Chapter 1: BE Verb in the Simple Present
Where We Live
 Learning Goals
Learning Goals
At the end of this chapter you should be able to:
Recognize and use the BE verb
- in the affirmative and negative
- with contractions
- with yes/no questions and short answers
- with information questions
and use parts of speech to construct simple sentences
Prepare
Activity 1.1: Prereading
Directions: Ask your partner the following questions. Write down the answers so you can report back to the class.
1. What’s your name?
_____________________________________________________________________
2. How old are you?
_____________________________________________________________________
3. Where are you from?
_____________________________________________________________________
4. What language(s) do you speak?
_____________________________________________________________________
5. What do you miss about your country?
_____________________________________________________________________
6. Where do you live now (city, town, or rural area)?
_____________________________________________________________________
7. Do you live in an apartment, house, mobile home, or something else?
_____________________________________________________________________
8. Please describe where you live. What do you see when you look out the window? Is there a yard, trees, plants, a sidewalk, a street, buildings, or something else?
_____________________________________________________________________
Now introduce your partner to your group or the whole class. Use the information you learned about your partner. Use the BE verb and other verbs.
Read
Directions: Read this story out loud with a partner. One person reads a paragraph, then the other person reads the next paragraph. When you are finished, read the story again. This time, read the paragraphs that you did not read.
Ana & Pedro
I am Ana. I am from Guatemala. I am 20 years old. My brother, Pedro is here too. Pedro is 19 years old. We both study English at CCC. We are Spanish-speakers. Pedro and I have black hair and black eyes. We are not tall, and we are not thin. We are average in height and weight.
We live with our aunt and uncle. We live in an apartment near a park. Our apartment is on the ground floor. There is a patio outside our back door. Next to the patio is the park. There are paths for walking and a playground for kids. It is really nice. We are outside on sunny days. However, there are not many trees! On hot days, there is not much shade.
We like Oregon, but we are homesick for Guatemala. We are not really “sick”. We just miss our country and its culture. Our mom is in Guatemala. She is a great “pupusa” cook. Pupusas are a thick corn tortilla filled with beans and meat. We are homesick for her and her cooking. We are also tired of the cold! We prefer a warmer climate. However, we like the green trees and blue skies of Oregon. The people are so nice, too! Oregonians are friendly and helpful people.
Activity 1.2: Comprehension
Directions: Ask and answer the following questions with your partner. Do you or your partner have anything in common with Ana and Pedro? Be prepared to discuss what you learn about Ana and Pedro with the class.
1. Who are Ana and Pedro?
_____________________________________________________________________
2. Where are they from?
_____________________________________________________________________
3. Where do they live now?
_____________________________________________________________________
4. Who do Ana and Pedro live with?
_____________________________________________________________________
5. Describe Ana and Pedro’s living situation. What is near their apartment?
_____________________________________________________________________
6. What do they miss in their country?
_____________________________________________________________________
7. What do they like about Oregon?
_____________________________________________________________________
8. What don’t they like about Oregon?
_____________________________________________________________________
Explore
Activity 1.3: Noticing
Part 1 Directions: Go back to the story about Ana and Pedro. Find all the BE verbs. There are three forms in the present tense: am, is, and are.
Every sentence in English must have a subject AND a verb. A subject is:
- the person, place, or thing doing the action of the verb, or
- the person, place, or thing being described by the verb.
The subject and verb always “go with,” “match,” or “agree with” each other.
Part 2 Directions: Write the form of the BE verb that comes after each subject.
1. What form of the BE verb agrees with (comes after) I?
_____________________________________________________________________
2. What form of the BE verb agrees with (comes after) he/she/it?
_____________________________________________________________________
3. What form of the BE verb agrees with (comes after) you/we/they?
_____________________________________________________________________
Activity 1.4: Try It Out!
Directions: Now that you have read the story about Ana and Pedro, write the correct form of the BE verb on the lines. You will write about yourself in numbers *5 and *8.
1. My name ___________________ Ana.
2. Ana ___________________ a student.
3. Pedro ___________________ from Guatemala.
4. Ana ___________________ 20 years old.
5. I ___________________ ___________________ years old. *
6. It ___________________ a sunny day.
7. Ana and Pedro ___________________ Spanish-speakers.
8. I ___________________ a ___________________ -speaker. *
9. They ___________________ in their apartment.
10. We ___________________ in our classroom.
*Talk about yourself here.
Discover
The BE verb describes, characterizes, defines, and shows time, place, or location. The words after the BE verb give more information about the words before the BE verb (except in “there” sentences).
Uses of the BE Verb
Look at the table for the uses of the BE verb. As you read across, you will find out when to use the BE verb, which parts of speech are important, and example sentences.
| BE Verb Uses | Words After BE Verb | Example Sentences |
|---|---|---|
| to describe people and things (including age) | Adjective: a describing word
good, bad, new, old, young, little, big, tired, married |
I am happy. Ana is 20 years old. She is young. The dogs are playful. You are smart. |
| to characterize or define the subject | Noun: person, place, thing, or idea | I am a student. Pedro is a man. Ana and Pedro are Guatemalans. |
| to show time, dates, or place | Preposition + noun = Prepositional Phrase | Our school is in Oregon City. Christmas is on December 25th. Our class is at 9:00 am. |
| to show location | Location words: here, there, near, far, inside, outside, upstairs, downstairs | Ana’s apartment is near a park. Pedro is upstairs studying. |
| to show place of origin | Use the preposition “from” | Ana and Pedro are from Guatemala. I am from Portland. Where are you from? |
| in “there” sentences | The subject comes after the BE verb. is → singular subjects are → plural subjects. |
There is a dog in the park. There are trees near our apartment. |
Activity 1.5: Writing
Now that you have written some sentences with the BE verb, think about what the BE verb does in the sentence. It links or connects the subject of the sentence to the rest of the sentence. The BE verb helps the writer say more about the subject.
- Nouns characterize or define the subject.
- Adjectives describe the subject.
- Prepositions (place-words) show time or location.
Examples
I am a student. → I = student
She is a young woman. → she = young woman
They are funny. → they = funny
She is at school. → she = location/at school
Class is at 9:00 am. → class = show time/9:00 am
Forms of the BE Verb
How do we form a BE verb sentence? In the Explore section above, you matched the subject pronouns to the BE forms: am, is, and are. Subject pronouns are: I, you, he, she, it, we, you, and they.
 Affirmative Statements with the BE Verb
Affirmative Statements with the BE Verb
| Subject | BE Verb | Noun, Adjective, or Prepositional Phrase |
|---|---|---|
| I | am | a student. |
| He She It |
is | inside the house. at work. a cat. |
| You We They |
are | beautiful. in class. smart. |
Activity 1.6: Complete the Table
Directions: What did you notice about the verbs you wrote in the Try It Out! activity? Which subject agreed with each verb form? Write the BE verb that agrees with each subject. A subject is the person, place, or thing doing the action or being described by the verb.
| Subject | BE Verb |
|---|---|
| I | 1. |
| you | 2. |
| he, she, it | 3. |
| we | 4. |
| they | 5. |
As you can see, there are three forms of the BE verb.
- am agrees with the subject I
- is agrees with the subjects he, she, it
- are agrees with the subjects you, we, they
Activity 1.7: Fill-in-the-Blank
Directions: Complete the sentences with the correct form of the BE verb.
1. He _______________ from China.
2. I _______________ a cashier.
3. She _______________ late for class.
4. They _______________ hungry.
5. You _______________ busy.
6. It _______________ dark now.
7. We _______________ students.
8. Kit _______________ a teacher.
Activity 1.8: Writing
Directions: Change the singular to plural or the plural to singular. Use the correct verb form with your new sentence. Use the information above to guide you.
Examples
She is a teacher. → They are teachers.
We are hungry. → He is hungry.
They are from Venezuela. → She is from Venezuela.
1. I am from Portland, Oregon.
We __________________________________________________________
2. I am from Guatemala.
You __________________________________________________________
3. I am 20 years old.
They _________________________________________________________
4. Pedro is here, too.
They _________________________________________________________
5. Mom is a great cook.
You __________________________________________________________
6. Pedro is a student at CCC.
We __________________________________________________________
7. We are not tall.
I _____________________________________________________________
8. Our apartment is beautiful.
The apartments ______________________________________________
9. All of the patios are lovely.
Our patio _____________________________________________________
10. The garden path is in the sun.
The garden paths _____________________________________________
Activity 1.9: Listening
Directions: Listen as your teacher reads a story about Ana and Pedro. Write the correct form of the BE verb (am, is, are) on the lines below. The verb needs to agree with the subject.
Ana and Pedro live with their aunt and uncle. Their aunt’s name (1)__________ Maria Carmen. Everyone calls her Carmen. Their uncle’s name (2)__________ Miguel. Carmen (3)__________ 40 years old, and Miguel (4)__________ 41 years old. Carmen (5)__________ a preschool teacher, and Miguel (6)__________ a landscaper. They (7)__________ married, and they have two children. Both children (8)__________ boys. Therefore, Ana and Pedro have two nephews. Their names (9)__________ Luis and Diego. Luis (10)__________ older than Diego. Both boys (11)__________ in high school. Luis (12)__________ in 10th grade. Diego (13)__________ in the 9th grade. Luis plays soccer, but Diego plays basketball. Both boys (14)__________ bilingual. They speak English at school and Spanish at home.
Affirmative Contractions
Here are the BE verb forms with their contractions. Contractions shorten and combine two words. This is very common in English.
Notice that SINGULAR pronouns (except the subject I) use is, while PLURAL pronouns use are.
| Full Forms | Contractions | Example Sentences |
|---|---|---|
| I am → | I’m | I’m a student. |
| He is → She is → It is → |
He’s She’s It’s |
He’s inside the house. She’s at work. It’s a cat. |
| You are → We are → They are → |
You’re We’re They’re |
You’re beautiful. We’re in class. They’re smart. |
Activity 1.10: Writing
Directions: Change the full forms to contractions.
Example
1. It is really nice in the park.
_____________________________________________________________________
2. We are average height.
_____________________________________________________________________
3. I am from Guatemala.
_____________________________________________________________________
4. We are homesick for Guatemala.
_____________________________________________________________________
5. He is a student.
_____________________________________________________________________
6. She is a great cook.
_____________________________________________________________________
7. We are hungry for Mom’s pupusas.
_____________________________________________________________________
8. We are tired of the cold!
_____________________________________________________________________
9. It is a good playground.
_____________________________________________________________________
10. We are outside on sunny days.
_____________________________________________________________________
Negative Statements with the BE Verb
To make sentences negative, we add the negative not after the BE verb. Do not use no. No does not usually appear in the middle of a sentence.
| Subject | BE + not | Nouns, Adjectives, and Prepositional Phrases |
|---|---|---|
| I | am not | in class. |
| He She It |
is not | hungry. |
| You We They |
are not | at school. |
Activity 1.11: Writing
Directions: Change the affirmative sentences to negative sentences. Add not between the BE verb and the adjective, noun, or prepositional phrase. Use full forms.
1. Tigers are blue and orange.
________________________________________________________________
2. Chicago is a country.
________________________________________________________________
3. The park is downtown.
________________________________________________________________
4. Dogs are quiet.
________________________________________________________________
5. Cats are loud.
________________________________________________________________
6. She is a nurse.
________________________________________________________________
7. He is tall.
________________________________________________________________
8. They are from China.
________________________________________________________________
Negative Contractions with the BE Verb
There are two ways to make negative contractions with the BE verb.
1. contract the subject and verb (he is not = he’s not), or
2. contract the verb and the negative (he is not = he isn’t).
Activity 1.12: Writing
Directions: Change the full forms to contractions.
Example
Tigers are not blue and orange. → Tigers aren’t blue and orange.
1. Ana and Pedro are not from France.
________________________________________________________________
2. Ana and Pedro are not tall.
________________________________________________________________
3. Our apartment is not on the third floor.
________________________________________________________________
4. Our mom is not a terrible cook.
________________________________________________________________
5. We are not thin.
________________________________________________________________
6. We are not students at Portland Community College.
________________________________________________________________
7. There is not a patio outside our front door.
________________________________________________________________
8. Ana is not 40 years old.
________________________________________________________________
Using Adjectives with the BE Verb
Activity 1.13: Writing
Directions: Make sentences by choosing a word from each column in the table. Write 5 affirmative sentences and 5 negative sentences. (You will need to add not). Use contractions. Use your own lined paper for this activity.
Examples
English is not easy.
I’m happy.
| Subject | Be Verb | Adjective | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Activity 1.14: Game
Directions: Your instructor will give you a BINGO card. You are trying to get a straight line across, diagonal, or down. First, write the correct form of the BE verb on the line. Second, the teacher will read a sentence. Listen for the sentence. When you hear it, make an X through that square.
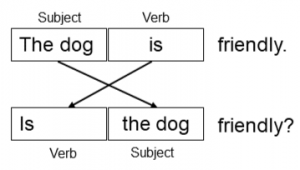
Yes/No Questions & Short Answers
Yes/no questions mean that the answer to the question is either yes or no. These questions don’t use wh- question words.
Remember
Activity 1.15: Interview
Part 1 Directions: Choose (by circling or otherwise marking) the subject of each sentence. Choose (by underlining or otherwise marking) the verb.
1. Cats are soft.
2. She is from Brazil.
3. The dog is cute.
4. We are happy.
5. The computer is broken.
6. He is a smart guy.
7. The truck is big.
8. They are busy.
Part 2 Directions: Now, on your own lined paper, change the sentences from Part 1 into yes/no questions. Turn this in to your teacher. Write your name, date, and Activity 1.15 at the top of your paper.
Part 3 Directions: Sit with a partner. Ask your partner the yes/no questions you just wrote. Your partner can answer any way he or she wants.
Example
B: Yes, they are. / No, they aren’t.
Short Answers
Study the table below for more information about answering a yes/no question. It includes short answers, which are very common in spoken English. We usually use contractions in negative answers (e.g., No, I’m not.), but the full forms in short answers are common, too (e.g., No, I am not.). Notice that there are NO contractions for affirmative short answers!
| BE Verb | Subject | Noun, Adjective, or Prepositional Phrase | AFFIRMATIVE Short Answers | NEGATIVE Short Answers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Am | I | hungry? | Yes, I am. | No, I’m not. |
| Is | he she it |
hungry? | Yes, he is. Yes, she is. Yes, it is. |
No, he’s not. No, she’s not. No, it’s not. |
| Are | you we they |
hungry? | Yes, I am. Yes, we are. Yes, they are. |
No, I’m not. No, we’re not. No, they’re not. |
Activity 1.16: Find Someone Who…
Directions: Your teacher will give you a worksheet to use. Walk around the room and ask your classmates questions about the topic in each box. With your partner, ask take turns asking a question. Use short answers to respond.
- If your partner answers, “Yes, I am,” write their name in the box. Find a new partner.
- If they answer, “No, I’m not,” ask another question until they say yes. Then find a new partner.
Example
A: Are you ______________?
B: Yes, I am. (or) No, I’m not.
Activity 1.17: Interview
Part 1 Directions: Change the following statements to yes/no questions.
Examples
You are from Peru. → Are you from Peru?
He is an immigrant. → Is he an immigrant?
1. The computer is broken.
___________________________________________________________________
2. He is lucky.
___________________________________________________________________
3. The cats are under the table.
___________________________________________________________________
4. Jacques is from Côte d’Ivoire.
___________________________________________________________________
5. Pigs are smart.
___________________________________________________________________
6. The desk is heavy.
___________________________________________________________________
7. I am hungry.
___________________________________________________________________
8. The boys are on the bus.
___________________________________________________________________
9. You are a mechanic.
___________________________________________________________________
10. We are late.
___________________________________________________________________
Part 2 Directions: Now ask your partner the questions. Your partner will answer using short answers. Answer using affirmative and negative short answers.
Activity 1.18: Interview
Part 1 Directions: Make statements and questions from the words given. Add a BE verb (am, is, are) to complete the statement. Then, turn the statement into a question.
Example
My friend / at school now
Statement: My friend is at school now.
Question: Is my friend at school now?
1. the old woman / from Moldova
Statement: _____________________________________________________________
Question: _____________________________________________________________
2. the train / at the station
Statement: _____________________________________________________________
Question: _____________________________________________________________
3. the men / construction workers
Statement: _____________________________________________________________
Question: _____________________________________________________________
4. the little girl / 4 years old
Statement: _____________________________________________________________
Question: _____________________________________________________________
5. the dog and cat / in the yard
Statement: _____________________________________________________________
Question: _____________________________________________________________
Part 2 Directions: Ask your partner the questions from above. Your partner can answer with affirmative or negative short answers.
Short Answers: An Expanded View
Short answers are very common in spoken English. However, there is only one way to answer in the affirmative. Contractions are not allowed. With negative short answers, there are different ways to answer depending on the amount of emphasis you want to make.
Affirmative Short Answers
| Yes/No Questions | No Contractions! |
|---|---|
| Am I hungry? | Yes, I am. |
| Is he/she/it hungry? | Yes, he is. |
| Are you hungry? | Yes, I am. Yes, we are. |
Negative Short Answers
| Most Common Contraction |
Alternative Contraction |
Without Contraction (Full Form) |
|---|---|---|
| No, I’m not. | No, I am not. | |
| No, he isn’t. No, she isn't. No, it isn't. |
No, he's not. No, she's not. No, it's not. |
No, he is not. No, she is not. No, it is not. |
| No, you aren’t. No, we aren’t. No, they aren’t. |
No, you're not. No, we're not. No, they're not. |
No, you are not. No, we are not. No, they are not. |
Less emphasis <——————————————–> More emphasis
Activity 1.19: Conversation
Information Questions with the BE Verb
We use wh- question words at the beginning of information questions.
Activity 1.20: Brainstorming
Directions: What are the wh- question words? Make a list with your partner:
_______________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________
Study the chart below about wh- question words and their meanings.
| Wh- Question Word | Asks About: | Example Questions |
|---|---|---|
| What | things names |
What is that? What is your name? |
| Who | people | Who is the teacher? Who is next to you? |
| Where | places location |
Where is your school? Where is the library? |
| How | manner feelings / emotions form / shape description |
How are you? How is your class? How far is it to Seattle? |
| When | time dates |
When is your birthday? When is the last day of class? |
| Why | reasons | Why are you late? Why is he absent? |
The formation of information questions is the same as yes/no questions. Add the wh- question word (who, where, what, why, when, how) to the beginning of the question.
| Wh- Question Word | Asks About: | Example Questions |
|---|---|---|
| What | things names |
What is that? What is your name? |
| Who | people | Who is the teacher? Who is next to you? |
| Where | places location |
Where is your school? Where is the library? |
| How | manner feelings / emotions form / shape description |
How are you? How is your class? How far is it to Seattle? |
| When | time dates |
When is your birthday? When is the last day of class? |
| Why | reasons | Why are you late? Why is he absent? |
Remember
ARE is followed by a plural subject.
Activity 1.21: Interview
Part 1 Directions: Unscramble the words to form information questions.
1. the weather / is / how / today?
___________________________________________________________________
2. is / where / your child?
___________________________________________________________________
3. on the table? / is / what
___________________________________________________________________
4. is / the last day of class? / when
___________________________________________________________________
5. our teacher? / is / who
___________________________________________________________________
6. are / you / late / why
___________________________________________________________________
Part 2 Directions: Ask your partner the questions you just unscrambled.
Activity 1.22: Interview
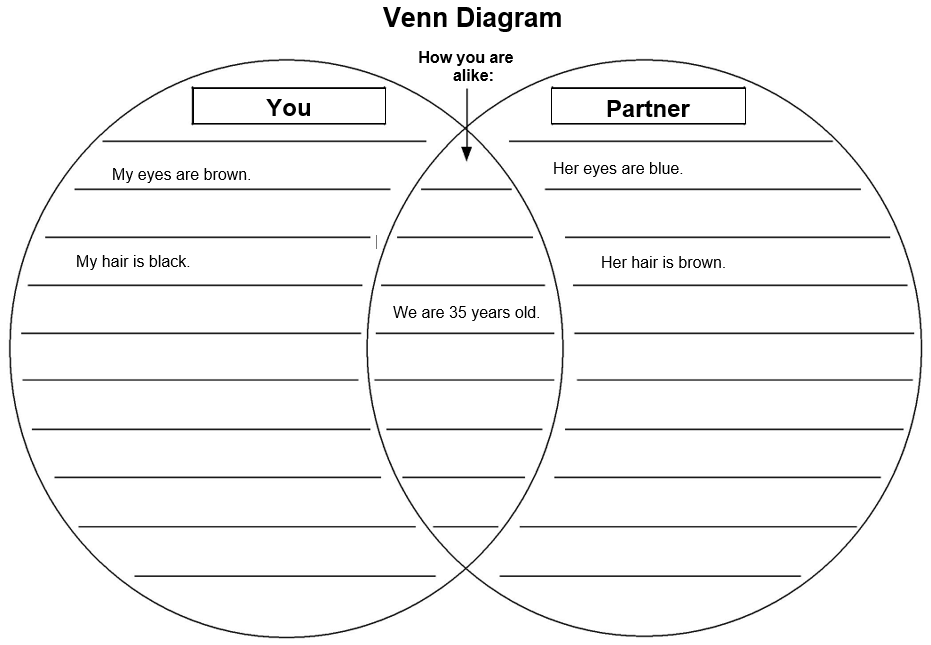
Part 1 Directions: Interview your partner. Ask your partner the questions below and write their answers. Later, you will put the answers into a Venn Diagram.
1. What is your name?
___________________________________________________________________
2. What color are your eyes?
___________________________________________________________________
3. What color is your hair?
___________________________________________________________________
4. How tall are you?
___________________________________________________________________
5. Where are you from?
___________________________________________________________________
6. Are you single, married, divorced, or widowed?
___________________________________________________________________
7. How old are you?
___________________________________________________________________
8. What is your job?
___________________________________________________________________
Part 2 Directions: Your instructor will give you a Venn Diagram to use. A Venn Diagram is used to organize ideas and take notes. With your partner, fill in the chart to find out what you have in common. In common means what you share or do that’s the same.
Part 3 Directions: Now write 5 sentences about your partner. Use the BE verb with nouns and adjectives.
1.__________________________________________________________________
2.__________________________________________________________________
3.__________________________________________________________________
4.__________________________________________________________________
5.__________________________________________________________________
Review
Activity 1.23: Complete the Table
| Subject Pronoun |
Affirmative Full Form | Affirmative Contractions | Negative Full Form | Negative Contractions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | am | I’m | I am not | I’m not |
| You | You’re | |||
| He | He is not | |||
| She | She isn’t | |||
| It | is | |||
| We | We’re | |||
| They | They aren’t |
 Snapshot: Sentence Patterns
Snapshot: Sentence Patterns
The word or words that come before the be verb are called the subject. The subject is the person or thing that does the action of the verb or describes the verb.
Examples
Subject + BE + noun I am Ana.
Subject + BE + adjective I am 20 years old.
Subject + BE + place word I am from Guatemala.
Activity 1.24: Writing
Directions:
A. Put the words in the correct order to make questions.
B. Answer yes/no questions with short answers, but answer wh- questions with complete sentences. Answer the questions in the affirmative or negative. It’s your decision.
Examples
birds / loud / are Is / where / the bird
A. Are birds loud? A. Where is the bird?
B. Yes, they are. OR No, they aren’t. B. It is in the tree.
1. he / is / a good teacher
A. _____________________________________________________
B. _____________________________________________________
2. doctor / is / your / friendly
A. _____________________________________________________
B. _____________________________________________________
3. the car parked / where / is
A. _____________________________________________________
B. _____________________________________________________
4. the students / are / busy
A. _____________________________________________________
B. _____________________________________________________
5. Luz / a good cook / is
A. _____________________________________________________
B. _____________________________________________________
6. clean / are / clothes / your
A. _____________________________________________________
B. _____________________________________________________
7. brother / tall / is / your
A. _____________________________________________________
B. _____________________________________________________
8. what / favorite sport / is / your
A. _____________________________________________________
B. _____________________________________________________
Activity 1.25: Conversation
Write
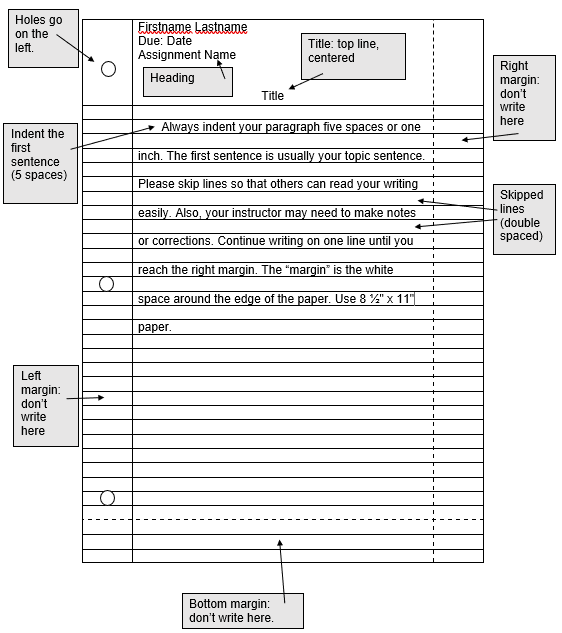
Directions: Write a paragraph describing your home using the BE verb in the present tense.
Format:
- Use your own 8.5″ x 11″ lined paper. Do not use other paper sizes, please.
- Heading: Put your full name, the due date, and Ch. 1 Writing Assignment at the top of your paper. Your instructor will tell you where the heading goes (left or right side).
- Indent the first sentence, skip lines (double space), and leave a 1-inch margin on the sides and bottom.
Writing and Grammar:
- First sentence: Begin writing by using this topic sentence: I like my home for many reasons.
- Write 5 affirmative sentences using the BE verb in the simple present tense.
- Write 5 negative sentences using the BE verb in the simple present tense.
- Use full forms; do not use contractions.
- Use capital letters and punctuation correctly.
- Use the rubric below to check your work.
- Do not copy the sentences in the model paragraph on the next page. You must write your own original sentences.
Assignment Rubric:
| Subject | BE Verb |
|---|---|
| I | 1. |
| you | 2. |
| he, she, it | 3. |
| we | 4. |
| they | 5. |
Model Paragraph:
My Home
I like my home for many reasons. My home is quiet. It is not noisy. It is near a lake. The lake is not big. There are many trees in the backyard. Squirrels are in the trees. There is a pond with frogs. The frogs are not big. My home is not on a busy street. My neighborhood is not very big. I love my home and neighborhood.
Paragraph Format:
Self-Assessment
These were our goals at the beginning of Chapter 1:
Recognize and use the BE verb in the simple present tense
-
- in the affirmative and negative
- with contractions
- with yes/no questions and short answers
Use parts of speech to construct simple sentences
| Subject | BE Verb |
|---|---|
| I | 1. |
| you | 2. |
| he, she, it | 3. |
| we | 4. |
| they | 5. |