35 DNA Replication in Prokaryotes
Recall that the prokaryotic chromosome is a circular molecule with a less extensive coiling structure than eukaryotic chromosomes. The eukaryotic chromosome is linear and highly coiled around proteins. While there are many similarities in the DNA replication process, these structural differences necessitate some differences in the DNA replication process in these two life forms.
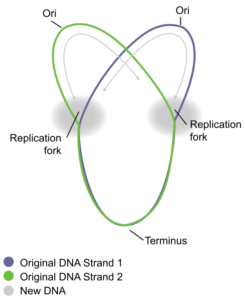
DNA replication has been extremely well-studied in prokaryotes, primarily because of the small size of the genome and large number of variants available. Escherichia coli has 4.6 million base pairs in a single circular chromosome, and all of it gets replicated in approximately 42 minutes, starting from a single origin of replication and proceeding around the chromosome in both directions. This means that approximately 1000 nucleotides are added per second. The process is much more rapid than in eukaryotes. Table 2 summarizes the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic replications.
Table 2: Differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Replication
| Property | Prokaryotes | Eukaryotes |
| Origin of replication | Single | Multiple |
| Rate of replication | 1000 nucleotides/s | 50 to 100 nucleotides/s |
| Chromosome structure | circular | linear |
| Telomerase | Not present | Present |
References
Unless otherwise noted, images on this page are licensed under CC-BY 4.0 by OpenStax.
OpenStax, Concepts of Biology. OpenStax CNX. May 18, 2016 http://cnx.org/contents/s8Hh0oOc@9.10:2ousESf0@5/DNA-Replication


Feedback/Errata