3 Educational Philosophies
“Theories are more than academic words that folx with degrees throw around at coffee shops and poetry slams; they work to explain to us how the world works, who the world denies, and how the structures uphold oppression.”
Bettina L. Love, 2019

Learning Objectives
- Learn the four key Educational Philosophies
- Explore non-systemically dominant educational systems and their philosophical roots
- Compare how the privileging of educational thought and philosophy in the US is based in social, political, and economic power
- Develop an initial personal philosophy of education through self-reflection and self examination taking into account narratives and counterstories
Activity – Educational Philosophy Assessment
In order to start reflecting on your own philosophy of education, complete the following:
-
Educational Philosophies Self Assessment – https://evaeducation.weebly.com/uploads/1/9/6/9/19692577/self_assessment.pdf
-
Scoring Guide for the Self Assessment: https://evaeducation.weebly.com/uploads/1/9/6/9/19692577/self_assessment_scoring_guide.pdf
What does this survey reveal about your underlying philosophy?
Do you agree or disagree with this assessment? Explain.
What might this survey reveal with your reasons in becoming a teacher?
Foundations of Educational Philosophy
Pause and Ponder – Education
You may have heard comments implying that education in the United States is not political, separate from religion, and accessible to everyone. The reality is that from its early existence in the western hemisphere in the 1600s, it was indeed political, religious, and accessible only to a select few. These traits continue to influence the evolution of education in the United States today.
The education system in the United States is a social institution. A social institution is a pattern of behaviors and social arrangements that have evolved to meet the needs of society. Quite often, how those needs are defined in official conversations is dependent on who has the social, economic, and legal power to do the defining.
Given this, and since the current system in the US was derived from a system that was explicitly designed to reproduce wealth and privilege for societal elites, it should be no surprise that the foundational theorists upon which the US education rests are representative of a narrow range of perspectives on education. Many educational approaches, perspectives, and philosophies have been neglected in the development of the US system. For instance, the educational system in the US is not rooted at all in the philosophies of Aztec or Mayan civilizations. Nor does it include understandings about teaching, learning, or intellectual growth from Muslim, Hindu, or Yoruba societies. It is accurate to say the US system of education and the philosophies on which it rests are decidedly Eurocentric.
Critical Lens – Eurocentrism
Eurocentrism (also Eurocentricity) is a worldview that is centered on or privileges European-based civilization or a biased view that favors it over nonEuropean-based civilizations.
In order to understand the educational system in the US in a way that supports educators in meeting the needs of all students, we offer the following orientation to the educational philosophies on which this system was founded.
A philosophy grounds or guides practice in the study of existence and knowledge while developing an ontology (the study of being) on what it means for something or someone to be—or exist. Educational philosophy, then, provides a foundation which constructs and guides the ways knowledge is generated and passed on to others. Therefore, when thinking and reflecting about your own philosophy of education, you need to acknowledge your values, beliefs and attitudes towards the educational system, as this will guide your practice. Therefore, it is of critical importance that teachers begin to develop a clear understanding of philosophical traditions and how the philosophical underpinnings inform their educational philosophies. Philosophies need to translate ideas into action. If you want to use certain techniques, then you need to understand how they are effective in the classroom to create that portion of your education philosophy.
Over the course of history, philosophy has experienced several paradigm shifts that influence teaching and learning. Philosophical traditions from the 19th century helped anchor the early foundations of educational philosophy and the development of public education in Europe and the United States.
Activity – Think and Reflect
Think and reflect on the following guiding questions:
- What does being a teacher mean to you?
- What are the skills that, from your perspective, effective teachers have?
- What should be taught?
- How should it be taught?
- What is knowledge?
- Why is it important to establish a trusting relationships between students, teachers and the community?
Whether you are aware or not, you have begun writing philosophical statements about education and being a teacher.
3.1 Philosophical Perspectives of Education
As students ourselves, we may have a particular notion of what schooling is and should be as well as what teachers do and should do. In his book entitled Schoolteacher: A Sociological Study, Dan Lortie (1975) called this the “apprenticeship of observation” (p. 62). Many people who pursue teaching think they already know what it entails because they have generally spent at least 13 years observing teachers as they work. The role of a teacher can seem simplistic because as a student, you only see one piece of what teachers actually do day in and day out. This one-dimensional perspective can contribute to a person’s idea of what the role of teachers in schools is, as well as what the purpose of schooling should be. The idea of the purpose of schooling can also be seen as an individual’s philosophy of schooling.
Philosophy can be defined as the fundamental nature of knowledge, reality and existence. In the case of education, one’s philosophy is what one believes to be true about the essentials of education. When thinking about your philosophy of education, consider your beliefs about the roles of schools, teachers, learners, families, and communities. There are four philosophical perspectives currently used in educational settings: essentialism, perennialism, progressivism, and social reconstructionism/critical pedagogy. Unlike the more abstract philosophical perspectives of ontology and axiology, these four perspectives focus primarily on what should be taught and how it should be taught, i.e. the curriculum. These are explained below.
3.2 Four Key Educational Philosophies
Essentialism
Essentialism adheres to a belief that a core set of essential skills must be taught to all students. Essentialists tend to privilege traditional academic disciplines that will develop prescribed skills and objectives in different content areas as well as develop a common culture. Typically, Essentialism argues for a back-to-basics approach on teaching intellectual and moral standards. Schools should prepare all students to be productive members of society. The Essentialist curriculum focuses on reading, writing, computing clearly and logically about objective facts concerning the real world. Schools should be sites of rigor where students learn to work hard and respect authority. Because of this stance, Essentialism tends to subscribe to tenets of Realism. Essentialist classrooms tend to be teacher-centered in instructional delivery with an emphasis on lecture and teacher demonstrations.
Video 3.1
Perennialism:
Perennialism advocates for seeking, teaching, and learning universal truths that span across historical time periods. These truths, Perennialists argue, have everlasting importance in helping humans solve problems regardless of time and place. While Perennialism resembles essentialism at first glance, Perennialism focuses on the individual development of the student rather than emphasizing skills. Perennialism supports liberal arts curricula that helps produce well-rounded individuals with some knowledge across the arts and sciences. All students should take classes in English Language Arts, foreign languages, mathematics, natural sciences, fine arts, and philosophy. Like Essentialism, Perennialism may tend to favor teacher-centered instruction; however, Perennialists do utilize student-centered instructional activities like Socratic Seminar, which values and encourages students to think, rationalize, and develop their own ideas on topics.
Video 3.2
Progressivism
Progressivism focuses its educational stance toward experiential learning with a focus on developing the whole child. Students learn by doing rather than being lectured to by teachers. Curriculum is usually integrated across contents instead of siloed into different disciplines. Progressivism’s stance is in stark contrast to both Essentialism and Perennialism in this manner. Progressivism follows a clear pragmatic ontology where the learner focuses on solving real-world problems through real experiences. Progressivist classrooms are student-centered where students will work in cooperative/collaborative groups to do project-based, expeditionary, problem-based, and/or service-learning activities. In progressivist classrooms, students have opportunities to follow their interests and have shared authority in planning and decision making with teachers.
Video 3.3
3.3 A Response to Dominant Systems:
Social Reconstructionism
Social reconstructionism was founded as a response to the atrocities of World War II and the Holocaust to assuage human cruelty. Social reform in response to helping prepare students to make a better world through instilling liberatory values. Critical pedagogy emerged from the foundation of the early social reconstructionist movement.
Video 3.4
Critical Lens – Liberatory Thinking
“Liberatory thinking is the re- imagining of one’s assumptions and beliefs about others and their capabilities by interrupting internal beliefs that undermine productive relationships and actions. Liberatory thinking goes beyond simply changing mindsets to creating concrete opportunities for others to experience liberation. The opportunities provides cover for and centers underrepresented and marginalized people. It pushes people to interrogate their own multiple identities in relation to others and to think about the consequences of our actions, especially for students of critical need. It explores how mindsets can impede or ignite progress in the classroom, school, and district.”
Chicago Public Schools
For more information in Liberatory Thinking, please refer to the Equity Framework from the Chicago Public Schools
Critical Pedagogy
Critical pedagogy is the application of critical theory to education. For critical pedagogues, teaching and learning is inherently a political act and they declare that knowledge and language are not neutral, nor can they be objective. Therefore, issues involving social, environmental, or economic justice cannot be separated from the curriculum. Critical pedagogy’s goal is to emancipate marginalized or oppressed groups by developing, according to Paulo Freire, conscientização, or critical consciousness in students.
Critical pedagogy de-centers the traditional classroom, which positions teachers at the center. The curriculum and classroom with a critical pedagogy stance is student-centered and focuses its content on social critique and political action.
Video 3.5
3.4 Ways of Knowing
Pause and Ponder – Ways of Knowing
In addition to the historically neglected thinkers and the theories presented above, it is important for educators to consider that there are many ways of knowing and acquiring knowledge
How do you know something is true?
In the US school system, for instance, students begin the day when a bell or signal goes off at the same predetermined time every day. This scheduling system shapes students’ awareness of how days in their lives will most likely be structured. Consider an alternative: What would happen if the school day started every day when the sun passes a certain point across the horizon. What would students learn about the world? How would students’ way of knowing about time and responsibility be changed?
Critical Lens – Cultural Practices
Here are two news stories with examples of cultural practices that are not taught in mainstream schools because they have been steered away from in this imperialistic, colonizing culture. Nevertheless, they have been sustained by thinkers and teachers and continue to be sustained today.
Culturally informed childbirth practices: Navajo woman starts nonprofit to improve maternal health
Traditional care of the land: For tribes, ‘good fire’ a key to restoring nature and people
Video 3.6
3.5 Educational Thinkers
The thinkers and perspectives in the preceding section of this text are considered foundational thinkers in mainstream formal education in the US, other thinkers from the same time period and throughout history are considered foundational contributors to education throughout the world. Some of this has to do with the notion of US colonialism, imperialism, exceptionalism (the belief that the United States is either distinctive, unique, or exemplary compared to other nations), and the legacy of the enslavement of Black Americans in the United States. Because of these legacies, very few people of color were accepted into the cannon of formal educational thinkers. As a result, the US system has been shaped by a very narrow sample of foundational theorists, and many educators who trained in the 20th and 21st centuries in the US had their perspectives formed under this narrow umbrella.
The following individuals and theories are presented so that you can broaden your perspective and better serve all students during your career in education.

William Edward Burghardt Du Bois
Du Bois was an American sociologist, historian and Pan-Africanist civil rights activist. Du Bois completed his graduate work at the University of Berlin and Harvard University, where he was the first African American to earn a doctorate. He became a professor of history, sociology and economics at Atlanta University. Du Bois was one of the founders of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) in 1909.
In an effort to portray the genius and humanity of the Black race, Du Bois published The Souls of Black Folk (1903), a collection of 14 essays. The introduction of the book famously proclaimed that “the problem of the Twentieth Century is the problem of the color line.” Each chapter begins with two epigraphs – one from a White poet, and one from a Black spiritualist – to demonstrate intellectual and cultural parity between Black and White cultures.
A major theme of The Souls of Black Folk is the double consciousness faced by African Americans: being both American and Black. This was a unique identity which, according to Du Bois, had been a handicap in the past, but could be a strength in the future: “Henceforth, the destiny of the race could be conceived as leading neither to assimilation nor separatism but to proud, enduring hyphenation.”
Double consciousness is the internal conflict experienced by subordinated or colonized groups in an oppressive society. Originally, double consciousness was specifically the psychological challenge African Americans experienced of “always looking at oneself through the eyes” of a racist white society and “measuring oneself by the means of a nation that looked back in contempt”. The term also referred to Du Bois’s experiences of reconciling his African heritage with an upbringing in a European-dominated society.
More recently, the concept of double consciousness has been expanded to other situations of social inequality, notably women living in patriarchal societies as well as LGBTQ2S+ people living in homophobic and transphobic societies.
The idea of double consciousness is important because it illuminates the experiences of Black people living in post-slavery America, and also because it sets a framework for understanding the position of oppressed people in an oppressive world. As a result, it became used to explain the dynamics of gender, colonialism, xenophobia and more alongside race. This theory laid a strong foundation for other critical theorists to expand upon.
Carter Godwin Woodson
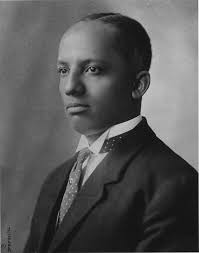
Woodson was an American educator, historian, author, and the founder of the Association for the Study of African American Life and History. He achieved a graduate degree at the University of Chicago and in 1912 was the second African American, after W. E. B. Du Bois, to obtain a PhD from Harvard University. Woodson remains the only person whose parents were enslaved in the United States to obtain a PhD. He taught at two historically Black colleges: “Howard University and West Virginia State University”. Woodson believed that education and increasing social and professional contacts among Black and white people could reduce racism, and he promoted the organized study of African-American history partly for that purpose. He would later promote the first Negro History Week in Washington, D.C., in 1926, forerunner of Black History Month.
Woodson published The Education of the Negro Prior to 1861. Believing that history belonged to everybody, not just the historians, Woodson sought to engage Black civic leaders, high school teachers, clergy, women’s groups and fraternal associations in his project to improve the understanding of African-American history. He founded the Association for the Study of African American Life and History whose purpose he described as the “scientific study” of the “neglected aspects of Negro life and history” by training a new generation of Black people in historical research and methodology
bell hooks

hooks is a US based educational theorist and social activist. In Teaching to Transgress: Education as the Practice of Freedom, she argues that a teacher’s use of control over students dulls the students’ enthusiasm and teaches obedience to authority, and keeps students from learning critical thinking. hook’s pedagogical practices exist as an interplay of anti-colonial, critical, and feminist pedagogies and are based on freedom. hooks also built a bridge between critical thinking and real-life situations, to enable educators to show students the everyday world instead of the stereotypical perspective of the world. hooks argues that teachers and students should engage in interrogations of cultural assumptions that are supported by oppression.
note: bell hooks intentionally does not capitalize her name, which follows her critical stance that language, even how we write one’s own name, is political and ideological.
Henry Giroux

Giroux is a foundational critical theorist in the US and Canada, best known for his pioneering work in critical pedagogy in K-12 and higher ed. His work advocates supporting students developing a consciousness of freedom and connecting knowledge to power, and the ability to take constructive action. His latest work examines the pitting of people against each other through the lens of class, race, and any other differences that don’t embrace white nationalism.
3.6 Latin American Thinkers
We will now analyze the impact of the pedagogical practice, as well as the educational thought, of different key educators in Latin America. These educators influenced a cultural change with ideas and concepts that modified the parameters of the educational system that was established in LatinAmerica.
Some of these educators have not been recognized in the educational system around the world. However, their work has been a catalyst in giving way to cultural and educational transformations in Latin America. The following educators stand out for their innovative tendencies who fought for an educational system to which all people had access.
When studying these Latin American educators, it should be noted that they generated a change that had a great impact on socio-cultural problems and that their success, or failure, depended on the government policies carried out in the corresponding countries.
Deeper Dive – Latin American Thinkers
You can watch the history of each Latin American thinkers in Spanish in the following video:
Video 3.7
Paulo Reglus Neves Freire

Freire is a Brazilian philosopher and educator, was one of the most influential thinkers behind social reconstructionism. He criticized the banking model of education in his best known writing, Pedagogy of the Oppressed, which is generally considered one of the fundamental texts of the critical pedagogy movement. Banking models of education view students as empty vessels to be filled by the teacher’s expertise, like a teacher putting “coins” of information into the students’ “piggy banks.” Instead, Freire supported problem-posing models of education that recognized the prior knowledge everyone has and can share with others. Conservative critics of social reconstructionists suggest that they have abandoned intellectual pursuits in education, whereas social reconstructionists believe that the analyzing of moral decisions leads to being good citizens in a democracy.
The installment dedicated to Paulo Freire covers the different stages of the life of the Brazilian pedagogue and politician. The documentary shows his Christian roots and his first steps related to literacy and adult education in Brazil, especially the one carried out in Angicos. Then, it continues with Freire’s years in exile, which included a diverse tour of Chile, the US, Nicaragua, etc. and the publication, in 1970, of two of his most important works: Education as a practice for freedom and Pedagogy of the oppressed. At the same time, it is argued that these works strengthened a political idea that became the organizer of the movement of the oppressed in Latin America.
Pause and Ponder – Dominant Narrative
The work of Freire, Giroux, and hooks are included as necessary responses to the exclusionary and marginalizing nature of the dominant narrative of educational systems. Even today, although educators may study their work, the systems they’re employed with tend to perpetuate the inequalities and dynamics Freire, Giroux, hooks, and others address.
Gabriela Mistral

Mistral, pseudonym of Lucila Godoy Alcayaga, was a Chilean poet, diplomat and pedagogue. She received the Nobel Prize for Literature in 1945 for her poetic work, she was the first Ibero-American woman and the second Latin American person to receive a Nobel Prize.
Her political-ideological profile is represented as a hybrid between her Catholic, but not conservative, beliefs and her liberal traits, although she is not strictly defined as liberal. Her words and poetry, which frequently gave life to various newspaper articles, generated multiple conflicts with the most conservative sectors of society. Mistral, however, continued on her way and affirmed her work in the rural and indigenous sectors. During her trip to Mexico, at the invitation of Vasconcelos, she fulfilled her full potential as a teacher, promoting a pedagogy based on the child, with Christian roots and that took into account the singularities of the rural and indigenous areas in which she worked. In 1945 she became the first woman to receive the Nobel Prize for Literature, something that made visible the impact of her teaching practice, intellectual and poetic practice.
Domingo Faustino Sarmiento

Sarmiento was an Argentine politician, writer, teacher, journalist, serviceman and statesman; governor of the province of San Juan between 1862 and 1864, president of the Argentine Nation between 1868 and 1874, national senator for his province between 1874 and 1879 and minister of the interior in 1879.
His controversial, anti-racist and unitary side is reaffirmed, and the fact that he belongs to a generation that understood writing as a political practice. He questioned what was the best educational system for all of the students in Latina America. He starts investigating the opposite approaches of education in Massachusetts and Prussia. He believed that the students had a better option to succeed and learn independently in a society under the Prussian system, which was centralized and under the management of the state. The educational system in Massachusetts, on the contrary, was decentralized and the society was the principal entity to promote education. Therefore, the habits of each state were instilled in the students. For example, a republican state will have a republican approach to education and he did not agree with this approach. Therefore, after his investigations he laid the programmatic foundations of a national educational system, in where it was centralized and Popular Education was provided to all of the children in Argentina.
Later on, his side as a statesman is taken up again with the contributions he made in the elaboration of the Law of Common Education of Buenos Aires (1875) and the sanction under his presidency of the National Law of Common Education (1884).
Jesualdo Sosa
Sosa, better known as Jesualdo, was a Uruguayan teacher, writer, pedagogue and journalist. His teaching led him to dedicate himself with greater purpose and knowledge on the activities, interests and needs of the child.
Starting from a critique of the traditional school and the capitalist system, Sosa combined there a proposal with Escolanovist overtones, which promoted the autonomy of children, their creativity, their expression, their work training, and was articulated with the activities of the community. That experience was collected in Vida de un maestro, a production that, despite the censorship attempts it suffered from dictatorial governments, was able to expand worldwide. After that publication, his life is described as a time of maturation, systematization and recognition, which gave him the chance to be called to collaborate in different parts of Latin America.
Simón Narciso de Jesús Carreño Rodríguez

de Jesús Carreño Rodríguez was a Venezuelan hero, educator, and politician. He was the tutor of Simón Bolívar and Andrés Bello. He contributed concepts and ideas including written works aimed at the process of freedom and American integration.
In the seventh installment, Simón Rodríguez is recognized as a great precursor of our American pedagogical thought, as a fighter for the emancipation of Latin America and for public education for all as a form of social progress. His philosophy favored the equality in education as he believed this was a right for all citizens. He highlights his conception of equality, which was not restrictive as he believed that equality started in educational practices. He sacrificed all his belongings and left everything for his ideals. In the miniseries,
José Vasconcelos Calderón

Vasconcelos Calderón was a Mexican lawyer, politician, writer, educator, public official and philosopher. He was part of the revolutionary movement led by Francisco Madero, which promoted the democratic transformation of a country that, at that time, was shaken by the dictatorships of Porfirio Díaz Mori. As a result of a political setup, Vasconcelos became Secretary of Education of the Federal Government (1921-1924). His management in this position is distinguished as short and intense, since there he carried out, with the support of Gabriela Mistral, his most recognized work, promoting high culture, rural literacy missions and muralism as ways of recovering Latin American roots. His work, The Cosmic Race, is considered a condensation of his position in favor of mestizaje, which is the biological and cultural encounter or its arrangement between different ethnic groups, in which they mix, giving birth to new species of families and new genotypes. This was a very controversial work as it was not aligned with the thinking of the people from this time.
José Carlos Mariátegui
Mariátegui, La Chira, was a Peruvian writer, journalist and political thinker, a prolific author despite his early death. He is also known in his country by the name of El Amauta. He was one of the main scholars of Socialism in Latin America.

“The revolution is not only the fight for bread, but also the conquest of beauty” is a representative phrase of José Carlos Mariátegui, which marks the beginning of the installment referring to the Peruvian writer, journalist and intellectual. At first, the documentary goes through what is considered his first school, recounting his initial steps in the writing of the newspaper La Razón, where he grew as a journalist and became involved in workers’ struggles and reformist ideals. Then it is analyzed how during his exile in Europe, Mariátegui was nurtured by Marxist ideas, the struggles of Italian workers and began to work on the notion of indigenism as a creative and revolutionary myth. During his return, it is stated that he strengthened his political proposal of autochthonous socialism, marked by a juxtaposition between Marxist theory, Latin Americanism and indigenism, with a strong emphasis also on gender equality and the depatriarchalizing of educational practices. These aspects are present in its most important editorial offering, Amauta. In 1928, he created the Peruvian Socialist Party and published Seven Interpretive Essays on Peruvian Reality, from which he criticized the liberal model of education (which placed the problem of indigenous people in education) and the lack of their recognition as subjects of law.
José Julián Martí Pérez

Martí Pérez was a writer and politician of Cuban origin. Democratic republican politician, thinker, journalist, philosopher and Cuban poet, creator of the Cuban Revolutionary Party and organizer of the War of 95 or Necessary War, named after the Cuban War of Independence. He suffered the vicissitudes of critical thought from a very young age, when he was imprisoned and exiled. Strongly involved in the struggles against Spanish colonization and US interference in the Caribbean, he claimed Bolivarian principles. His political and educational thought is described through four topics: the decolonization of Latin American knowledge, the formation of good people and the role of love in pedagogy, the special place given to creative work and the recovery of Latin American identity. In 1892, a time of exile, he founded the Cuban Revolutionary Party as a tool for the independence of the island and finally died on the battlefield years later.
Jorge J. E. Gracia
Gracia was born in Cuba in 1942 and was a Cuban refugee in the USA. He studied at both Universidad de La Habana and Escuela Nacional de Bellas Artes San Alejandro in Havana before moving to the U.S., where he earned a degree in philosophy from Wheaton College in 1965. He went on to receive a master’s degree in philosophy from University of Chicago in 1966, a licentiate in medieval studies from Pontifical Institute of Medieval Studies in 1970 and his doctorate in medieval philosophy from University of Toronto in 1971.
Gracia’s areas of research included metaphysics, ethnic and racial issues, philosophy of religion, and medieval and Latin American philosophy. These topics led him to author over 20 books and edit more than two dozen volumes of works by others. One of his most notable contributions was his 1984 edited anthology on Latin American philosophy, “Philosophical Analysis in Latin America,” which was the first work of its kind published in English by a philosopher.
Beyond his vast collection of writings, he was also a leader for many important organizations. He was the founding chair for the American Philosophical Association’s Committee for Hispanics in Philosophy and sat as president of the Society for Medieval and Renaissance Philosophy, Society for Iberian and Latin American Thought, American Catholic Philosophical Association and the Metaphysical Society of America.
Gracia worked for the State University of New York at Buffalo from 1971 until he retired in January 2020 as SUNY Distinguished Professor and Samuel P. Capen Chair in the departments of philosophy and comparative literature.
Héctor-Neri Castañeda
Castañeda was a Guatemalan American philosopher who emigrated to the U.S. in 1948 as a refugee. He attended the University of Minnesota to earn his bachelor’s, master’s and PhD degrees.
After graduating with his PhD, Castañeda studied at Oxford University for a year before returning to the U.S. to work at Duke University for a short period of time. He went on to work at Wayne State University, where he founded the philosophical journal Noûs, which is still in production to this day.
Eventually, he moved to Indiana University in 1969 and became the Mahlon Powell Professor of philosophy as well as that university’s first dean of Latino affairs.
Castañeda is most notable for developing the guise theory, which applies to the analysis of thought, language and the structure of the world through abstract objects. He is also credited with the discovery of the concept of the quasi-indexical or quasi-indicator. This is a linguistic expression in which a person referencing another can shift from context to context, much like in the way ‘you’ can refer to a specific person in one context and another person in a different context.
In addition to his research, he was awarded a fellowship from the Guggenheim Foundation and received grants from the National Endowment for the Humanities, the Andrew W. Mellon Foundation and the National Science Foundation. He was also given the Presidential Medal of Honor by the government of Guatemala in 1991, among many other accomplishments.
Activities – Personal Philosophy of Education
In order to start building your own personal philosophy of education, it’s important to be able to articulate how you will incorporate diverse perspectives and ways of knowing into your teaching.
Instructions:
- Watch “The Danger of a single story” TED talk by Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie
Video 3.8
- Select a mainstream-culture based single story about education and analyze it. Examine how an ideology or stereotype is perpetuated through it
- Explore some or all of the story’s origins functions impact on education
- Then examine the alternative stories: those told by the survivors of the single story
- Propose ways to change the story both in your teaching and in the educational system in general
Conclusion
Like learning, teaching is always developing; it is never realized once and for all. Our public schools have always served as sites of moral, economic, political, religious and social conflict and assimilation into a narrowly defined standard image of what it means to be an American. According to Britzman (as quoted by Kelle, 1996), “the context of teaching is political, it is an ideological context that privileges the interests, values, and practices necessary to maintain the status quo.” Teaching is by no means “innocent of ideology,” she declares. Rather, the context of education tends to preserve “the institutional values of compliance to authority, social conformity, efficiency, standardization, competition, and the objectification of knowledge” (p. 66-67).
It should be no surprise then that contemporary debates over public education continue to reflect our deepest ideological differences. As Tyack and Cuban (1995) have noted in their historical study of school reform, the nation’s perception toward schooling often “shift[s]… from panacea to scapegoat” (p. 14). We would go a long way in solving academic achievement and closing educational gaps by addressing the broader structural issues that institutionalize and perpetuate poverty and inequality.
References
AFT – American Federation of Teachers – A Union of Professionals. (n.d.). American Federation of Teachers. https://www.aft.org/
April 14, 1947: Mendez v. Westminster Court Ruling – Zinn Education Project. (2023, May 25). Zinn Education Project. https://www.zinnedproject.org/news/tdih/mendez-v-westminster/
ASU Local-Los Angeles welcomes its 3rd cohort of students. (2021, September 24). ASU News. https://news.asu.edu/20210924-latin-american-philosophers-you-should-know-about
BBC News. (2021, June 24). Canada: 751 unmarked graves found at residential school. BBC News. https://www.bbc.com/news/world-us-canada-57592243
Bennett, Jr., Lerone (2005). “Carter G. Woodson, Father of Black History”. United States Department of State. Archived from the original on April 1, 2011. Retrieved May 30, 2011.
“Carter G. Woodson: Winona, WV – New River Gorge National Park and Preserve (U.S. National Park Service)”. www.nps.gov. Retrieved April 17, 2021.
Daryl Michael Scott, “The History of Black History Month” Archived July 23, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, on ASALH website.
Del Maestro Cmf, W. (2023). Maestros de América Latina, una serie que todo educador y estudiante de educación tiene que ver. Web Del Maestro CMF. https://webdelmaestrocmf.com/portal/maestros-de-america-latina-una-serie-que-todo-educador-y-estudiante-de-educacion-tiene-que-ver/
Du Bois, William Edward Burghardt (1997). The correspondence of W. E. B. Du Bois, Volume 3. University of Massachusetts Press. p. 282. ISBN 1-55849-105-8. Retrieved May 30, 2011.
Du Bois, W. E. B. The Souls of Black Folk. New York, Avenel, NJ: Gramercy Books; 1994
Evans, N. E. C. (2021, July 11). A Federal Probe Into Indian Boarding School Gravesites Seeks To Bring Healing. NPR. https://www.npr.org/2021/07/11/1013772743/indian-boarding-school-gravesites-federal-investigation
Hine, Darlene Clark (1986). “Carter G. Woodson, White Philanthropy and Negro Historiography”. The History Teacher. JSTOR. 19 (3): 407. doi:10.2307/493381. ISSN 0018-2745. JSTOR 493381.
Hooks, Bell (1994). Teaching to transgress: education as the practice of freedom. New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0415908078. OCLC 30668295.
Jan. 5, 1931: Lemon Grove incident – Zinn Education Project. (2023, January 6). Zinn Education Project. https://www.zinnedproject.org/news/tdih/lemon-grove-incident/
Kahn, Jonathon S., Divine Discontent: The Religious Imagination of W. E. B. Du Bois, Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-530789-4.
Lewis, David Levering (1993). W. E. B. Du Bois: Biography of a Race 1868–1919. New York City: Henry Holt and Co. p. 11. ISBN 9781466841512.
Liberatory thinking. (n.d.). https://www.cps.edu/sites/equity/equity-framework/equity-lens/liberatory-thinking/
Love, B. (2019). We Want To Do More Than Survive: Abolitionist Teaching and the Pursuit of Educational Freedom. Beacon.
National Education Association | NEA. (n.d.). https://www.nea.org/
Paulo Freire | Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy. (n.d.). https://iep.utm.edu/freire/
PBS Online: Only A Teacher: Schoolhouse Pioneers. (n.d.). https://www.pbs.org/onlyateacher/john.html
Perez, D. (2022b, January 3). Social foundations of K-12 education. Pressbooks. https://kstatelibraries.pressbooks.pub/dellaperezproject/
Perez, D. (2022a, January 3). Chapter 4: Foundational Philosophies of Education. Pressbooks. https://kstatelibraries.pressbooks.pub/dellaperezproject/chapter/chapter-3-foundational-philosophies-of-education/
Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind in society: The development of higher psychological processes (A. R. Luria, M. Lopez-Morillas & M. Cole [with J. V. Wertsch], Trans.) Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press. (Original work [ca. 1930-1934)
Wamba, Philippe (1999). Kinship. New York, New York: Penguin Group. p. 82. ISBN 978-0-525-94387-7.
IMAGES
3.1 – “Two silhouette profile or a white vase.” by Wikimedia Commons is in the Public Domain, CC0
3.2 – “W.E.B. Du Bois” by James E. Purdy, Wikimedia Commons is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
3.3 – “Carter Godwin Woodson” by Flickr is licensed under CC BY 4.0
3.4 – “bell hooks” by Wikimedia Commons is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
3.5 – “Henry Giroux” by Flickr is licensed under CC BY 4.0
3.6 – “Paulo Freire” by Wikimedia Commons is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
3.7 – “Gabriela Mistral sonriendo” by Wikimedia Commons is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
3.8 – “Sarmiento” by Get Archive is in the Public Domain, CC0
3.9 – “Simón Rodriguez” by Wikipedia is licensed under CC BY 4.0
3.10 – “Jose Vasconsuelos” by Wikipedia is licensed under CC BY 4.0
3.11 – “Jose Carlos Mariategui” by Wikipedia is licensed under CC BY 4.0
3.12 – “Jose Marti” by Wikipedia is licensed under CC BY 4.0
Videos
3.1 –Essentialism in Education (Essentialist Philosophy of Education, Essentialist Theory of Education)s” by PHILO-notes, YouTube is licensed under CC BY 4.0
3.2 -“Perennialism: Overview & Practical Teaching Examples” by Shayla Czuchran, YouTube is licensed under CC BY 4.0
3.3 – “Progressivism: Overview & Practical Teaching Examples” by Teea Shook, YouTube is licensed under CC BY 4.0
3.4 – “Social Reconstruction” by Sarah Barlowe, YouTube is licensed under CC BY 4.0
3.5 – “Paulo Freire’s Critical Pedagogy” by Dr. Yu-Ling Lee, YouTube is licensed under CC BY 4.0
3.6 – “The Earth Talks: Indigenous Ways of Knowing – with Pat McCabe” by Dartington Trust, YouTube is licensed under CC BY 4.0
3.7 – “Presentación de la serie Maestros de América Latina” by UNIPE Universidad Pedagógica Nacional, YouTube is licensed under CC BY 4.0
3.8 – “The danger of a single story “ by Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie, YouTube is licensed under CC BY 4.0

