8.2 Your Professional Identity
The field of human services as the profession we are familiar with today dates back to the late 19th and early 20th centuries when nationalized systems of welfare provision were established. Today the field of human services spans several disciplines, adding versatility to the profession. When you enter the field, your professional identity contributes to your sense of purpose and self-worth. Studies suggest that when your identity is tied to your profession, you will be more successful and remain in your profession longer (Moorhead, 2019; Shim, Hwang, & Lee, 2009).
A study based on literature reviews identified five components that are critical for professional identity development:
- reflection
- mentoring
- professional socialization
- self-efficacy
- critical thinking
By reflecting on past experiences, you can learn from the past and apply those lessons to future activities. Mentorship helps to share and expose the intern to social norms, values, and behavioral standards held by the profession. Professional socialization strengthens the sense of belonging and identification with those who share common experiences, thus helping in confidence building and trust in other professionals. Self-efficacy refers to the belief that you are capable of engaging in behavior to create desired changes. It contributes to job satisfaction and job performance. Critical thinking, the self-directed, self-disciplined, self-monitored, and self-corrective thinking used in problem solving allows us to reflect, examine, and gauge our professional identity development. The internal work we do on ourselves has a ripple effect on our identities. Much like Sigmund Freud explained, we wear masks for every occasion, but underneath all those masks is our bare essence. As interns, as we develop our personal and professional identities, we must always remember that reflection as a tool for transformation.
8.2.1 Looking Back, Looking Forward
Most of the concepts you have learned in this and other classes have given you a foundation for building your professional identity. One of the most important building blocks for human service workers is developing an assertive professional personality. It is a definite advantage to be assertive with clients and other service providers. Just like setting boundaries helps people protect themselves against unwanted and often draining experiences, assertiveness is communicating to be heard so you can get your needs met.
Along with assertive communication comes the responsibility of facing interpersonal conflict in a mature and responsible manner. Conflicts are part of the human experience and result from not getting our needs met. Sound familiar? Yes, in assertiveness you express your desire to be heard, in conflict resolution you work toward a solution that works the best for all of the parties involved. This can be difficult when people have two different goals in the same situation.
8.2.2 Developing Assertiveness
Assertiveness relies on communication and respecting the needs and wishes of others while honoring their boundaries. As part of being an assertive person, there is the responsibility of being clear about your intentions and expectations, but above all, having a sense of self-control for those times when others around you are creating a toxic environment. If needing to confront someone, be clear as to what you want; take a firm stand without turning to rude behavior.
Assertiveness does not mean aggressiveness, quite the contrary. An assertive person is action-oriented and emotionally strong, but does not rely on getting their needs met by ignoring the needs of others. Reduce your stress level by knowing what to accept and when to say ‘no.’ If you not getting clear feedback, repeat the point in a non-confrontational way using “I” statements, such as “I feel/think/believe.” Learn to be observant, and pick your battles judiciously. Base your decisions on facts and keep your emotions under control. Apologize when it is appropriate. Being assertive does not mean you have to always be right. You will soon see yourself as having a higher sense of self-confidence and self-esteem. Avoid being a “victim” and the emotional doormat of others. Practice assertiveness.
8.2.3 Conflict Resolution
Conflicts are bound to occur during an internship where differences of opinions or miscommunication exists. Conflicts are about not getting our needs met.Whether these needs appear factual or fictitious to others, they are real to the person with the conflict, and a solution needs to be found before it escalates into a major dispute. Conflicts that have the potential to negatively influence the organization’s productivity have to be addressed as soon as possible.
The Thomas-Kilmann Instrument (TKI), an assessment tool for measuring a person’s conflict-handling style, has been the standard for professionals for decades. The TKI uses an individual’s behavior measured along two dimensions:
- assertiveness, the extent to which the person attempts to satisfy their own concerns.
- cooperativeness, the extent to which the person attempts to satisfy the other person’s concerns.
These two dimensions are used to define five different styles for responding to conflict situations:
- Competing (assertive and uncooperative)
- Accommodating (unassertive and cooperative)
- Avoiding (unassertive and uncooperative)
- Collaborating (both assertive and cooperative – this is an ideal solution)
- Compromising (moderate in both assertiveness and cooperativeness)
Figure 9.1 plots out these different styles according to their level of assertiveness and cooperativeness.
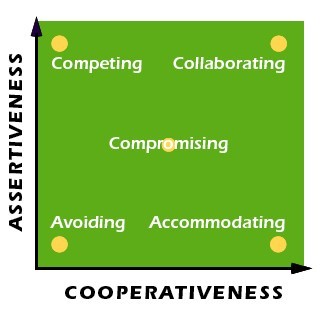 Figure 9.1-Understanding your conflict style can help you learn to be more effective at dealing with difficult situations
Figure 9.1-Understanding your conflict style can help you learn to be more effective at dealing with difficult situations
Now that you know what is the conflict-handling style of the parties involved, apply the following standard techniques for reaching a solution:
- Separate the person from the problem (focus on the issue not the person).
- Meet in a mutually agreeable place (meet in a safe, neutral environment).
- Brainstorm ideas for possible solutions that benefit both parties.
- Agree on a solution (select the best mutually acceptable solution and document it).
8.2.4 Self-Control
Self-control is mastering one’s desires, exercising delayed gratification, to ensure that we do not over- or under-indulge. Individuals with high self-control are happier, healthier, and wealthier and this is because almost all traits and behaviors are partly influenced by genetic factors (Polderman et al., 2015). Genes significantly contribute to individual differences in self-control across the lifespan.
There are three components of self-control:
- impulsivity (the ability to avoid making thoughtless decisions))
- emotions (the ability to control one’s response to difficult circumstances)
- desires (the ability to prevent actions or emotions that impact good judgment)
Too much self control results in perfectionism. People with low self-control have difficulty regulating their feelings, actions, self-discipline, and goals, and lack willpower and the ability to control their emotions. People with low self-control have difficulty building self-confidence, making friends and getting along with at work.
8.2.5 Mentors, Role Models, and Accountability Partners
As you develop your professional role, it is important to identify other professionals or colleagues who can provide support and guidance. Mentors, role models, and accountability partners can each serve a role in your professional development.
Mentors are essential to the success of interns as they are introduced to the field or their internship. The mentoring relationship affords important experiences including improved job performance, recognition by others, personal fulfillment, increased job satisfaction and commitment. The mentor can impart life-altering experiences fostering professional maturity.
Mentors tend to be senior professionals who encourage and support the younger interns in their transition from student to practitioner and also in professional development. A unique aspect of the mentor- intern relationship that differs from other personal relationships is the focus on career development and growth. The “role model” helps the intern primarily by serving as an example and facilitating a professional identity development. Role modeling is less formal than mentoring, although both teach responsibilities and expectations of their professions, role models are more of people who embody ideal behaviors, whereas the mentor is actually teaching or guiding directly.
Often internships will include the establishment of a “buddy system” or “accountability partners.” The role of the accountability partner is similar to that used by recovery support groups, in that the person in recovery is assigned a sponsor who is there to ensure that the person in recovery does not fall back into old habits. Ideally, an accountability partner should be someone that makes interns comfortable enough to share their confidences with them. The accountability partner encourages the interns to continue in their progress and help in areas where progress is lacking. Accountability peers are dedicated to maintaining the interns on track. They also do not judge when interns do not live up to the standards or relapse into old habits. Accountability partners promote, coach and sometimes offer a shoulder to cry on. Ideally the accountability partner is a fellow intern whose mature judgment is known and trusted.
8.2.6 Licenses and Attributions for Your Professional Identity
“Your Professional Identity” by Ivan Mancinelli-Franconi PhD is licensed under CC BY 4.0.
