46 Meiosis II
In meiosis II, the connected sister chromatids remaining in the haploid cells from meiosis I will be split to form four haploid cells. The two cells produced in meiosis I go through the events of meiosis II in synchrony. Overall, meiosis II resembles the mitotic division of a haploid cell. During meiosis II, the sister chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle fibers and move toward opposite poles.
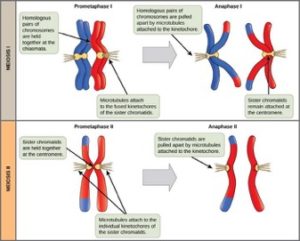
Nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes. Cytokinesis separates the two cells into four genetically unique haploid cells. At this point, the nuclei in the newly produced cells are both haploid and have only one copy of the single set of chromosomes. The cells produced are genetically unique because of the random assortment of paternal and maternal homologs and because of the recombination of maternal and paternal segments of chromosomes—with their sets of genes—that occurs during crossover.
References
Unless otherwise noted, images on this page are licensed under CC-BY 4.0 by OpenStax.
OpenStax, Biology. OpenStax CNX. May 27, 2016http://cnx.org/contents/s8Hh0oOc@9.10:1Q8z96mT@4/Meiosis


Feedback/Errata