2.7 Directional Control Valves
Describe the purpose of a valve in a fluid power system
Describe the purpose of a directional control valve in a fluid power system
Define the following features of directional control valves: positions, ports/ways, return springs, actuation method, deactivated state
Draw the schematic symbol for a 2 position, 2 way, solenoid actuated, spring offset, NC directional control valve. Describe its behavior and use in a fluid power system.
Draw the schematic symbol for a 2 position, 2 way, solenoid actuated, spring offset, NO directional control valve. Describe its behavior and use in a fluid power system.
Draw the schematic symbol for a manual override and discuss its purpose
Draw the schematic symbol for a 2 position, 3 way, manually actuated directional control valve spring offset to a deactivated position that blocks flow at 2 and allows flow from 1 to 3. In its activated state it allows flow from 2 to 3 and blocks flow at 1. Draw three different configurations of this valve.
- selector valve – 1 A, 2 P, 3 B
- spring retracted, hydraulically extended single acting cylinder – 1 T, 2 A, 3 P
- spring retracted, hydraulically extended single acting cylinder – 1 P, 2 A, 3 T
Draw the schematic symbol for a 2 position, 3 way, solenoid actuated directional control valve, spring offset to a position that dumps A to T and when activated routes P to A, describe how this can be used in a failsafe braking application
Draw the schematic symbol for a purposely blocked or plugged port, describe how blocked ports can be used to change the functionality of a directional control valve.
Draw the schematic symbol for a 2 position, 4 way, manually actuated directional control valve used to control a double acting cylinder. Describe the cross connect position. Describe the straight through position.
Describe detents used to position a valve. Describe how an automatic detent with kickout works. Describe the operation of a double solenoid 2 position valve with detents.
Draw the schematic symbol for a 3 position, 4 way, manually actuated directional control valve used to control a double acting cylinder. Describe the closed center position and how it affects the actuator and pressure relief valve.
Describe the tandem center position and how it affects the actuator and pressure relief valve.
Describe the float center position and how it affects the actuator and pressure relief valve.
Describe the open center position and how it affects the actuator and pressure relief valve.
Describe the behavior of a double acting cylinder with both cap and rod end at the same pressure.
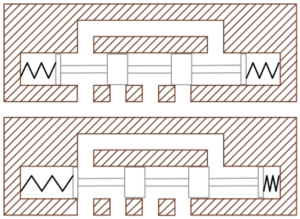
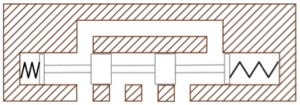
Use these cutaway diagrams to describe how the spool affects the position of a directional control valve. Label each position given ports are assigned: A, P, B, T
Describe how flow control restrictions are implemented in a directional control valve and their purpose.
Describe what check valves in a directional control valve position box imply
Describe the shape of the pressure drop for different flow rates performance curve and how to read it
Describe the shape of the operating limits performance curve and how to read it
Identify common entries found on a directional control valve data sheet (Bul 2531-M11 D1VL Data Sheet)