5.1 Chapter Learning Objectives and Overview
Learning Objectives
- Identify different groups within real world situations.
- Explain the ways that group size and structure influences group dynamics.
- Differentiate among styles of leadership and types of authority.
- Interpret the impact of groups on individual behavior.
- Distinguish strong and weak ties in your social networks.
- Distinguish the types of formal organizations.
- Recognize the characteristics of bureaucracies and collectivist organizations.
- Explain why organizations tend to appear similar.
Overview
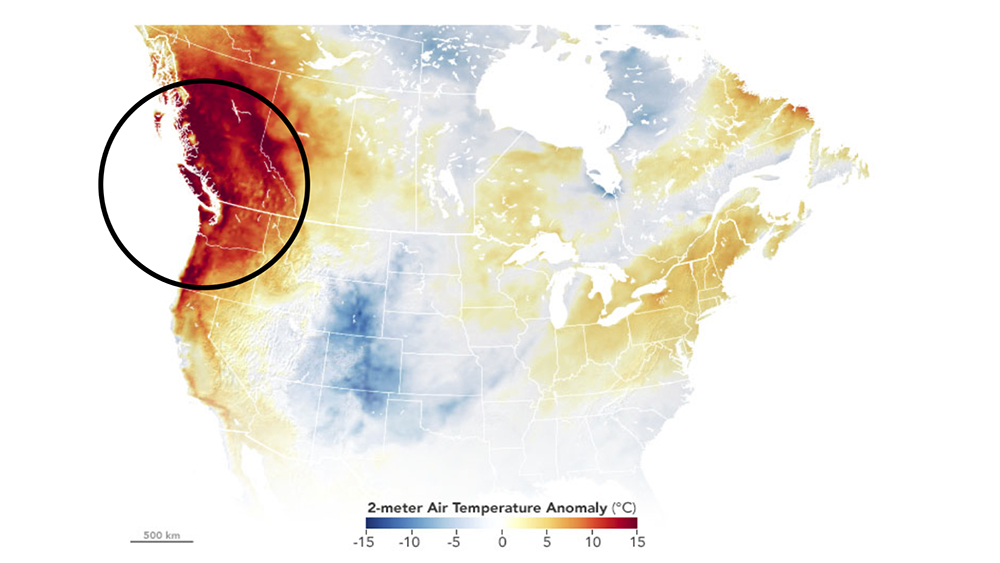
In late June 2021, temperatures across the Pacific Northwest region of the United States spiked to over 100 degrees (figure 5.1). This was particularly problematic because it was early in the summer when people had not adjusted to the summer heat. In addition, temperatures did not cool off much at night, so it was difficult to cool down living spaces if you did not have an air conditioner.
In preparation for the heat wave, Oregon’s Multnomah County government opened several cooling centers and nine libraries to serve as spaces for those without air conditioning. County employees reached out to vulnerable residents, while teams of people roamed the city handing out water and other items to help people cool off (Flaccus 2021).
Lyle Crawford, in his early 60s, was in his home as the temperatures hit 108 degrees. He was alone. He had few close friends and was further isolated because of the pandemic. He had a box fan to help provide some air circulation. When his sister called him to see how he was doing, he didn’t pick up. She left a message on his answering machine. It would be the last time she heard his voice (Guernsey and Vines 2021).
By some estimates, over 800 people died in Oregon, Washington, and British Columbia as a result of the heat wave (Guilfoil 2022). Heat waves are often the deadliest type of severe weather in the United States (Lewis 2021). How could we use our sociological imagination to explain the consequences of the heat wave? What social factors explain some people’s exposure to the risks associated with the heat wave? What role did organizations play in response?
In this chapter, we will explore meso-level phenomena that exist between the micro and macro aspects of social life. In what follows, we will explore different types of groups and how they are structured. We will then turn our attention to social networks, social capital, and social isolation. We will end this chapter by focusing on organizations and some of their dynamics.
Licenses and Attributions for Chapter Learning Objectives and Overview
Open Content, Original
“Overview” by Matthew Gougherty is licensed under CC BY 4.0.
Open Content, Shared Previously
Figure 5.1. “NASA Earth Observatory image of temperature anomalies on June 27th, 2021, compared to 2014-2020 average for the same day during the 2021 western North America heat wave” by NASA Earth Observatory/Joshua Stevens is in the Public Domain.
any collection of at least two people who interact with some frequency and who share some sense of aligned identity.
people in your network that you are not that close to.
organizations that have a clear division of labor, a hierarchy, and formal rules and procedures.
organizations concerned with pursuing their mission or values. Often the opposite of a bureaucratic organization.
an awareness of the relationship between a person’s behavior and experience and the wider culture that shaped the person’s choices and perceptions.
using social connections and networks as a resource.

