considerations when planning to analyze documents and other artifacts as a strategy for qualitative data gathering, including preparations, tools, and skills to support it
- Assess whether analyzing documents and other artifacts is an effective approach to gather data for your qualitative research proposal
Qualitative researchers may also elect to utilize existing documents (e.g. reports, newspapers, blogs, minutes) or other artifacts (e.g. photos, videos, performances, works of art) as sources of data. Artifact analysis can provide important information on a specific topic, for instance, how same-sex couples are portrayed in the media. They also may provide contextual information regarding the values and popular sentiments of a given time and/or place. When choosing to utilize documents and other artifacts as a source of data for your project, remember that you are approaching these as a researcher, not just as a consumer of media. You need to thoughtfully plan what artifacts you will include, with a clear justification for their selection that is solidly linked to your research question, as well as a plan for systematically approaching these artifacts to identify and obtain relevant information from them.
Obtaining your artifacts
As you begin considering what artifacts you will be using for your research study, there are two points to consider: what will help you to answer your research question and what can you gain access to. In addressing the first of these considerations, you may already have a good idea about what artifacts are needed because you have done a substantial amount of preliminary work and you know this area well. However, if you are unsure, or you need to supplement your existing knowledge, some general sources can include: librarians, historians, community experts, topical experts, organizations or agencies that address the issue or serve the population you will be studying, and other researchers who study this area. In considering access, if the artifacts are public the answer may be a straightforward yes, but if the documents are privately held, you may need to be granted permission – and remember, this is permission to use them for research purposes, not just to view them. When obtaining permission, get something in writing, so that you have this handy to submit with your IRB application. While the types of artifacts you might include are almost endless (given they are relevant to your research question), Table 18.4 offers a list of some ideas for different sources you might consider:
| Newspapers | Films | Meeting Minutes |
| Organizational Charts | Autobiographies | Blogs |
| Web Pages | Text Message Discussions | Pieces of Art |
| Objects in a Special Collection of a Museum | Pamphlets | Dance Recitals |
| Speeches | Historical Records | Letters |
Artifact analysis skills
Consistent with other areas of research, but perhaps especially salient to the use of artifacts, you will require organizational skills. Depending on what sources you choose to include, you may literally have volumes of data. Furthermore, you might not just be dealing with a large amount of data, but also a variety of types of data. Regardless of whether you are using physical or virtual data, you need to have a way to label and catalog (or file) each artifact so that you can easily track it down. As you collect specific information from each piece, make sure it is tagged with the appropriate label so that you can track it back down, as you very well may need to reference it later. This is also very important for honest and transparency in your work as a qualitative researcher – documenting a way to trace your findings back to the raw data.
In addition to staying organized, you also need to think specifically about what you are looking for in the artifacts. This might seem silly, but depending on the amount of data you are dealing with and how broad your research topic is, it might be hard to ‘separate the wheat from the chaff’ and figure out what is important or relevant information. Sometimes this is more clearly defined and we have a prescribed list of things we are looking for. This prescribed list may come from existing literature on the topic. This prescribed list may be based on peer-reviewed literature that is more conceptual, meaning that it focuses on defining concepts, putting together propositions, formulating early stage theories, and laying out professional wisdom, rather than reporting research findings. Drawing on this literature, we can then examine our data to see if there is evidence of these ideas and what this evidence tells us about these concepts. If this is the case, make sure you document this list somewhere, and on this list define each item and provide a code that you can attach when you see it in each document. This document then becomes your codebook.
However, if you aren’t clear ahead of time what this list might be, you may take an emergent approach, meaning that you have some general ideas of what you are seeking. In this event, you will actively create a codebook as you go, like the one described above, as you encounter these ideas in your artifacts. This helps you to gain a better understanding of what items should be included in your list, rather than coming in with preconceived notions about what they should be. There will be more about tracking this in our next chapter on qualitative analysis. Whether you have a prescribed list or use a more emergent design to develop your codebook, you will likely make modifications or corrections to it along the way as your knowledge evolves. When you make these changes, it is very important to have a way to document what changes you made, when, and why. Again, this helps to keep you honest, organized, and transparent. Just as another reminder, if you are using predetermined codes that you are looking for, this is reflective of a more deductive approach, whereas seeking emergent codes is more inductive.
Finally, when using artifacts, you may also need to bring in some creative, out-of-the-box thinking. You may be bringing together many different pieces of data that look and sound nothing alike, yet you are seeking information from them that will allow you tell a cohesive story. You may need to be fluid or flexible in how you are looking at things, and potentially challenge your preconceived notions.
Capturing the data
As alluded to above, you may have physical artifacts that you are dealing with, digital artifacts or representations of these artifacts (e.g. videos, photos, recordings), or even field notes about artifacts (for instance, if you take notes of a dramatic performance that can’t be recorded). A large part of what may drive your decisions about how to capture your data may be related to your level of access to those artifacts: can you look at it? Can you touch it, can you take it home with you, can you take a picture of it? Depending on what artifacts we are talking about, some of these may be important questions. Regardless of the answers to these questions, you will need to have a clearly articulated and well-documented plan for how you are obtaining the data and how you will reference it in the future. Table 18.4 provides a list of data gathering activities you might consider, both for documents and for other audiovisual materials.
Exercises
What types of artifacts might you have access to that might help to answer your research question(s)?
Tips
- These could be artifacts available at your field placement, publically available media, through school, or through public institutions
- These can be documents or they can be audiovisual materials
- Think outside the box, how can you gather direct or indirect indications of the thing you are studying
Generate a list of at least 3
- _
- _
- _
Again, drawing on Creswell’s (2013) suggestion of capturing ‘descriptive’ and ‘reflective’ aspects in your field notes, Table 18.5 offers some more detailed description of what to include as your capture your data and corresponding examples when focusing on an artifact.
| Areas to capture | Aspects to consider in each area | Example |
| Demographic Info | What details help to frame the logistics of the interaction
|
Date: 1/22/19
Artifact: Moved to Tears by Nieves Dominguez, Photo Exhibit Source: NY Arts for Action Studios Source Information: Studio is a non-profit that hosts artistic work and events that are intended to raise consciousness and produce change for groups experiencing inequality and oppression Nieves is a world-renown photographer who specializes in capturing the experience of immigrant journeys and is a vocal advocate for immigrant rights |
| Descriptive Aspects | What you observe externally
|
As you begin moving through the exhibit, you first encounter a number of photographs of people in tears. There are pictures of people crying alone, crying in groups, wailing, subdued, appearing joyous, appearing sorrowful…
The room is silent. Despite the hall being quite crowded, you can hear a pin drop. Based on proximity to each other, it generally seems that people are attending in small groups (3-6). A few single people appear to be viewing, as well. |
| Reflective Aspects | What you observe internally
|
I want to know more about the focal point of the photographs. While all of these initial photos contain someone in tears, they rarely seem to be the focus of the picture. I don’t know if this is meant to convey the often hidden sufferings and joys of these subjects or perhaps the many and varied forces that influence their lives. |
Resources to learn more about qualitative research with artifacts.
Bowen, G. A. (2009). Document analysis as a qualitative research method.
Rowsell, J. (2011). Carrying my family with me: Artifacts as emic perspectives.
Hammond, J., & McDermott, I. (n.d.). Policy document analysis.
Wang et al. (2017). Arts-based methods in socially engaged research practice: A classification framework.
A few exemplars of studies utilizing documents and other artifacts.
Casey, R. C. (2018). Hard time: A content analysis of incarcerated women’s personal accounts.
Green, K. R. (2018). Exploring the implications of shifting HIV prevention practice Ideologies on the Work of Community-Based Organizations: A Resource dependence perspective.
Sousa, P., & Almeida, J. L. (2016). Culturally sensitive social work: promoting cultural competence.
Secondary data analysis
I wanted to briefly provide some special attention to secondary data analysis at the end of this chapter. In the past two chapters we have focused our sights most often on what we would call raw data sources. However, you can of course conduct qualitative research with secondary data, which is data that was collected previously for another research project or other purpose; data is not originating from your research process. If you are fortunate enough to have access and permission to use qualitative data that had already been collected, you can pose a new research question that may be answered by analyzing this data. This saves you the time and energy from having to collect the data yourself!
You might procure this data because you know the researcher that collected the original data. For instance, as a student, perhaps there is a faculty member that allows you access to data they had previously collected for another project. Alternatively, maybe you locate a source of qualitative data that is publicly available. Examples of this might include interviews previously conducted with Holocaust survivors. Finally, you might register and join a research data repository. These are sites where contributing researchers can house data that other researchers can view and request permission to use. Syracuse University hosts a repository that is explicitly dedicated to qualitative data. While there are more of these emerging, it may be a challenge to find the specific data you are looking for in a repository. You should also anticipate that data from repositories will have all identifiable information removed. Sharing data you have collected with a repository is a good way to extend the potential usefulness and impact of data, but it also should be anticipated before you collect your data so that you can build it into any informed consent so participants are made aware of the possibility.
Computer Assisted Qualitative Data Analysis Software (CAQDAS)
Some qualitative researchers use software packages known as Computer Assisted Qualitative Data Analysis Software (CAQDAS) in their work. These are tools that can aid researchers in managing, organizing and manipulating/analyzing their data. Some of the more common tools include NVivo, Atlas.ti, and MAXQDA, which have licensing fees attached to them (although many have discounted student rates). However, there are also some free options available if you do some hunting. Taguette Project is the only free and open source CAQDAS project that is currently receiving updates, as previous projects like RQDA which built from the R library are not in active development. Taguette is a young project, and unlike the free alternatives for quantitative data analysis, it lacks the sophisticated analytical tools of commercial CAQDAS programs.
It is unlikely that you will be using a CAQDAS for a student project, mostly because of the additional time investment it will take to become familiar with the software and associated costs (if applicable). In fact the best way to avoid spending money on qualitative data analysis software is to do your analysis by hand or using word processing or spreadsheet software. If you continue on with other qualitative research projects, it may be worth some additional study to learn more about CAQDAS tools. If you do choose to use one of these products, it won’t magically do the analysis for you. You need to be clear about what you are using the software for and how it supports your analysis plan, which will be the focus of our next chapter.
Resources to learn more about CAQDAS.
Maher et al. (2018). Ensuring rigor in qualitative data analysis: A design research approach to coding combining NVivo with traditional material methods.
Woods et al. (2016). Advancing qualitative research using qualitative data analysis software (QDAS)? Reviewing potential versus practice in published studies using ATLAS. ti and NVivo, 1994–2013.
Zamawe, F. C. (2015). The implication of using NVivo software in qualitative data analysis: Evidence-based reflections.
As you continue to plan your research proposal, make sure to give practical thought to how you will go about collecting your qualitative data. Hopefully this chapter helped you to consider which methods are appropriate and what skills might be required to apply that particular method well. Revisit the table in section 18.3 that summarizes each of these approaches and some of the strengths and challenges associated with each of them. Collecting qualitative data can be a labor-intensive process, to be sure. However, I personally find it very rewarding. In its very forms, we are bearing witness to people’s stories and experiences.
Key Takeaways
- Artifact analysis can be particularly useful for qualitative research as a means of studying existing data; meaning we aren’t having to collect the data ourselves, but we do have to gather it. As a limitation, we don’t have any control over how the data was created, since we weren’t involved in it.
- There are many sources of existing data that we can consider for artifact analysis. Think of all the things around us that can help to tell some story! Artifact analysis may be especially appealing as a potential time saver for student researchers if you can gain permission to use existing artifacts or use artifacts that are publicly available.
- Artifact analysis still requires a systematic and premeditated approach to how you will go about extract information from your artifacts.
Exercises
Reflexive Journal Entry Prompt
Here are a few questions to get you thinking about the role that you play as you gather qualitative data.
- What are your initial thoughts about qualitative data collection?
- Which of these data collection strategies are you drawn to?
- Why might that be?
- What excites you about this process?
- What worries you about this process?
- What aspects of yourself will strengthen or enhance this process?
- What aspects of yourself may hinder or challenge this process?
Exercises
Decision Point: How will you go about qualitative data collection?
- What approach(es) will you use to collect your qualitative data?
- Justify your choice(s) here in relation to your research question and availability of resources at your disposal
- What steps will you need to put in place to ensure a high quality, systematic process for data collection?
- who will be collecting data
- what will be involved
- how will it be safely stored and organized
- how are you protecting human participants
- if you have a team, how is communication being established so everyone is “on the same page”
- how will you know you are done
- What additional information do you need to know to use this approach?
- Swarbrick, M. (2006). A wellness approach. Psychiatric Rehabilitation Journal, 29(4), 311. ↵
- Creswell, J. W. (2013). Chapter 7. Data collection. In J. W. Creswell, Qualitative Inquiry & Research Design: Choosing Among Five Approaches (3rd ed.), Los Angeles: Sage ↵
- Harris, M. and Fallot, R. (2001). Using trauma theory to design service systems. New Directions for Mental Health Services. Jossey Bass; Farragher, B. and Yanosy, S. (2005). Creating a trauma-sensitive culture in residential treatment. Therapeutic Communities, 26(1), 93-109. ↵
A form of data gathering where researchers ask individual participants to respond to a series of (mostly open-ended) questions.
A form of data gathering where researchers ask a group of participants to respond to a series of (mostly open-ended) questions.
Observation is a tool for data gathering where researchers rely on their own senses (e.g. sight, sound) to gather information on a topic.
The identity of the person providing data cannot be connected to the data provided at any time in the research process, by anyone.
For research purposes, confidentiality means that only members of the research team have access potentially identifiable information that could be associated with participant data. According to confidentiality, it is the research team's responsibility to restrict access to this information by other parties, including the public.
Fake names assigned in research to protect the identity of participants.
Numbers or a series of numbers, symbols and letters assigned in research to both organize data as it is collected, as well as protecting the identity of participants.
A process through which the researcher explains the research process, procedures, risks and benefits to a potential participant, usually through a written document, which the participant than signs, as evidence of their agreement to participate.
an administrative body established to protect the rights and welfare of human research subjects recruited to participate in research activities conducted under the auspices of the institution with which it is affiliated
For the purposes of research, authenticity means that we do not misrepresent ourselves, our interests or our research; we are genuine in our interactions with participants and other colleagues.
An approach to research that more intentionally attempts to involve community members throughout the research process compared to more traditional research methods. In addition, participatory approaches often seek some concrete, tangible change for the benefit of the community (often defined by the community).
A research journal that helps the researcher to reflect on and consider their thoughts and reactions to the research process and how it may be shaping the study
The point where gathering more data doesn't offer any new ideas or perspectives on the issue you are studying. Reaching saturation is an indication that we can stop qualitative data collection.
A combination of two people or objects
An interview guide is a document that outlines the flow of information during your interview, including a greeting and introduction to orient your participant to the topic, your questions and any probes, and any debriefing statement you might include. If you are part of a research team, your interview guide may also include instructions for the interviewer if certain things are brought up in the interview or as general guidance.
Context is the circumstances surrounding an artifact, event, or experience.
Notes that are taken by the researcher while we are in the field, gathering data.
Expanded field notes represents the field notes that we have taken during data collection after we have had time to sit down and add details to them that we were not able to capture immediately at the point of collection.
A statement at the end of data collection (e.g. at the end of a survey or interview) that generally thanks participants and reminds them what the research was about, what it's purpose is, resources available to them if they need them, and contact information for the researcher if they have questions or concerns.
Interview that uses a very prescribed or structured approach, with a rigid set of questions that are asked very consistently each time, with little to no deviation
An interview that has a general framework for the questions that will be asked, but there is more flexibility to pursue related topics that are brought up by participants than is found in a structured interview approach.
Interviews that contain very open-ended talking prompt that we want participants to respond to, with much flexibility to follow the conversation where it leads.
starts by reading existing theories, then testing hypotheses and revising or confirming the theory
when a researcher starts with a set of observations and then moves from particular experiences to a more general set of propositions about those experiences
Emergent design is the idea that some decision in our research design will be dynamic and change as our understanding of the research question evolves as we go through the research process. This is (often) evident in qualitative research, but rare in quantitative research.
Probes a brief prompts or follow up questions that are used in qualitative interviewing to help draw out additional information on a particular question or idea.
Testing out your research materials in advance on people who are not included as participants in your study.
Someone who has the formal or informal authority to grant permission or access to a particular community.
A document that will outline the instructions for conducting your focus group, including the questions you will ask participants. It often concludes with a debriefing statement for the group, as well.
Ethnography is a qualitative research design that is used when we are attempting to learn about a culture by observing people in their natural environment.
Making qualitative observations that attempt to capture the subjects of the observation as unobtrusively as possible and with limited structure to the observation.
The analysis of documents (or other existing artifacts) as a source of data.
unprocessed data that researchers can analyze using quantitative and qualitative methods (e.g., responses to a survey or interview transcripts)
A code is a label that we place on segment of data that seems to represent the main idea of that segment.
A document that we use to keep track of and define the codes that we have identified (or are using) in our qualitative data analysis.
study publicly available information or data that has been collected by another person
in a literature review, a source that describes primary data collected and analyzed by the author, rather than only reviewing what other researchers have found
Data someone else has collected that you have permission to use in your research.
These are sites where contributing researchers can house data that other researchers can view and request permission to use
These are software tools that can aid qualitative researchers in managing, organizing and manipulating/analyzing their data.

