22 4.3 Acid-Base Reactions
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Identify some common acids and bases
- Define acid-base reactions
- Recognize and identify examples of acid-base reactions
- Predict the products of acid-base reactions.
Acids and Bases
The definition of an acid is often cited as: any compound that increases the amount of hydrogen ion (H+) in an aqueous solution. The chemical opposite of an acid is a base. The equivalent definition of a base is that a base is a compound that increases the amount of hydroxide ion (OH−) in an aqueous solution. These original definitions were proposed by Arrhenius (the same person who proposed ion dissociation) in 1884, so they are referred to as the Arrhenius definition of an acid and a base, respectively.
You may recognize that, based on the description of a hydrogen atom, an H+ ion is a hydrogen atom that has lost its lone electron; that is, H+ is simply a proton. Do we really have bare protons moving about in aqueous solution? No. What is more likely is that the H+ ion has attached itself to one (or more) water molecule(s). To represent this chemically, we define the hydronium ion H3O+(aq), a water molecule with an extra hydrogen ion attached to it. as H3O+, which represents an additional proton attached to a water molecule. We use the hydronium ion as the more logical way a hydrogen ion appears in an aqueous solution, although in many chemical reactions H+ and H3O+ are treated equivalently.
For purposes of this brief introduction, we will consider only the more common types of acid-base reactions that take place in aqueous solutions. In this context, an acid is a substance that will dissolve in water to yield hydronium ions, H3O+. As an example, consider the equation shown here:
The process represented by this equation confirms that hydrogen chloride is an acid. When dissolved in water, H3O+ ions are produced by a chemical reaction in which H+ ions are transferred from HCl molecules to H2O molecules (Figure 1).
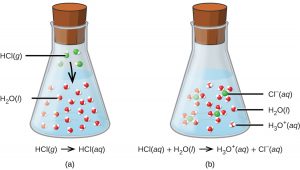
The nature of HCl is such that its reaction with water as just described is essentially 100% efficient: Virtually every HCl molecule that dissolves in water will undergo this reaction. Acids that completely react in this fashion are called strong acids, and HCl is one among just a handful of common acid compounds that are classified as strong (Table 1).
| Compound Formula | Name in Aqueous Solution | |
|---|---|---|
| HBr | hydrobromic acid | |
| HCl | hydrochloric acid | |
| HI | hydroiodic acid | |
| HNO3 | nitric acid | |
| HClO4 | perchloric acid | |
| HClO3 | chloric acid | |
| H2SO4 | sulfuric acid | |
| Table 1. Common Strong Acids | ||
A far greater number of compounds behave as weak acids and only partially react with water, leaving a large majority of dissolved molecules in their original form and generating a relatively small amount of hydronium ions.
| Compound Formula | Name in Aqueous Solution |
|---|---|
| HF | hydrofluoric acid |
| HCN | hydrocyanic acid |
| HC2H3O2 | acetic acid |
| HNO2 | nitrous acid |
| HClO | hypochlorous acid |
| HClO2 | chlorous acid |
| H2SO3 | sulfurous acid |
| H2CO3 | carbonic acid |
| H3PO4 | phosphoric acid |
| Table 2. Common Weak Acids | |
Weak acids are commonly encountered in nature, being the substances partly responsible for the tangy taste of citrus fruits, the stinging sensation of insect bites, and the unpleasant smells associated with body odor. A familiar example of a weak acid is acetic acid, the main ingredient in food vinegars:
A base is a substance that will dissolve in water to yield hydroxide ions, OH−. The most common bases are ionic compounds composed of alkali or alkaline earth metal cations (groups 1 and 2) combined with the hydroxide ion—for example, NaOH and Ca(OH)2. When these compounds dissolve in water, hydroxide ions are released directly into the solution. For example, KOH and Ba(OH)2 dissolve in water and dissociate completely to produce cations (K+ and Ba2+, respectively) and hydroxide ions, OH−. These bases, along with other hydroxides that completely dissociate in water, are considered strong bases.
Consider as an example the dissolution of lye (sodium hydroxide) in water:
This equation confirms that sodium hydroxide is a base. When dissolved in water, NaOH dissociates to yield Na+ and OH− ions. This is also true for any other ionic compound containing hydroxide ions. Since the dissociation process is essentially complete when ionic compounds dissolve in water under typical conditions, NaOH and other ionic hydroxides are all classified as strong bases.
Unlike ionic hydroxides, some compounds produce hydroxide ions when dissolved by chemically reacting with water molecules. In all cases, these compounds react only partially and so are classified as weak bases. These types of compounds are also abundant in nature and important commodities in various technologies. For example, global production of the weak base ammonia is typically well over 100 metric tons annually, being widely used as an agricultural fertilizer, a raw material for chemical synthesis of other compounds, and an active ingredient in household cleaners (Figure 3). When dissolved in water, ammonia reacts partially to yield hydroxide ions, as shown here:
Under typical conditions, only about 1% of the dissolved ammonia is present as NH4+ ions.

Acid-Base Reactions
An acid-base reaction is one in which a hydrogen ion, H+, is transferred from one chemical species to another. Such reactions are of central importance to numerous natural and technological processes, ranging from the chemical transformations that take place within cells and the lakes and oceans, to the industrial-scale production of fertilizers, pharmaceuticals, and other substances essential to society. The subject of acid-base chemistry, therefore, is worthy of thorough discussion.
The reaction between an acid and a base is called an acid-base reaction or a neutralization reaction. Although acids and bases have their own unique chemistries, the acid and base cancel each other’s chemistry to produce a rather innocuous substance—water. In fact, the general acid-base reaction is
acid + base [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex] water + salt
where the term salt is used to define any ionic compound (soluble or insoluble) that is formed from a reaction between an acid and a base. In chemistry, the word salt refers to more than just table salt. For example, the balanced chemical equation for the reaction between HCl(aq) and KOH(aq) is
HCl(aq) + KOH(aq) [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex] H2O(ℓ) + KCl(aq)
where the salt is KCl. By counting the number of atoms of each element, we find that only one water molecule is formed as a product. However, in the reaction between HCl(aq) and Mg(OH)2(aq), additional molecules of HCl and H2O are required to balance the chemical equation:
2 HCl(aq) + Mg(OH)2(aq) [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex] 2 H2O(ℓ) + MgCl2(aq)
Here, the salt is MgCl2. This is one of several reactions that take place when a type of antacid—a base—is used to treat stomach acid.
There are acid-base reactions that do not follow the “general acid-base” equation given above. For example, the balanced chemical equation for the reaction between HCl(aq) and NH3(aq) is
HCl(aq) + NH3(aq) [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex] NH4Cl(aq)
Example 1
Write the neutralization reactions between each acid and base.
a) HNO3(aq) and Ba(OH)2(aq) b)H3PO4(aq) and Ca(OH)2(aq)
Solution
First, we will write the chemical equation with the formulas of the reactants and the expected products; then we will balance the equation.
a) The expected products are water and barium nitrate, so the initial chemical reaction is
HNO3(aq) + Ba(OH)2(aq) [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex] H2O(ℓ) + Ba(NO3)2(aq)
To balance the equation, we need to realize that there will be two H2O molecules, so two HNO3 molecules are required:
2HNO3(aq) + Ba(OH)2(aq) [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex] 2H2O(ℓ) + Ba(NO3)2(aq)
This chemical equation is now balanced.
b) The expected products are water and calcium phosphate, so the initial chemical equation is
H3PO4(aq) + Ca(OH)2(aq) [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex] H2O(ℓ) + Ca3(PO4)2(s)
According to the solubility rules, Ca3(PO4)2 is insoluble, so it has an (s) phase label. To balance this equation, we need two phosphate ions and three calcium ions; we end up with six water molecules to balance the equation:
2 H3PO4(aq) + 3 Ca(OH)2(aq) [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex]6 H2O(ℓ) + Ca3(PO4)2(s)
This chemical equation is now balanced.
Test Yourself
Write the neutralization reaction between H2SO4(aq) and Sr(OH)2(aq).
Answer
H2SO4(aq) + Sr(OH)2(aq) [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex]2 H2O(ℓ) + SrSO4(aq)
Neutralization reactions are one type of chemical reaction that proceeds even if one reactant is not in the aqueous phase. For example, the chemical reaction between HCl(aq) and Fe(OH)3(s) still proceeds according to the equation
3 HCl(aq) + Fe(OH)3(s) [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex]3 H2O(ℓ) + FeCl3(aq)
even though Fe(OH)3 is not soluble. When one realizes that Fe(OH)3(s) is a component of rust, this explains why some cleaning solutions for rust stains contain acids—the neutralization reaction produces products that are soluble and wash away. Washing with acids like HCl is one way to remove rust and rust stains, but HCl must be used with caution!
Complete and net ionic reactions for neutralization reactions will depend on whether the reactants and products are soluble, even if the acid and base react. For example, in the reaction of HCl(aq) and NaOH(aq),
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex]H2O(ℓ) + NaCl(aq)
the complete ionic reaction is
H+(aq) + Cl−(aq) + Na+(aq) + OH−(aq) [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex]H2O(ℓ) + Na+(aq) + Cl−(aq)
The Na+(aq) and Cl−(aq) ions are spectator ions, so we can remove them to have
H+(aq) + OH−(aq) [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex] H2O(ℓ)
as the net ionic equation. If we wanted to write this in terms of the hydronium ion, H3O+(aq), we would write it as
H3O+(aq) + OH−(aq) [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex] 2H2O(ℓ)
With the exception of the introduction of an extra water molecule, these two net ionic equations are equivalent.
Gas-forming Acid-Base reactions
A driving force for certain acid-base reactions is the formation of a gas. Common gases formed are H2, O2, and CO2.
For example:
2HCl(aq) + Na2CO3(aq) [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex] H2CO3(aq) + 2NaCl(aq) [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex] CO2(g) + H2O(l) + 2NaCl(aq)
The above example can be viewed as an acid-base reaction followed by a decomposition. The driving force in this case is the gas formation. The decomposition of H2CO3 into CO2 and H2O is a very common reaction. Both Na2CO3 and NaHCO3 mixed with acid result in a gas-forming acid-base reaction.
HCl(aq) + NaHCO3(aq) [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex] H2CO3(aq) + NaCl(aq) [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex] CO2(g) + H2O(l) + NaCl(aq)
Food and Drink App: Acids in Foods
Many foods and beverages contain acids. Acids impart a sour note to the taste of foods, which may add some pleasantness to the food. For example, orange juice contains citric acid, H3C6H5O7. Note how this formula shows hydrogen atoms in two places; the first hydrogen atoms written are the hydrogen atoms that can form H+ ions, while the second hydrogen atoms written are part of the citrate ion, C6H5O73−. Lemons and limes contain much more citric acid—about 60 times as much—which accounts for these citrus fruits being more sour than most oranges. Vinegar is essentially a ~5% solution of acetic acid (HC2H3O2) in water. Apples contain malic acid (H2C4H4O5; the name malic acid comes from the apple’s botanical genus name, malus), while lactic acid (HC3H5O3) is found in wine and sour milk products, such as yogurt and some cottage cheeses.
Table 3 “Various Acids Found in Food and Beverages” lists some acids found in foods, either naturally or as an additive. Frequently, the salts of acid anions are used as additives, such as monosodium glutamate (MSG), which is the sodium salt derived from glutamic acid. As you read the list, you should come to the inescapable conclusion that it is impossible to avoid acids in food and beverages.
| Acid Name | Acid Formula | Use and Appearance |
|---|---|---|
| acetic acid | HC2H3O2 | flavouring; found in vinegar |
| adipic acid | H2C6H8O4 | flavouring; found in processed foods and some antacids |
| alginic acid | various | thickener; found in drinks, ice cream, and weight loss products |
| ascorbic acid | HC6H7O6 | antioxidant, also known as vitamin C; found in fruits and vegetables |
| benzoic acid | HC6H5CO2 | preservative; found in processed foods |
| citric acid | H3C6H5O7 | flavouring; found in citrus fruits |
| dehydroacetic acid | HC8H7O4 | preservative, especially for strawberries and squash |
| erythrobic acid | HC6H7O6 | antioxidant; found in processed foods |
| fatty acids | various | thickener and emulsifier; found in processed foods |
| fumaric acid | H2C4H2O4 | flavouring; acid reactant in some baking powders |
| glutamic acid | H2C5H7NO4 | flavouring; found in processed foods and in tomatoes, some cheeses, and soy products |
| lactic acid | HC3H5O3 | flavouring; found in wine, yogurt, cottage cheese, and other sour milk products |
| malic acid | H2C4H4O5 | flavouring; found in apples and unripe fruit |
| phosphoric acid | H3PO4 | flavouring; found in some colas |
| propionic acid | HC3H5O2 | preservative; found in baked goods |
| sorbic acid | HC6H7O2 | preservative; found in processed foods |
| stearic acid | HC18H35O2 | anticaking agent; found in hard candies |
| succinic acid | H2C4H4O4 | flavouring; found in wine and beer |
| tartaric acid | H2C4H4O6 | flavouring; found in grapes, bananas, and tamarinds |
Table 3. Various Acids Found in Food and Beverages
Key Concepts and Summary
Chemical reactions are classified according to similar patterns of behaviour. Acid-base reactions involve the transfer of hydrogen ions between reactants.
General acid-base reactions, also called neutralization reactions can be summarized with the following reaction equation:
ACID(aq) + BASE(aq) [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex] H2O(l) + SALT(aq) or (s)
The DRIVING FORCE for a general acid-base reaction is the formation of water.
Gas-forming acid-base reactions can be summarized with the following reaction equation:
ACID(aq) + NaHCO3 or Na2CO3(aq) [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex] H2O(l) + CO2(g) + SALT(aq) or (s)
The DRIVING FORCE for a gas-forming acid-base reaction is the formation of gas. There are three ways of
There are three ways of representing a neutralization reaction, using a molecular equation, complete ionic equation or net ionic equation, as described in section 6.1.
Review-Reflect, Extend
1. Predict the products of each acid-base combination listed. Assume that a neutralization reaction occurs.Write a balanced chemical equation for each neutralization reaction.
a) HCl and KOH
b) H2SO4 and KOH
2. Explain why the net ionic equation for the neutralization reaction between HCl(aq) and KOH(aq) is the same as the net ionic equation for the neutralization reaction between HNO3(aq) and RbOH.
3. Write the complete and net ionic equations for the neutralization reaction between HCl(aq) and KOH(aq) using the hydronium ion in place of H+. What difference does it make when using the hydronium ion?
Extend
Many pharmaceuticals contain N atoms in their chemical structures, and can act as weak bases in a similar fashion to ammonia. When this occurs the nitrogen picks up a hydrogen, and the molecule becomes a cation. Two important consequences arise: first, the cation can be paired an ion such as chloride or succinate to produce an ionic compound which can be made into a solid tablet. Second, the drug molecule will have increased water solubility. Why would that matter? Do a little searching on the web for “drug solubility switch” and see what you can learn.
Answers
1. a) KCl and H2O HCl + KOH [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex] KCl + H2O
b) K2SO4 and H2O H2SO4 + 2 KOH [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex] K2SO4 + 2 H2O
2. Because the salts are soluble in both cases, the net ionic reaction is just H+(aq) + OH−(aq) [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex] H2O(ℓ).
3. Complete ionic equation:
H3O+(aq) + Cl−(aq) + K+(aq) + OH−(aq) [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex] 2 H2O(ℓ) + K+(aq) + Cl−(aq)
Net ionic equation:
H3O+(aq) + OH−(aq) [latex]\longrightarrow[/latex] 2 H2O(ℓ)
The difference is simply the presence of an extra water molecule as a product.
Glossary
acid: substance that produces H3O+ when dissolved in water
acid-base reaction: reaction involving the transfer of a hydrogen ion between reactant species
base: substance that produces OH− when dissolved in water
neutralization reaction: reaction between an acid and a base to produce salt and water
salt: ionic compound that can be formed by the reaction of an acid with a base that contains a cation and an anion other than hydroxide or oxide
strong acid: acid that reacts completely when dissolved in water to yield hydronium ions
strong base: base that reacts completely when dissolved in water to yield hydroxide ions
weak acid: acid that reacts only to a slight extent when dissolved in water to yield hydronium ions
weak base: base that reacts only to a slight extent when dissolved in water to yield hydroxide ions