Lesson 2.1: World View and Self Efficacy
World View

Most textbook chapters on management tasks involved in effective learning start with the famous (and infamous) topic of procrastination. The term comes from Middle French and Latin and, of course, means putting something off until later.
It is hardly necessary to define this common problem at school–and everywhere else–in any language, however. We all know what it is. We all do it, and we’ve all suffered to some extent because of it (missed deadlines tend to make instructors–and bosses–crabby).
But here is a problem: some people procrastinate more than others. And NOT just because they are lazy, disorganized, unmotivated, or confused about what to do. Those might be the surface assumptions and sometimes true, but at other times, or perhaps beneath what appear to be the behaviors listed above, defeating habits like procrastination have to do with deeper issues, maybe beliefs and thought patterns such as:
- “What’s the use if I get this done, or not?”
- “I do better under stress, so leaving things until the last minute actually helps me.”
- “I’m just naturally disorganized.”
- “I never manage to do anything on time. I’ve always been that way!”
This is why Unit 2 begins with “foundational issues,” perspectives and beliefs about ourselves such as our world view that operates at the bottom of our pile of motivations, and our sense of self-efficacy (or lack thereof) that generates thoughts that either work for or against us when it comes to successfully managing time, tools, and environments of learning. Lesson 2.2 deals with procrastination itself, often a by-product of a negative or unexamined world view and a low sense of self-efficacy, but with an emphasis on how to overcome it.
First, here is a look at world view, a concept some experts put at the foundational level of how we think and perceive the world. On top of our world view, so to speak, and as a result of it, are our beliefs. And on top of beliefs lay our conscious-level feelings and thoughts.
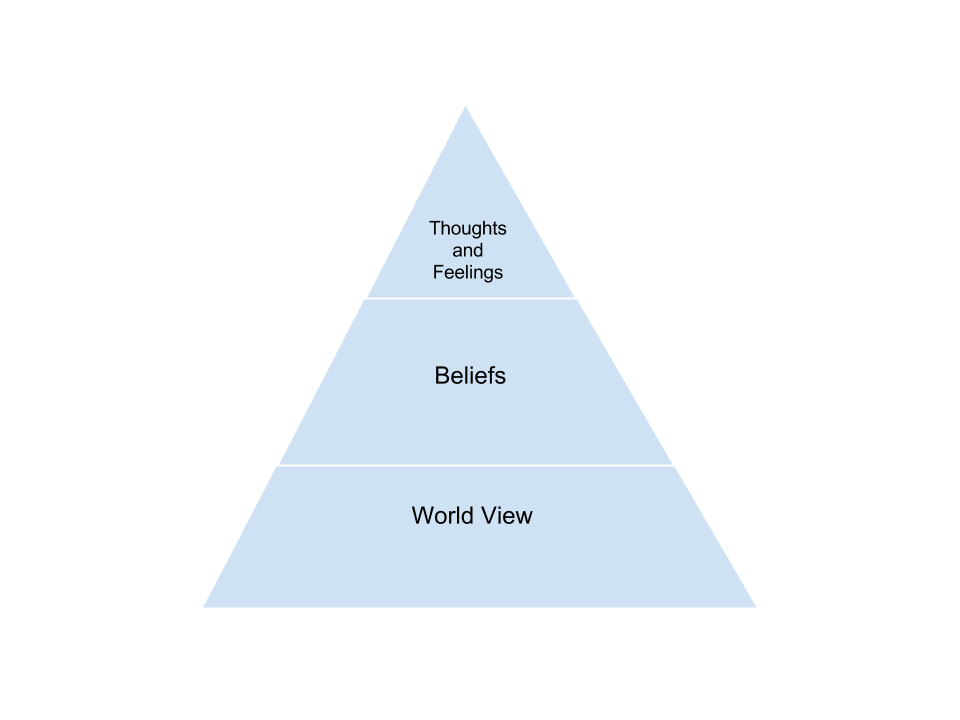
Our world view, as researcher F. Heylighen defines it, is “a framework that ties everything together, that allows us to understand society, the world, and our place in it, and that could help us to make the critical decisions which will shape our future.” In his article What is a world view? Heylighen, citing the work of Belgian philosopher Leo Apostel, lists seven basic components of a person’s world view:
- A model of the world (how the world functions/how it is structured)
- Explanation (of the model)
- Futurology (where are we going?)
- Values (good/evil)
- Action (plans of action based on our values)
- Knowledge (true and false)
- Building Blocks (what fragments of others’ world views helped us shape ours)
These components cover the fundamental questions about existence human beings find themselves mulling over in time, questions that ultimately guide beliefs, thoughts, and feelings.
Exercise 2.1 is based on Heylighen’s article. Whereas this exercise is not a “personal inventory” per se, it has value in guiding the learner to discovering, perhaps, some foundational issues that can hinder a successful approach to overcoming non-productive actions and habits such as procrastination.
For example, if a person has a world view that is post modern, he/she views the world with a heavy dose of skepticism and distrust of ideologies, rationality, and absolute truth. Therefore, it might be easy to subscribe to a “What’s the use?” thought and feeling when it comes to academic and work-world norms such as being on time and getting one’s work done.
Note: it is not necessary, however, to know precisely which world view one has been influenced by to complete the exercise. Indeed, most people more or less absorb their world views from parents, institutions, and the culture in which they grew up. The value in knowing such information about oneself is in understanding how to deal with certain attitudes and beliefs that work against successful learning, and success in life in general. It is also valuable to know what has contributed to successful attitudes and beliefs so that these can be affirmed and reinforced for future success.
UNIT 2, EXERCISE 2.1
- Read the article by Heylighen, linked above, for a more detailed explanation of world view and the seven components he cites.
- Briefly respond to your thoughts on each of the seven components. If you have not given much thought to some of them as of yet, take time to consider them now. Three to five sentences will likely be sufficient for each component, for a total of approximately 21-35 sentences. It would be helpful to number the components. This does not have to be completed as an essay.
Self Efficacy
Self efficacy, or one’s sense of being able to achieve goals, is an essential ingredient in a learner’s ability to succeed. Thoughts and feelings on this topic, which stem from one’s beliefs (remember the pyramid illustration) contribute to more, or less, success.
A key element of self efficacy is the concept of locus of control. As the definition indicates, the locus, or place, of control is usually either internal or external, but sometimes it is both.
Obviously if a person believes that he/she is in control of situations and outcomes (an internal locus) achieving goals is more likely. If a person believes he/she is controlled by external forces, achieving goals is less likely. But everyone experiences both internal and external forces for various reasons. For example, choosing to do the right thing on the job is based on the external control of workplace rules. Yet, one might apply for the job based on one’s internal belief that he/she can succeed. And both internal and external loci of control are in operation when one chooses to do the right thing at any time based on one’s beliefs about God.
For a more detailed explanation and the relationship of self efficacy to locus of control, complete exercise 2.2.
UNIT 2, EXERCISE 2.2
After reading the definition of this concept in the article cited above, answer the following questions:
- List three attitudes and/or perspectives that a person with a primarily internal locus of control might have that will help him/her succeed in life, and why.
- List three attitudes and/or perspectives that a person with a primarily external locus of control might have that might hinder his/her success, and why.
- List three instances where both internal and external loci of control help a person, and why.
A chart might help you organize your response.
INTERNAL EXTERNAL BOTH
UNIT 2, EXERCISE 2.3
Write about FIVE ways the information in this lesson can help you to create and achieve more success in your life-long learning career, whether in a classroom or in any of your other learning arenas. While you are gathering your thoughts about this topic, consider learning situations at school, work, home, and in relationships. 200-300 words (about one page, typed, double-spaced).

