2 Histology review
- A short history of histology
- 4 main tissue types (by adult appearance)
- epithelia
- connective tissue
- muscle
- nervous
- 3 main tissue types (by embryonic lineage)
- ectoderm
- mesoderm
- endoderm
A short history of histology
The aim of this chapter is to review histology covered in Anatomy & Physiology classes– just he tissues located in the head and neck, and only the parts relevant to dental hygiene. This is not a comprehensive review of histology. If you need an extra review on general histology, try these links:
An interactive histology flowchart(link provided if content above does not show in your eReader)- by Laird C. Sheldahl, Ph.D.
The Internet Pathology Laboratory for Medical Education- at The University of Utah, Eccles Health Sciences Library.
Histologyguide.org- by T. Clark Brelje, Ph.D. and Robert L. Sorenson, University of Minnesota.
- Open Science Laboratory
- a virtual microscope on the internet, with focus and everything.
Histology is the study of what tissues look like under a microscope. A tissue is a group of cells, all of the same type, working together to perform a function. Because most cells are transparent, microscopists use of a number of different stains to highlight different parts of cells. Fig 2.1 is an image of a very common staining technique using the dyes Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E). These two stains turn molecules with negative charges blue, and positive charges pink. We don’t actually care about charges, we need to make different parts of the cell different colors so we can see them. DNA and RNA take up both colors, which makes nucleuses purple, while most proteins turn pink. Unfortunately, most cells are full of proteins and their cytoplasm turns pink, but the ECM is also full of protein, so it turns pink as well. This leaves us freueqntly trying to differentiate between similar-looking seas of pinks with purple spots. Sound familiar? On the plus side, if you purchase a histology coloring book, you only need two crayons.
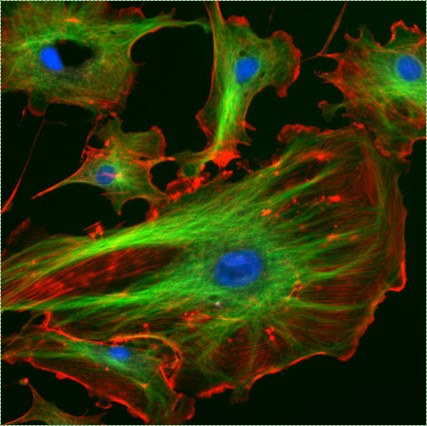
"Fluorescent cells" by NIH image is in the Public Domain CC0Imaging
Most of the images you see in histology textbooks use stains such as H&E stains– this type of technology dates back to the 1800s. Microscope technology has improved since then, such as the image in Fig. 2.2, which comes from a confocal microscope. The confocal microscope uses expensive lasers to generate very beautiful images, and uses stains that are much more specific than H&E. Sadly, most textbooks still use the old-fashioned (uglier) images. Since you should be using neither the newer nor the older microscopes in your line of work, we have illustrated most of the histology images in this book. This allows us to focus on the concepts, and spend less time developing the skills necessary to interpret pictures of pink blobs with purple spots. We presume that in the Anatomy and Physiology classes you took to get into a Dental Hygienist program, you were taught to spot the differences between different types of tissues. We review those differences in this chapter. That’s great, especially in Anatomy, which focuses on classifying and naming things. You have a more important task now. If you didn’t do so before, keep an eye out for similarities between different tissues (aside from most look like pinkish blobs with purple spots). Anothe way to say that is you should look for patterns←. If you jump ahead and read the embryology chapters, you’ll have a better idea of what to look for. For now, keep that thought in the back of your head as we cover the major tissues of the head and neck.
Enough embryology to start learning about histology
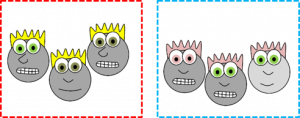
Classification: the old way, and a better way.
Histology categorizes tissues based on what the cells look like in adulthood. If we determined people’s families based off what they look like as adults, we might do an OK job of it, or we might make mistakes. For instance, we might lump the cartoon faces in Fig. 2.3 into two families based primarily on hair and eye color. That is how the four major tissues types are categorized. The problem with this sort of classification system is it is hard to tell what physical traits are due to nature (genetics, such as eye color) versus nurture (environmental factors, such as hair dye).

When we learn about embryology, we see we can do better. We can categorize tissues using cell lineage instead, tracing who the adult cells are related to. Early embryologists stained individual cells and followed them through cell division after cell division to see what they became. Others, such as Hans Spemann, moved cells from one place to another and asked whether they still turned into what was expected, based on their new location. When transplanting just a few cells lead to embryos growing two complete heads, Spemann concluded that was unexpected (actually, that was the conclusion of his graduate student, Hilde Mangold, whose doctoral thesis became the basis for the work that won Spemann the Nobel Prize).
To get a better idea how that happens, science had to wait for the end of WWII. Suddenly, a large number of physicists no longer had jobs building deadly rockets and atomic bombs. Many turned their skills to studying genetics, creating the field of molecular biology. With new tools, developmental biologists like Christiane Nüsslein-Volhard identified mechanisms by which a single embryonic cell becomes different types of cells in an adult. Her organism of choice was flies, and for that work she won the Nobel Prize. Unlike earlier histologists and embryologists who named everything after themselves, more recent embryologists gave their discoveries fun names like Bicoid, Dickkopf, Frizzled and Sonic Hedgehog.
So, rather than use the appearance of our cartoon people, if we identify their lineage (you might also see the fancier term ontogeny), we can classify them into more accurate families, with one sub-family (Fig. 2.4). When you see the word lineage, think family tree, where differentiated← cells are the youngest generation, and stem cells← are their parents or grandparents. Sadly, this is not how histology is taught, so we’re going back to what adult cells look like and classify tissues based on physical characteristics. But as we do, look to see whether two tissues have distinct borders (likely different lineages) or blended borders (often the same lineage).
The 4 main tissue types
| The 4 main tissue types |
|---|
| Epithelial |
| Connective Tissue |
| Muscle |
| Nervous |
Epithelia
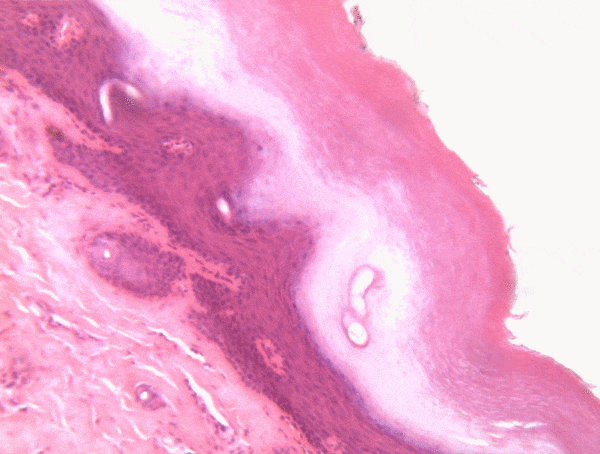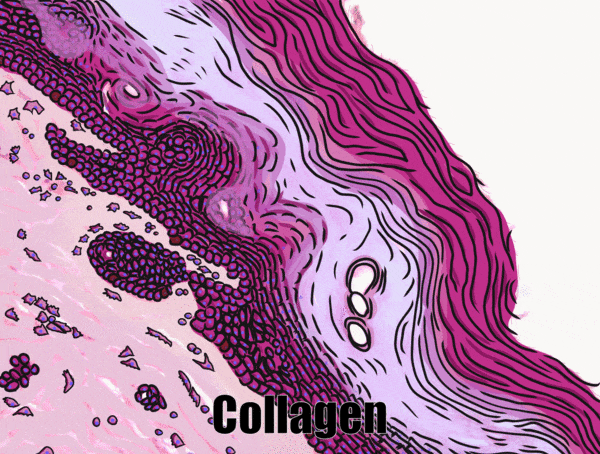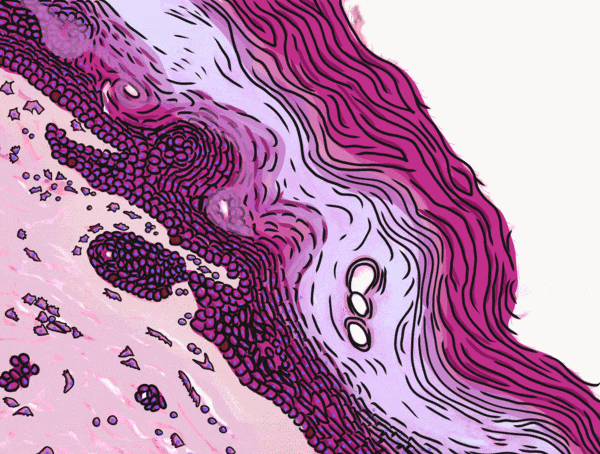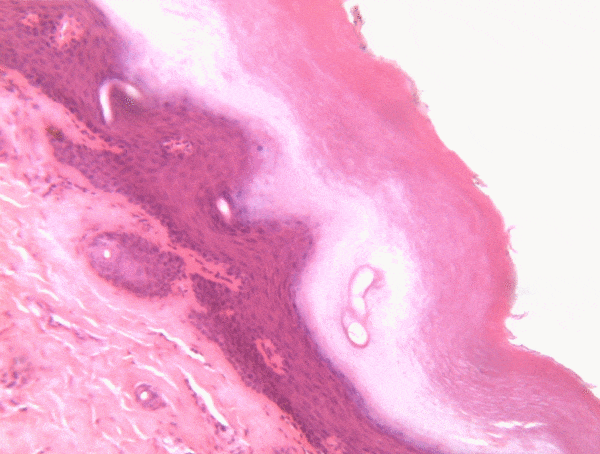
Location of epithelia
An epithelium is composed of epithelial cells, usually connected to one another in a sheet. There is very little ECM in an epithelium. Epithelia are mostly cells, but they do make a small amount of ECM called the basement membrane. The basement membrane is located on the basal side (see below) and holds an epithelium in a single sheet. The cells are anchored to the basemement membrane by hemi-desmosomes, and to each other by CAMs← and desmosomes←. Desmosomes also hold an epithelium in a sheet. Tight junctions← ensure that the things that travel from one side of the epithelium to the other must pass through the epithelial cells. To cross an epithelium, molecules must either be lipid-soluble, or be recognized by trans-membrane proteins← on the apical and basolateral plasma membrane←. An epithelium therefore has apical-to-basolateral polarity. The apical surface faces the outside of the body, and the basolateral inward, and polarity means the two sides are different. The outside can mean the outer surface of the skin, or an inner surfaces, such as the lumen of the oral cavity, stomach, and bladder. Every surface of the human body is an epithelium. Therefore, under the microscope, if you see an empty space, an epithelium borders that space. The inner lining of a sweat duct is an epithelium. The inner lining of a blood vessel is an epithelium. All other tissues are between that epithelium and the epithelium on the outer surface of the body. Even enamel is made by an epithelium, so if anyone tells you enamel is a connective tissue because it looks similar to bone tissue, they haven’t studied embryology, and need to be educated. Use words like ontogeny.
Epithelia are thin
Epithelial tissue is good at healing because it contains numerous stem cells← capable of undergoing mitosis← (you can identify them when they have visible chromosomes, rather than chromatin). For thicker epithelia, stem cells reside in the basal layer. Epithelia cannot be terribly thick, however, because they are avascular (without their own blood vessels). Nutrients for an epithelium must diffuse from underlying connective tissue, which is why in Fig. 2.6, the epithelial cells on the apical side lack nucleusses. The cells are dead, but still connected to the rest of the epithelium by desmosomes←. The down-side of being good at mitosis is it means those cells are a few steps closer to becoming cancerous. Many people regularly expose themselves to high doses of carcinogens found in alcoholic beverages and tobacco, which can lead to oral cancers.
In addition to flat sheets, epithelial cells form glands. Exocrine glands, such as salivary glands, contain single layers of epithelial cells rolled up into tubes called ducts. These ducts bring exocrine secretions to a surface of the body. Endocrine glands are different. They are not arranged in a sheet, but are amorphous clusters of epithelial cells. Endocrine glands aren’t avascular, either. Blood vessels grow into the epithelia of an endocrine gland. This is important because endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream.
| Number of layers | Shape of cells |
|---|---|
| Simple | Squamous |
| Stratified | Cuboidal |
| Columnar |
Epithelia are mostly classified based on two criteria. With a few exceptions, epithelia have a name from the first column plus a name from the second column of Table 2.2. Simple epithelia have just one layer of cells, while stratified epithelia have more than one. Squamous means the cells are flat, like fried eggs. Cuboidal means square-ish in appearance (cells are 3-D, but look 2-D under the microscope). Columnar means the cells are tall (like columns).
Simple squamous epithelia
If you look at the lining of a capillary, you might be able to see the simple squamous epithelium that lines the inner surface. These cells, called endothelial cells, are functionally really cool cells, even if they are hard to see. The tissue that is composed of the endothelial cells is called an endothelium. The endothelium forms the barrier between the blood (or lymph) and surrounding tissues, but can become damaged, such as during probing, flossing, coughing, or from systemic inflammation due to an infection or auto-immune reaction. During an intraoral exam, damaged capillary walls may present as punctate bleeds called petechia (often on the palatal mucosa).
An intact endothelium regulates the permeability of materials in or out of a tissue. Furthermore, endothelia perform important functions in signal cell signaling← by secreting hormones, including VEGF which regulates angiogenesis and von Willebrand factor which regulates blood clotting.
Another important simple squamous epithelium is the one that lines organs in the ventral body cavity (such as the lungs and intestines), called a mesothelium. The main function of a mesothelium is to secrete serous fluid, composed primarily of glycoproteins and the water they attract. A mesothelium also play important roles in cell signaling, including the inflammatory response and tissue growth.
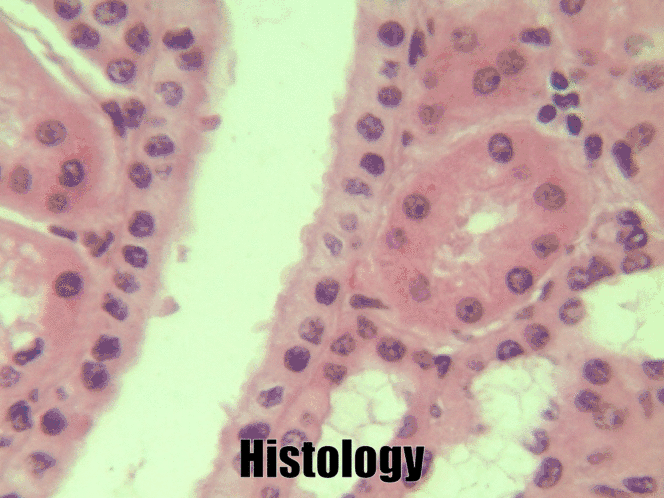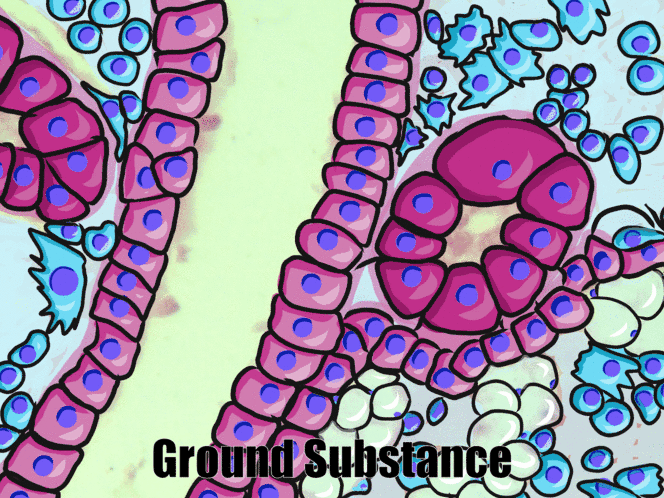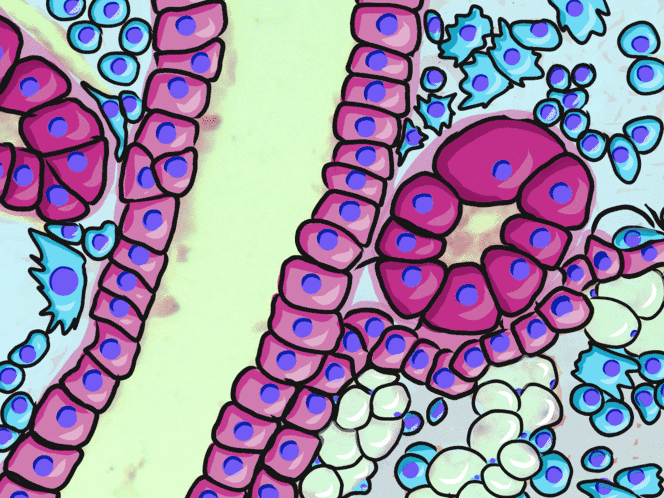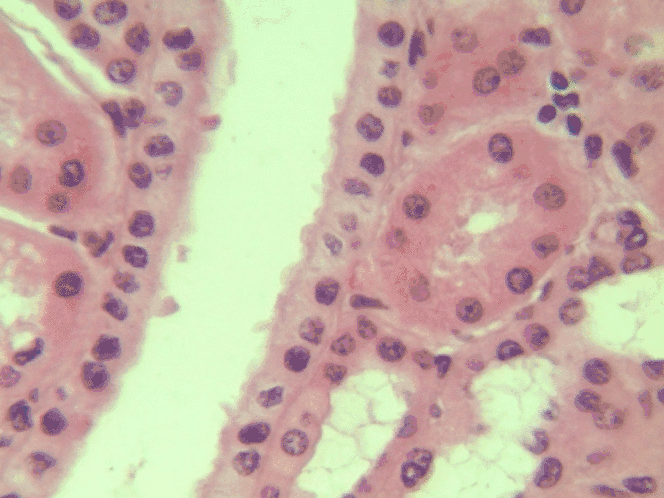
Simple cuboidal epithelia
At one point in your life, you were a simple cuboidal epithelium. In adults, we find simple cuboidal epithelia lining most exocrine gland ducts, such as sweat and salivary glands. In Fig. 2.8, you should see two ducts coming out towards the camera, and one duct running up-and-down. The lumen of each duct is lined by a simple cuboidal epithelium. The cuboidal cells in the epithelium are connected to their neighbors on the sides by CAMs← and desmosomes←. Where two ducts are close together, there are two simple cuboidal epithelia, not one stratified epithelium. There are two separate layers of epithelia, with a little ground substance← between them. Stratified cuboidal epithelia exist, such as in parts of the parotid salivary gland, but they are rare enough that we don’t need to look at them. The capillaries in Fig. 2.7 are lined by flat cells to allow for bulk flow of fluids (including nutrients) out of the capillary and waste products in. The salivary ducts in Fig. 2.8 have thicker cells to keep the flow of saliva down the tube, not leaking out of the tube creating a ranula.
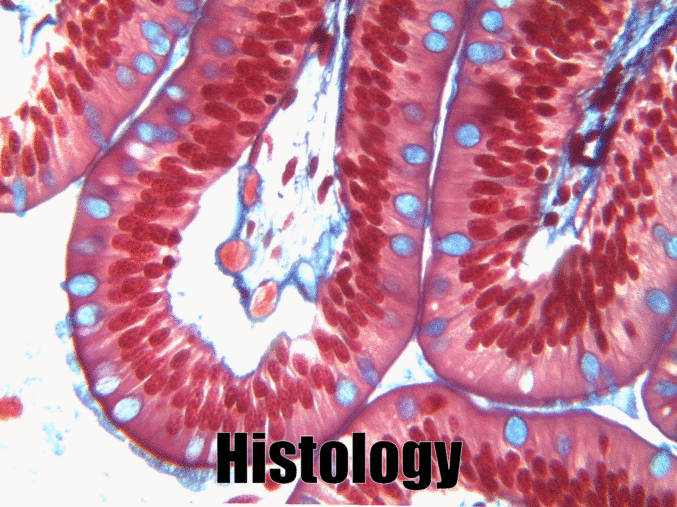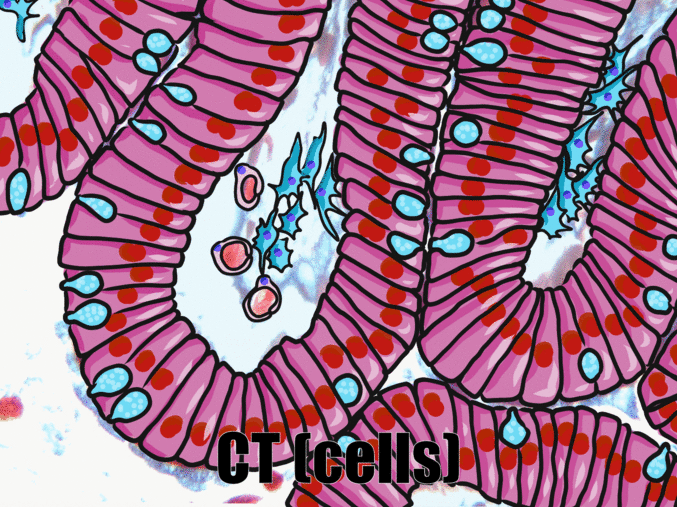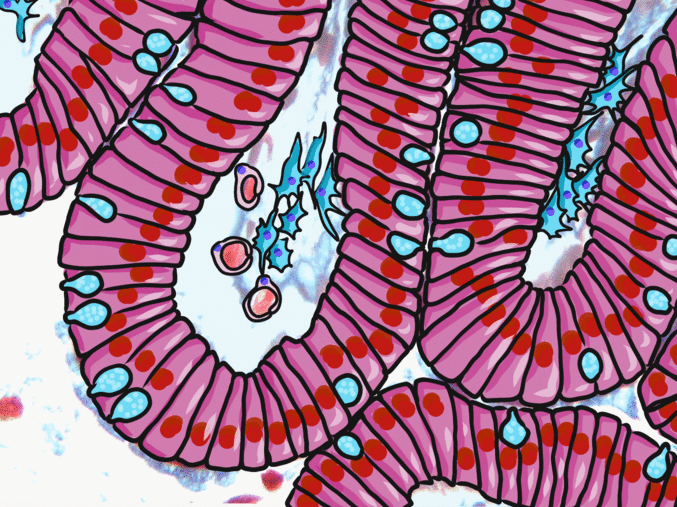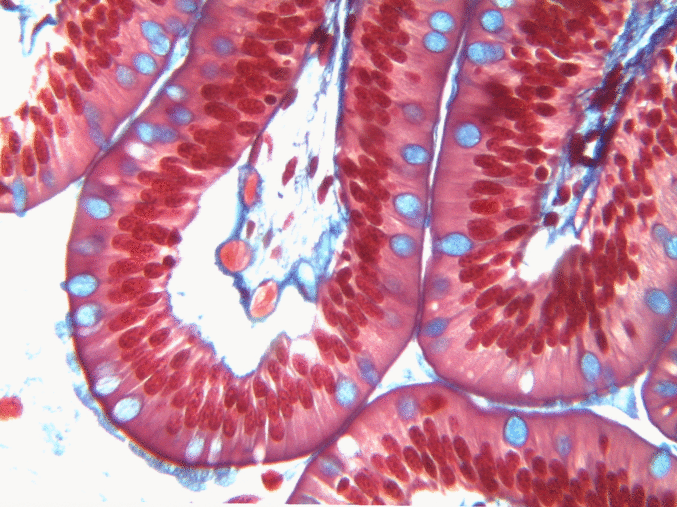
Simple columnar epithelia
Simple columnar epithelia are not found in the adult oral cavity. In an embryo, the columnar IEE differentiates← into enamel-producing ameloblasts during the 6th week after fertilization. The shape isn’t important other than it helps histologists identify which cells are fated to become ameloblasts in a developing tooth.

"photo" by unknown is in the Public Domain, CC0If you are looking at the illustration in Fig. 2.9, you may wonder why there are fewer cartoon nucleuses than the histology picture. Did the illustrator mistakenly give you a picture of a stratified columnar epithelium and try to pass it off as simple? No. When we say an epithelium is simple, it means one cell thick from apical-to-basolateral. But when we cut a tissue sample to view under the microscope, the slice may be several cells thick from side-to-side. And when we lay the tissue sample on its side, the cells that were running side-to-side are now sitting on top of one another. We have illustrated what a simple epithelium should look like if we had the ideal one-cell-thick slice of tissue. This is a good time to bring up perspective. Epithelia form flat sheets or membranes, and in Fig. 2.9 we are looking at a (folded) sheet in cross section. Imagine slicing through your bed and looking at it from the side view. You could make out the individual, simple layers of your unfolded bed sheet and comforter. Furthermore, you might note that while each is a single layer, the bed sheet is thin (squamous) and the comforter is thicker (columnar). You could identify the basolateral surface of your bed sheet (the side that touches you when you sleep) and the apical surface (the side close to the comforter). In Fig. 2.10, if there was a second cat on top of the first cat, we could say the layers of cats is stratified. But if the bed sheet was covered in a single layer of cats, side-to-side and front-to-back, the layer of cats would be simple. Under the microscope, we’re doing the same thing, but cells are semi-transparent (unlike cats, which you understand if you work at home on a laptop). Histology gets messy. When we call Fig. 2.9 a simple epithelium, it means there is only one pink cell between the white space (the lumen of the intestines) and the very light-blue space (the connective tissue, where nutrients are absorbed into blood vessels). Folding a sheet doesn’t turn it into multiple sheets. The cells in Fig. 2.9 are thicker than the cells in Fig. 2.8, but there are no columns on top of other columns.

Stratified squamous epithelia
While we have different names for the skin and the oral mucosa, if we pay attention to their lineage rather than their location or moistness, we note both contain a stratified squamous epithelium on their outer surface. Fig. 2.11 shows a keratinized stratified squamous epithelium, covered in more detail in Chapter 3. Keratin is a tough, water-resistant protein made by the main type of epithelial cell in this tissue, the keratinocyte. The stratified squamous epithelium of the skin changes at the vermilion zone to less-keratinized, and the stratified squamous epithelium of the oral mucosa is either less or non- keratinized. Based on that information, should we classify the vermilion zone as oral mucosa, skin, or it’s own thing? Or is there a line in the vermilion zone that divides into a skin half and an oral mucosa half? After you learn about embryology, decide for yourself. If you change careers and go into proctology, use this same information down there.
Stratified cuboidal, stratified columnar and transitional epithelium
These tissues do not appear in this book.
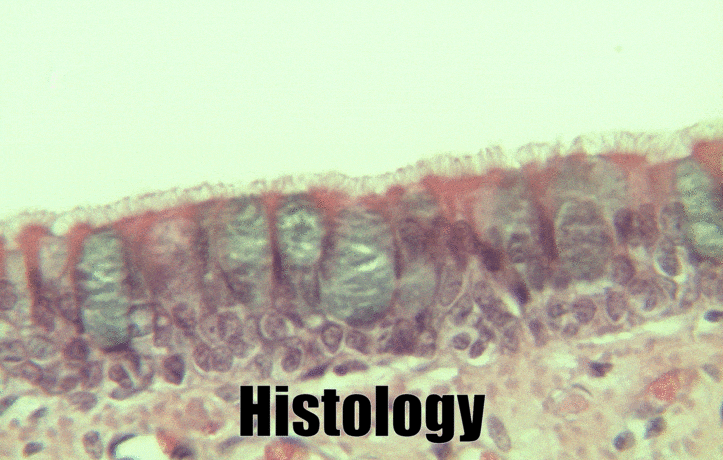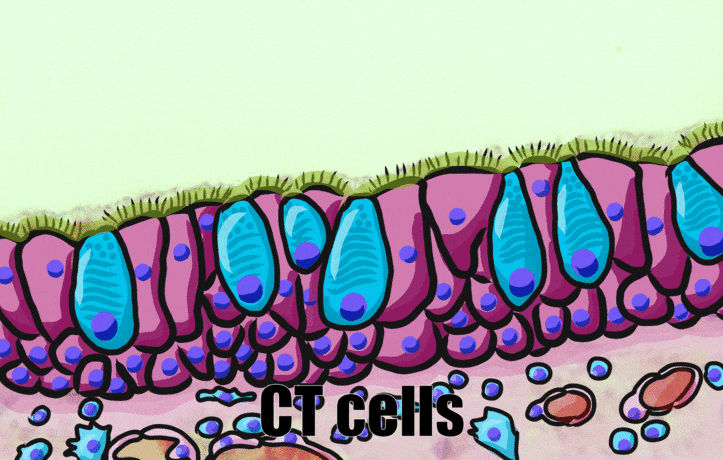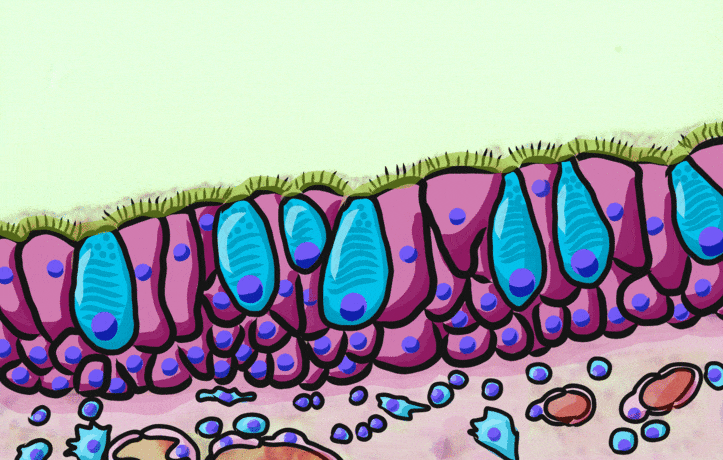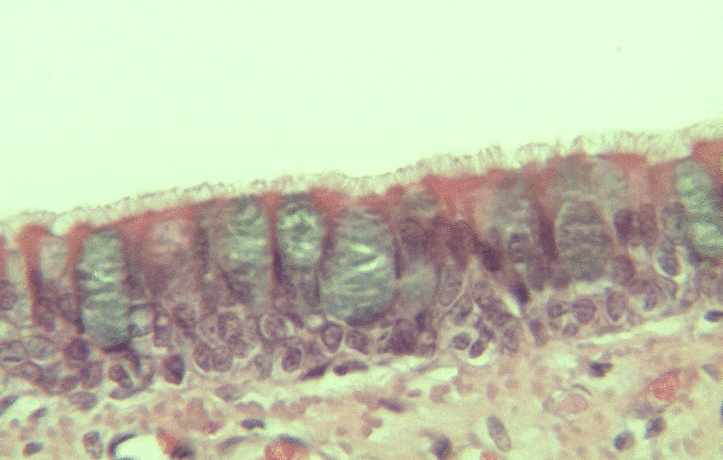
Pseudo-stratified epithelia
Ciliated pseudo-stratified columnar epithelium, or as many people say, pseudostratified epithelium, is found in upper portions of the respiratory tract, such as lining the nasal cavity and the para-nasal sinuses. This tissue deserves a different name from the stratified squamous epithelia of the skin, vermilion zone and oral mucosa. However, it probably didn’t need to break the naming rules outlined in Table 2.2. A pseudostratified epithelium has more than one layer, but it is hard to count how many. As a result, someone named this tissue pseudo-stratified (think of it as sort-of-stratified). The big blue cells in Fig. 2.12, which don’t have cilia, are goblet cells. These cells produce mucus. Goblet cells synthesize mucous proteins within their rER← and secrete them, and when they attract water, they become mucus. Mucus is very similar to ground substance←. However, mucus is secreted out of the body, ground substance is secreted into the body. The blue coloring of the goblet cells tells us that mucus proteins do not carry the same ionic charges as most proteins found within the epithelial cells of the pseudo-stratified epithelium. Due to this difference in color, they are classified as a distinct cell– a unicellular gland found within the pseudo-stratified epithelium. But what does our friend the embryologist say? Well, the columnar cells can’t become goblet cells, and the goblet cells can’t become columnar cells, but they do share a common ancestor (or stem cell←). We should consider the goblet cells part of the pseudo-stratified epithelium. Does it matter? No, but questions like this matter later in the book, it’s good to start practicing now.
Connective tissue (CT)
General characteristics of connective tissue
Many textbooks tell you connective tissue connects two other tissues. That sounds like a simple and straight-forward job. But that’s like saying your smart-phone connects you to other people. It is technically true, but glosses over the fact these could be people you know, people you don’t know, or people you don’t want to know. It ignores the fact you could be communicating synchronously with people on the other side of the world, communicating asynchronously over email, accessing information from the near sum-of-all human knowledge (the internet), or reading the sophomoric rant of some knuckle-dragger who, years ago, posted a rude comment on a YouTube video of a histology lecture (also the internet). So far, we’ve tried to skip information about histology that is not relevant to dental hygiene. But here we go into more detail than your average undergraduate histology class.
Many connective tissues come from segments in an embryo called somites (Fig. 2.13). Because of their shared lineage, connective tissues share a number of features. The average connective tissue has few cells, and is mostly composed of ECM. That matrix includes glycoproteins and polysaccharides made by the cells. These molecules attract water to form the gel matrix of ground substance←. Some important ground substance molecules covered earlier are fibronectin← and hyaluronic acid←. ECM also includes visible fibers. The three visible fibers are collagen←, reticular and elastic fibers. Connective tissues are typically highly vascular, meaning they contain blood vessels. There are a number of different cell types found within a connective tissue. The stem cells← are mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Mesenchymal stem cells are extremely important cells (here is further reading). Since you can find them in adult tissues they are called a type of adult stem cell. These cells are capable of undergoing mitosis← to produce more stem cells, which can differentiate← into fibroblasts, chondroblasts, osteoblasts, hemocytoblasts, myoblasts , adipocytes and other cell types. Thus, they form most connective tissues, including bone, cartilage, and blood (both red and white blood cells). Mesenchymal stem cells share lineage with muscle stem cells (myoblasts), and differentaite into muscle cells in the right environment. That’s pretty much everything except epithelia and neural tissue, which mesenchymal stem cells can form after going through an mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition←.
Indian Muntjac fibroblast cells by Michael W. Davidson is licensed CC BY 2.0In a basic connective tissue, mesenchymal stem cells← divide and differentiate← into fibroblasts. Fibroblasts are the cells that blast out fibers and ground substance← (the ECM). There may be other cells found in a connective tissue, including adipocytes, red and white blood cells, or other cells that have emigrated from a different tissue. In a mature connective tissue, the fibroblasts are sometimes called fibrocytes, which fits with the nomenclature for a cell going through stages of differentiation (from stem to blast to cyte). More frequently, however, they are called fibroblasts and we don’t worry about whether they are actively blasting out fibers or taking a rest.
Human Mesenchyme” By Jpogi at Wikipedia is in the Public Domain CC0Mesenchyme
Mesenchyme is the first type of connective tissue an embryo makes. It differentiates← into other connective tissues. It is an embryonic tissue that has yet to decide what it will become when it grows up. It is composed mainly of mesenchymal stem cells and mucous ground substance← (mucous is an adjective to describe loose ECM, while mucus is a substance secreted from the body). There is a special type of mesenchyme important to face and tooth development, called neuro-mesenchyme. The lineage of neuro-mesenchyme is not strictly from mesoderm like most connective tissues. Neuro-mesenchyme includes a special type of neuronal cell called a neural crest cell←. Neuro-mesenchyme forms connective tissues we have yet to mention: dentin, cementum, alveolar bone and the PDL.

Areolar connective tissue
Areolar connective tissue is the quintessential connective tissue, or the most boring depending on how you look at it. It contains a little of everything other connective tissues might have: cells, ground substance←, and all 3 fibers. Because it has a good amount of ground substance, it is an ideal tissue to occupy places where blood vessels might need space to grow in the future. Hence areolar connective tissue is found in regions that are highly vascular. This is why you can find a small layer of areolar connective tissue directly underneath nearly every epithelium, including the stratified squamous epithelium of the skin and oral mucosa. Ground substance also absorbs water and swells in size. This can be caused by changes in blood flow, which is why the areolar connective tissue of the nasal cavity may also be referred to as erectile tissue. The swelling of areolar connective tissue in response to inflammation, on the other hand, is called edema.
Dense irregular connective tissue
Underneath the areolar connective tissue of the oral mucosa is dense irregular connective tissue. Fibroblasts secrete the bulk of the tissue: collagen← fibers, the strongest of the 3 fiber types. In a dense irregular connective tissue, the collagen fibers point in all directions. This makes this tissue strong in all directions. In Fig. 2.17, most of the pink is extracellular collagen fibers, and the white space ground substance←. In addition to the sub-mucosa of the oral cavity, you find dense irregular connective tissue (along with its buddy, areolar connective tissue) in the dermis of the skin. Why in both places, you ask? Lineage!
Dense regular connective tissue
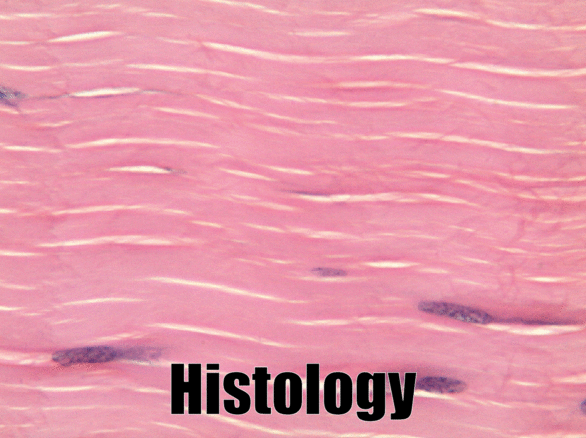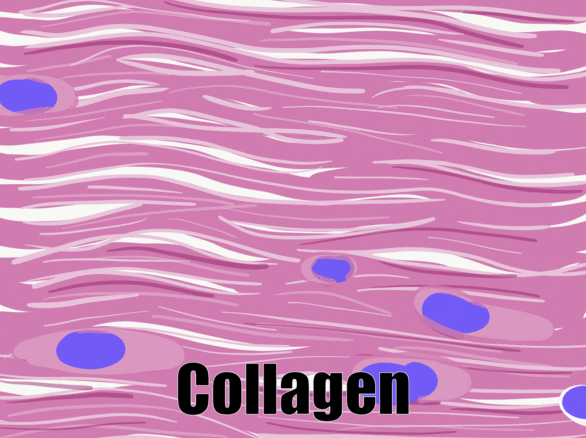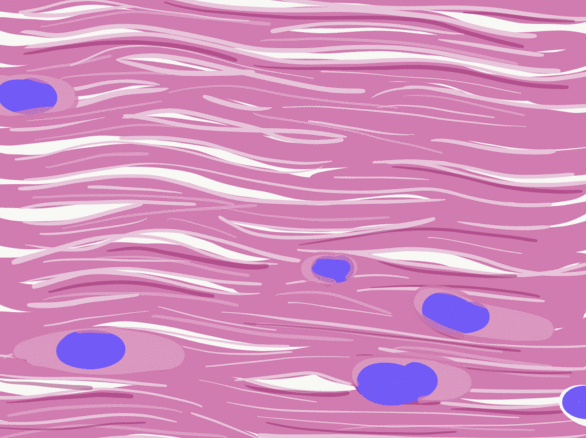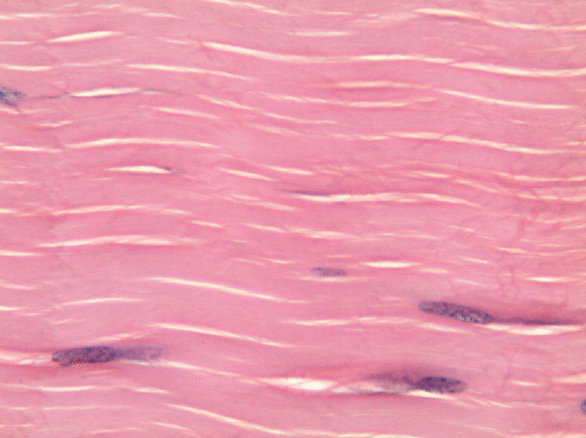
Like dense irregular connective tissue, dense regular connective tissue is mostly collagen← fibers, only the fibers run parallel to one another. That makes this tissue strong in one direction. You mostly find dense regular connective tissue between muscle and bone (tendons), or between bone and bone (ligaments). The place in this book where we find dense regular connective tissue is the PDL, between bone and tooth. Because dense regular connective tissue has very little ground substance, tendons and ligaments undergo very little edema when injured. They do experience pain, however.
You might be thinking the collagen fibers in Fig. 2.18 look wavy, not parallel. When someone sliced this section of a tendon, they sliced through the tissue using a thin blade. As a blade cuts softer tissue, the blade pushes fibers in one direction, then pulls fibers back, then pushes them again. For the best results, an expensive device that freezes or embeds soft tissues in wax can be used, such as a microtome, cryotome, or vibratome. We bring this up because many textbooks suggest histology is a nearly-perfect representation of what is found in the human body. In reality, there are artifacts, or errors, that histologists learn to ignore when we see them. We have chosen to illustrate many of the images in this book to avoid discussion of artifacts where possible, and focus on concepts relevant to dental hygiene.
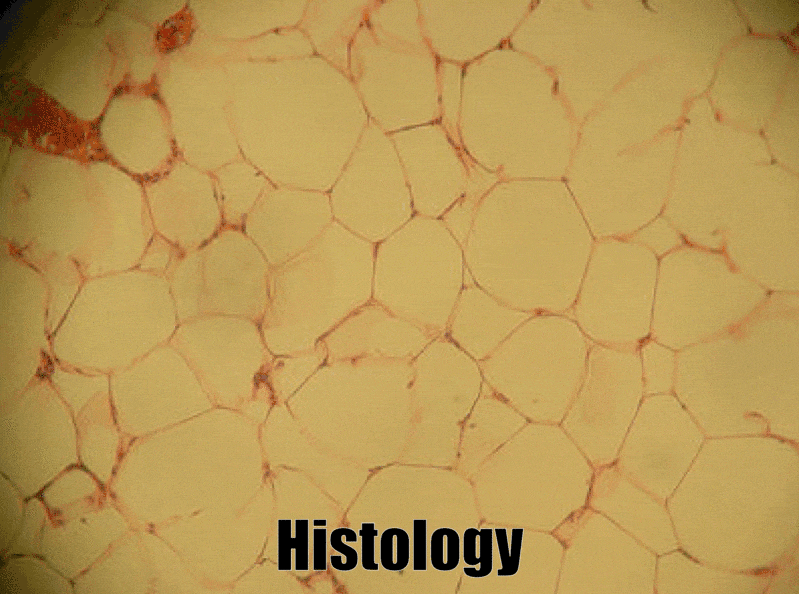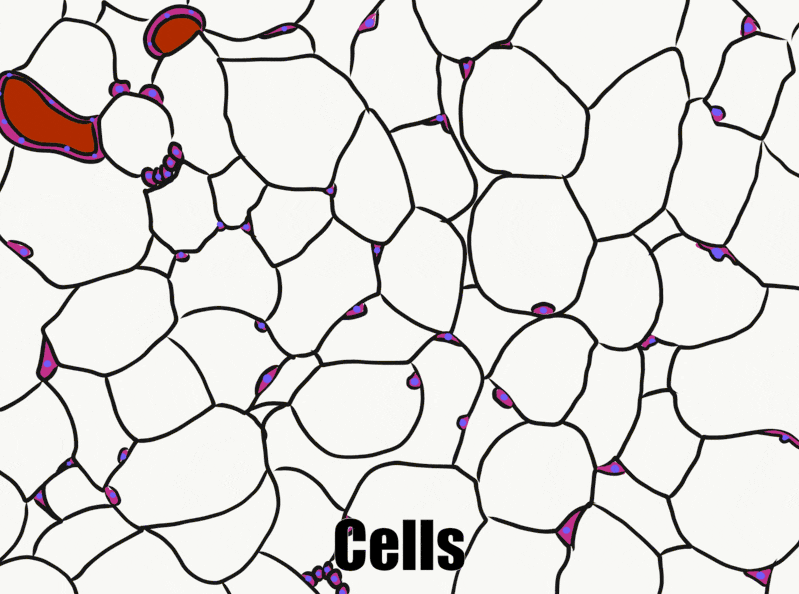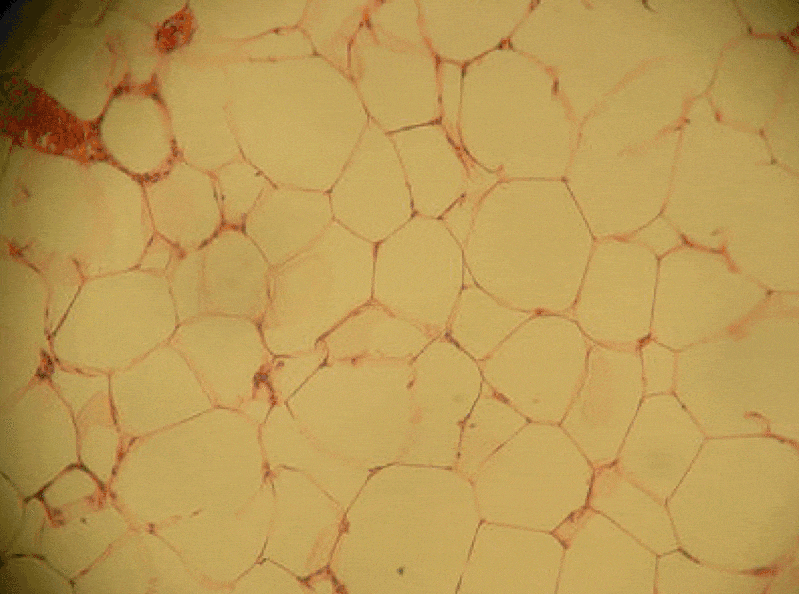
Adipose connective tissue
Adipose tissue is a type of connective tissue. It is special in that is has very little ECM. It contains mostly adipocytes, the mature cells that store triglycerides. It also contains mesenchymal stem cells, so when a person needs more adipose tissue, these cells divide and differentiate← into more adipocytes. Technically, mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into a lipoblast first, but this is only important for the sake of staying consistent with a naming system. Maybe if someone had named the cells adipoblast and adipocyte, we’d use the -blast name more frequently, but someone messed that up. Many textbooks place adipose tissue next to areolar connective tissue and categorize them both “loose”, on account of their low number of visible fibers and high vascularity. That’s fine if you like categories based on adult appearances, but you don’t need to call either of them “loose”. Instead, we need to focus on embryonic lineage.
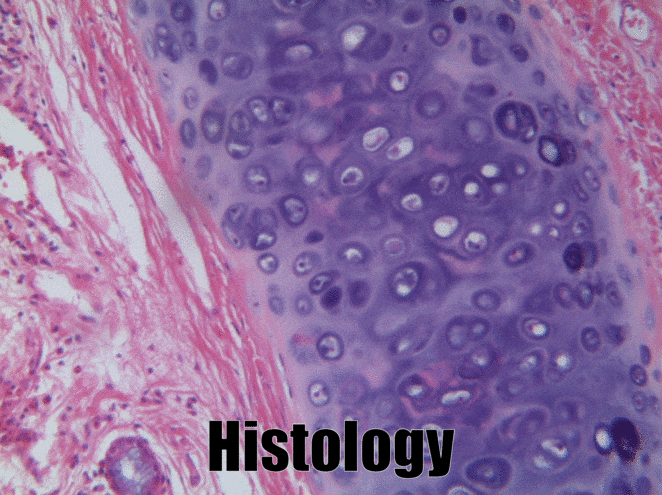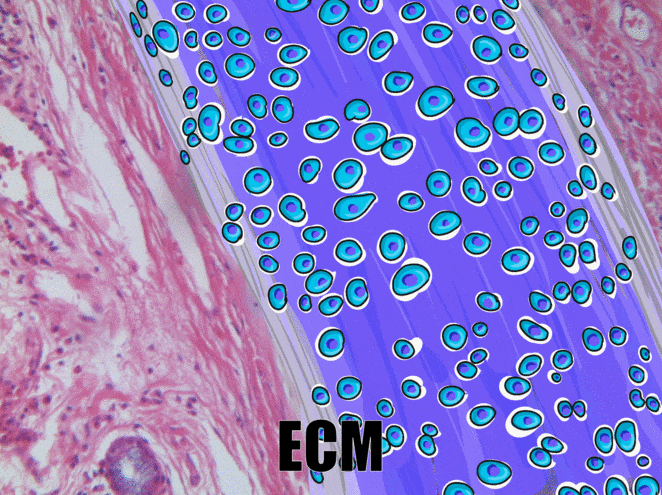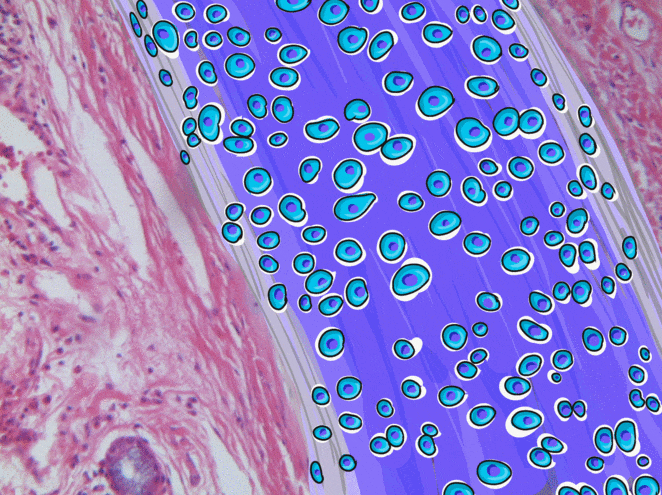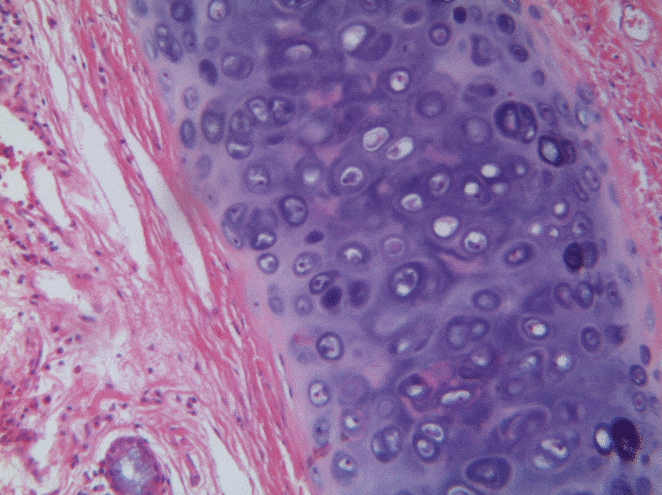
Cartilage tissue
Cartilage, a connective tissue, comes in three basic flavors: hyaline cartilage, fibrocartilage and elastic cartilage. The hallmark feature of cartilage tissue is its large amount of ground substance←. Chondroblasts secrete glycosaminoglycans, glycoproteins, and hyaluronic acid, which attract water, forming a very dense but slippery gel. The ECM of cartilage also contains collagen←. There is more collagen in the fibrocartilage of the temporo-mandibular joint, whereas the elastic cartilage of the epiglottis has more elastic fibers. After secreting ECM, chondroblasts differentiate← into chondrocytes, and reside within the tissue in spaces called lacunae (lakes).
At the outer edge of cartilage is a thin layer of dense collagen fibers known as the perichondrium. If you look at Fig 2.20, the perichondrium appears to be a layer of dense regular connective tissue (it is, perichondrium is its second name). Keep looking, and the edge of the perichondrium blends into dense irregular connective tissue. The reason the cartilage blends into dense regular connective tissue which blends into dense irregular connective tissue is they share the same lineage: chondroblasts and fibroblasts both differentiate from mesenchymal stem cells.
Unlike most connective tissues, cartilage is avascular. As a result, cartilage is mostly unable to undergo tissue repair following injury. Other connective tissues, like bone and the sub-mucosa in the oral cavity, can repair damage much more easily. It also means cartilage undergoes significant less remodeling throughout life.
Bone tissue
Bone tissue (or osseus tissue) has similarity to dentin, cementum and enamel. Therefore, we cover bone tissue in a fair amount of detail. Like any connective tissue, bone tissue starts as mesenchymal stem cells, which differentiate← into an intermediate stem cell← called an osteo-chondro-progenitor cell. This stem cell can in turn decide to adopt an osteoblast or a chondroblast fate. The choice depends on what signals it receives from its environment (nurture). A stem cell that has chosen the osteoblast fate (and denied the chondroblast fate) would be an osteo-progenitor cell. These osteo-progenitor cells are stem cells within the connective tissues surrounding bones, the periosteum (superficial) and endosteum (deep). When stimulated, they undergo mitosis←, one daughter cell reamins an osteo-progenitor cell and the other daughter differentiates into an osteoblast. An osteoblast is the cell that secretes the ECM that makes up the bulk of bone tissue. Osteoblasts secrete collagen← fibers and ground substance←, which later mineralizes, trapping the osteoblasts inside of lacunae. Once trapped, osteoblasts differentiate into osteocytes and maintain the bone tissue. Next, a new set of osteoblasts lay down another layer of bone tissue around the previous one. This creates either the concentric layers of bone tissue found in the osteons of compact bone, or the thinner spiral layers of bone tissue found in the trabeculae of spongy bone.

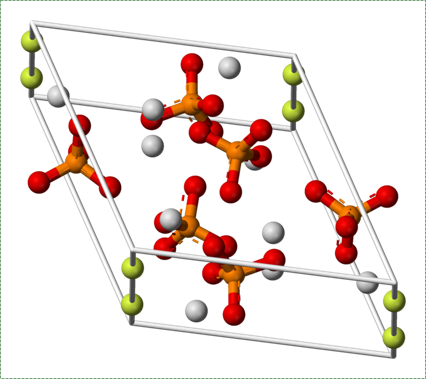
Fluorapatite by Von Benjah-bmm27 in the Public Domain CC0The ECM of bone tissue is roughly 1/3rd collagen← fibers (organic protein) and 2/3rds mineral (inorganic salts). The mineral component is a mixture of positive-charged Ca2+ ions, which react with negative-charged phosphate ions (PO43-) to form crystals. Because most cells are full of phosphate, Ca2+ levels in the cytoplasm must be kept very low. To store Ca2+ for secretion, an osteoblast does so within the sER. After secretion, Ca2+PO43- reacts with water (or more specifically, hydroxide ions OH–) and small amounts of fluoride (F–) to form a harder crystal named calcium hydroxyapatite. Collagen fibers run parallel to each other within one layer of bone tissue, and 90° in the next layer. While the mineral component of bone and tooth tissues provides strength, the collagen provides flexibility, reducing the chances the tissue will shear off under stress. Collagen fibers, therefore, have a function similar to the rebar in reinforced concrete. Dentin, enamel and cementum have ECM very similar to bone tissue, with varying amounts of collagen versus mineral components. The higher percentage of minerals found in enamel makes enamel harder and more resistant to dental caries than dentin or cementum, but susceptible to fracture if enough force is applied.
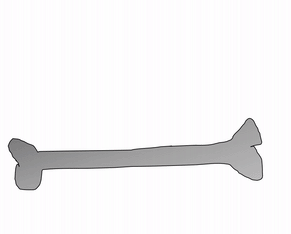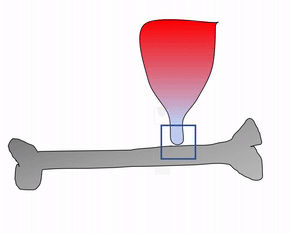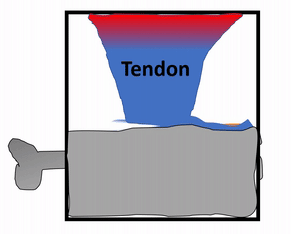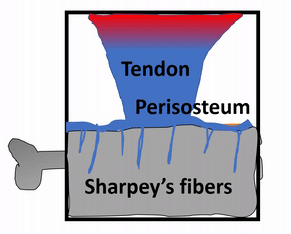
The periosteum is a continuation of (not separate from) the dense regular connective tissue of tendons and ligaments. In addition to collagen fibers and fibroblasts, the periosteum contains osteo-progenitor cells, osteoblasts and osteoclasts (coming up). In anatomy class, you learn about tendons and the periosteum in separate chapters. Sure, the perisoteum has some extra cells. But the options aren’t binary. The perisoteum blends into a tendon. Lets apply that same idea to the other connection the periosteum makes: to bone. Where does the perisoteum end and bone tissue begin? Collagen fiber bundles from the periosteum named Sharpey's fibers penetrate the superficial layers of compact bone. This creates a strong connection between bones and tendons. Can you guess why these three tissues have such a tight connection? We hope you didn’t guess, but answered lineage. But maybe this raises the question: is the connection between muscle tissue and tendons as strong?
Bone remodeling
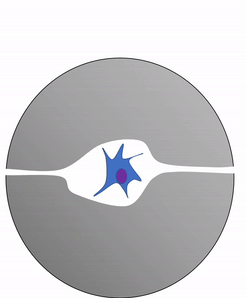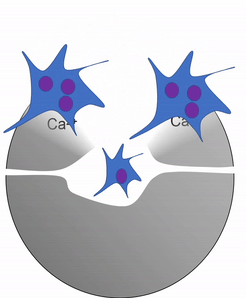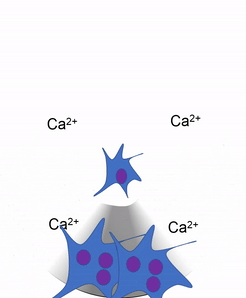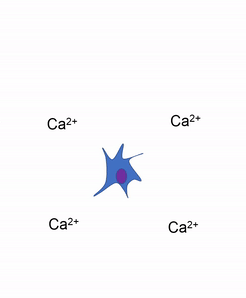
Another important cell found in the periosteum and endosteum is the osteoclast. This cell is not derived from the osteo-progenitor cell that gives rise to osteoblasts and osteocytes. The lineage of an osteoclast traces to the bone marrow, from a stem cell← that also gives rise to red and white blood cells. An osteoclast is a closer relative of a white blood cell called a macrophage, more than it is to bone cells. Osteoclasts demineralize bone tissue, releasing Ca2+ into the bloodstream. This is important because muscle and nervous tissue cannot function without Ca2+, which our diet cannot provide continuously. Hence, bone tissue can be thought of as a calcium storage organ.
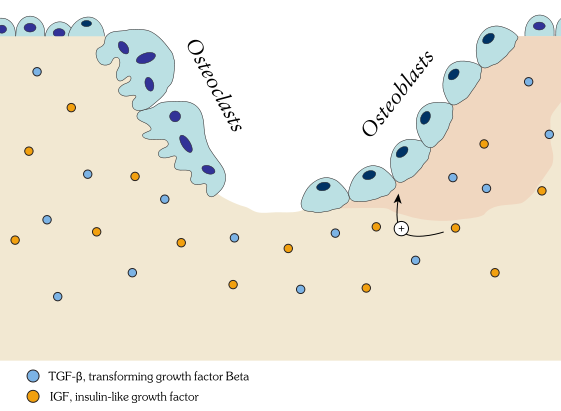
Own work By Shandristhe Azylean is licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0Osteoclast activity is important during tooth eruption← and during the exfoliation of teeth. To help teeth move, bone tissue is removed to loosen the connection between bone and tooth. Osteoclasts activity is also key to the mechanism by which orthodontia works. Lastly, osteoclasts play an important role in maintaining bone health– this may seem counter-intuitive, because osteoclasts destroy bone tissue. But recall how we said programmed cell death (apoptosis) is essential to multicellular life. Bone tissue is constantly being repaired by a group of osteoblasts and osteoclasts working together, known as a remodeling unit. Because compact bone tissue is dense, there is little room for cells to work. Osteocytes can repair small amounts of damage, but larger amounts of damage would build up over time. To prevent this, remodeling units constantly work to remove bone tissue and replace it with fresh bone tissue. The remodeling units cannot find damaged bone tissue, they simply keep removing and replacing bone tissue. In healthy bone tissue, the activity of osteoblasts and osteoclasts is equal. Therefore, healthy bone tissue is in dynamic equilibrium— it is constantly changing and staying the same. Physical tension on bone tissue causes osteoblasts to work harder, which leads to increased bone density. Lack of tension causes osteoblasts to work more slowly than osteoclasts, which lowers bone density and potentially leads to osteoporosis.
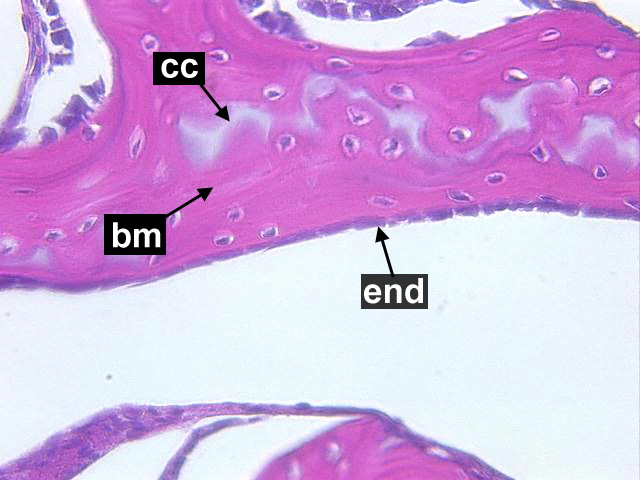
Cancellous Bone, Decalcified preparation, Human.“ by Steven Gallick, Ph.D. is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0Fig. 2.21 shows the histology of compact bone, while Fig. 2.27 shows spongy bone. Because spongy bone has more surface area for remodeling units to work on, it undergoes more remodeling than compact bone. As a result, symptoms of osteoporosis often show up first in bones with high amounts of spongy bone, such as the mandible.

To understand bone tissue well, we must understand its lineage. Bones form either by endochondral ossification, or by intra-membranous ossification. The two processes are similar, the major difference is that endochondral ossification begins with a cartilage scaffold←, whereas intra-membranous ossification begins with a dense connective tissue scaffold. Most of the skull develops by intra-membranous ossification, except the face, which uses both. Because of their similarity, we only cover endochondral ossification. Don’t worry. After learning about endochondral ossification, if you replace the word cartilage with dense connective tissue, you understand intra-membranous ossification pretty well.

"Dissected skull, Maison Tramond model, Paris, nineteenth century" by Centre for Research Collections University of Edinburgh is licensed under CC BY-SA 2.0Do sharks have a skeleton? Most of the human skeleton starts off as cartilage. Cartilage is typically avascular, but when chondrocytes receive the correct signals, they induce blood vessels to grow into their ground substance←. The growth of new blood vessels into a tissue is called angiogenesis. Angiogenesis provides the pathway that mesenchymal stem cells use to migrate into the central area, where they differentiate← into osteoblasts. After that, osteoblasts replace cartilage tissue with woven bone tissue (an immature form of bone tissue where collagen fibers are disorganized). This first site of ossification is named the primary ossification center. In long bones, it is located in the future shaft of the bone. Next, blood vessels grow into the epiphyses and begin the same process at what are named the secondary ossification centers. After producing woven bone, osteoblasts remodel the collagen fibers to produce lamellar bone (either compact bone or spongy bone), and differentiate into osteocytes. Ultimately, most of the cartilage is replaced, except in two important places. First, cartilage remains between the primary and secondary ossification centers, leaving growth plates (such as in bones of the arms and legs). Cartilage also remains at the ends, providing the articular cartilage cushions found in synovial joints. Intra-membranous ossification begins with a dense connective tissue. It leaves fontanels (soft-spots) between bones until ossification is complete, rather than cartilaginous connections.
If you are wondering if we are going to answer the question about whether sharks have a skeleton, try a quick google search. Instead, we ask you a second question: why would we bring up such a distant relative of ours (speaking on an evolutionary scale) when describing the embryological development of bone tissue? It is because our evolutionary lineage helps us understand our developmental lineage. Sorry, but the job of shark dental hygienist has already been filled by the remora.
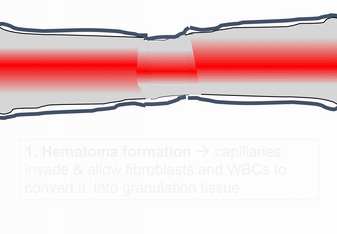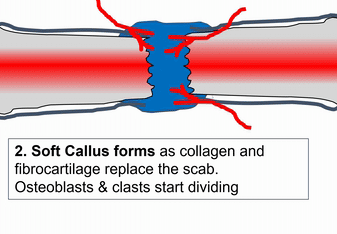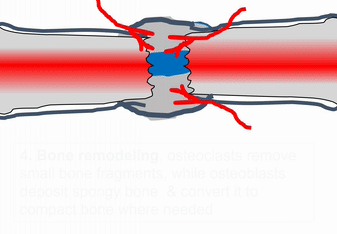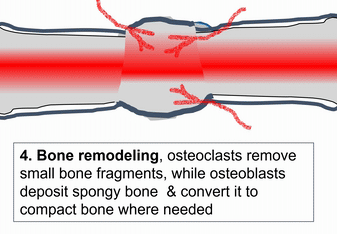
When bone tissue is injured, it goes through a healing process similar to endochondral ossification. Perhaps you remember mention of how wound healing recapitulates development. Here is an example of an adult tissue re-using a mechanism to heal that was used during embryogenesis to grow. Similar to an injury to the skin, bone tissue first goes through an inflammatory process, and damaged blood vessels form clots. An external blood clot is a scab, but inside the body it is named a hematoma. A blood clot contains ECM fibers named fibrin that act as a scaffold←. This scaffold allows blood vessels to grow into the area, by angiogenesis. This in turn allows mesenchymal stem cells to leave the blood and migrate into the injured area along the scaffold, and differentiate← into chondroblasts. The chondroblasts replace the fibrous hematoma with fibrocartilage. This cartilage step is the only step that is does not have a homologous step (a shared step) in wound repair in the skin. Injured skin uses the fibrin scaffold, but bone tissue needs a cartilage scaffold to grow. With a cartilage scaffold, more mesenchymal stem cells migrate and differentiate into osteoblasts, and replace the cartilage with woven bone tissue. Later, woven bone is remodeled so that it roughly matches the original compact and spongy bone layers. One difference can be seen afterwards, the former site of injury is a little bit thicker after it is repaired. This is similar to the way skin tissue is made stronger after an injury (scar tissue).
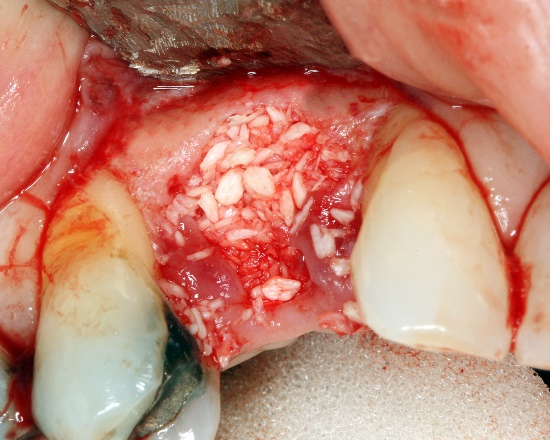
Alloplastic particulate graft by Coronation Dental Specialty Group is licensed CC BY SA 3.0Knowing the steps of endochondral ossification and bone fracture repair are important. Stimulating or mimicking the natural healing process can reduce the need for surgeries and implants. For instance, patients may lose a significant amount of bone tissue with prolonged periodontitis (for example, take a look at this periapical abcess now located at the Royal College of Surgeons of London). If enough bone tissue is lost, a surgeon may use a bone graft to replace it. Bone tissue from a cadaver can be ground up, destroying the cells but leaving the collagen← and minerals. Other sources may include a patient’s own bone tissue (a full set of ribs or fibulas is less important than an intact set of jaw bones and teeth). The harvested ECM is spread into the injured site, where it acts as a scaffold←, not as a replacement. The patient’s mesenchymal stem cells migrate through the scaffold and begin the healing process, which can proceed quickly because plenty of raw materials are close by. Scaffolding does not have to come from actual bone tissue. It can be ground-up dentin, fibrin, or a synthetic polymer printed using a 3-D printer. The scaffolds, synthetic or biological, are ultimately replaced, which is why you may see this referred to as Guided Tissue Regeneration← (further reading here). A scaffold is just one part of the healing process, there are important signals that can be used to guide mesenchymal stem cell migration, mitosis← and differentiation←. These signals are growth factors and morphogens←, which are covered inchapters 6-11. If you wish to learn more, we have a short YouTube video that covers this new technology in more detail, aimed at 200-level Anatomy and Physiology students (the concept is essentail knowledge for your program periodontology course topics).

"The origin of bone" by Darja Obradovic Wagner and Per Aspenberg is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Lastly, it is interesting to consider, from an evolutionary viewpoint (phylogeny), the lineage of the four mineralized tissues (bone, enamel, dentin and cementum) in humans and other vertebrates. Did one evolve first, and the others develop from the original? Thinking about the development of tissues in terms of their evolution (called evo-devo) tells us a lot about their similarities and differences. Fig. 2.32 provides a hint. We consider this question of lineage from a developmental viewpoint (ontogeny) in chapters 6 through 11.
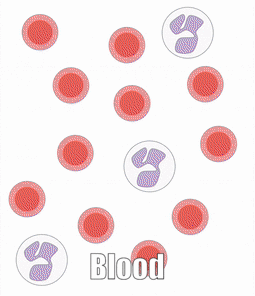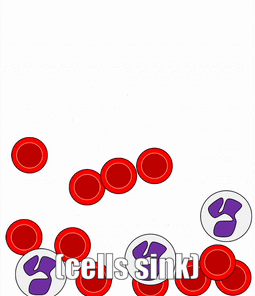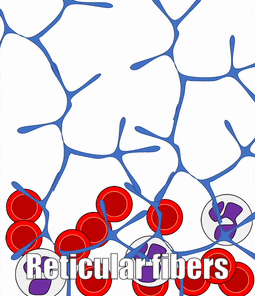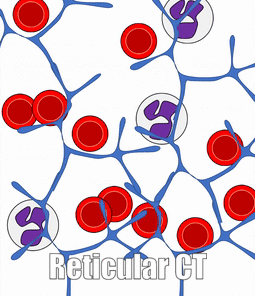
Blood, Reticular, and Lymph Connective Tissue
There are other connective tissues covered in histology classes, here we cover them briefly. Blood is a type of connective tissue, composed of cells (red blood cells, mostly), liquid ground substance (blood plasma) and fibers (fibrin). Lymph is primarily white blood cells, plus liquid ground substance. Reticular connective tissue contains blood cells, liquid ground substance and reticular fibers. It can be found in lymphatic organs where blood cells tend to rest rather than flow, such as lymph nodes.
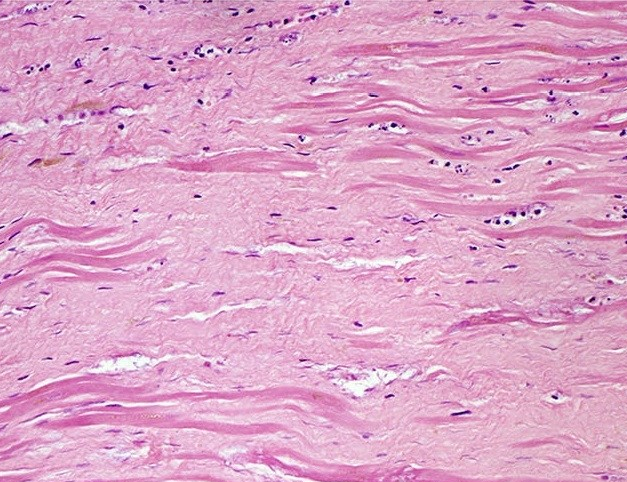
"Histopathology of dense fibrous scar replacing myocyte loss in myocardial infarction" by Katarzyna Michaud et al is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0There are other forms of connective tissue that aren’t typically covered in 200-level histology classes, we cover one: scar tissue (or granulation tissue). Scar tissue is made by fibroblasts following an injury. If an injury occurs that is large enough the tissue cannot be replaced quickly by stem cells←, fibroblasts can fill in the area with collagen←. Scar tissue is very similar to dense regular connective tissue, except the collagen fiber moleculess in scar tissue are extensively cross-linked. This makes scar tissue very strong, but also reduces its mobility and capacity to be remodeled. Because scar tissue is difficult to remodel, it is more-or-less permanent.
After learning about the histology of the oral mucosa in Chapter 3, knowledge of the histology of scar tissue helps explain oberved changes to the gingiva. Repated periodontal infections and subsequent ifnlammation can trigger the production of scar tissue, creating firbotic or scarred gingival tissue. Chronic insults to the gingiva create thick, tough gums which don’t function well to support and cover tooth roots. This can lead to exposed roots, which are not designed to endure continued exposure to the oral cavity environment.
Muscle tissue

General characteristics of muscle tissue
Skeletal muscle tissue, like connective tissues, is derived from mesoderm. Fig. 2.35 shows regions of mesoderm known as somites. The stem cell← that differentiates← into one of the several types of muscle cells is called a myo-satellite cell. These cells resemble a mesenchymal stem cell, which is not unusual given their shared lineage. However, the fate of a myo-satellite cell is different. Given the correct extra-cellular signals, myo-satellite cells differentiate into small myoblasts. Hundreds of myoblasts fuse together and differentiate into skeletal muscle cells. This occurs not only during development, but also late in life. Myo-satellite cell are responsible for the repair and growth of muscle tissue following excercise. Exercise can damage muscle cells and cause them to release inflammatory molecules, which (in part) trigger myosatellite cells to undergo mitosis←, differentiate into myoblasts and trigger tissue repair and growth. We can think of this as an example of how wound healing recapitulates development. Like healthy bone tissue, maintaining healthy muscle tissue requires dynamic equilibrium: ongoing destruction and re-growth of muscle cells.
Unlike fibroblasts, myoblasts create protein fibers that are mostly intra-cellular (such as actin thin filaments and myosin thick filaments). After fusing with other myoblasts, muscle cells are often confusingly referred to as muscle fibers. They are cells, not molecules like the protein and glycoprotein fibers found within ECM. They can also be called muscle cells or myocytes. We see skeletal muscle in the tongue and underneath regions of oral mucosa. We do not cover smooth or cardiac muscle tissue.
Muscle tissue is composed primarily of muscle cells and extra-cellular collagen← fibers. Recall how connective tissue cells move along collagen using integrin← trans-membrane proteins . Muscle cells anchor in place and move the collagen fibers. To do this, muscle cells express different proteins that bind collagen, including the protein dystrophin. For people studying musculo-skeletal diseases like muscular dystrophy, there is interest in creating myoblasts for patients. There are a larger number of mesenchymal stem cells in the bone marrow compared to myo-satellite cells in the muscle of a child or adult. Thanks to how closely related mesenchymal stem cells are to myo-satellite cells, it may be possible to trick mesenchymal stem cells into differentiating into myoblasts instead of fibroblasts. This could, in turn, reduce or reverse muscle tissue loss. If novel treatments result from this research, it could make dental hygiene procedures for patients with muscular dystrophy more effective.
The layers of collagen are thin between muscle cells, and thicker on the outer surface of a muscle. These layers of collagen fibers ultimately become the dense regular connective tissue of a tendon. Under the microscope, it is difficult to determine where muscle tissue ends and dense regular connective tissue begins because of the collagen fibers in both tissues. By extension, it is also difficult to tell where the tendon ends and the periosteum begins. Some histologists draw lines between these tissues, but the junction is better described as a blending. This is because both muscle tissue and connective tissue have the same lineage, from mesenchyme.
Nervous tissue
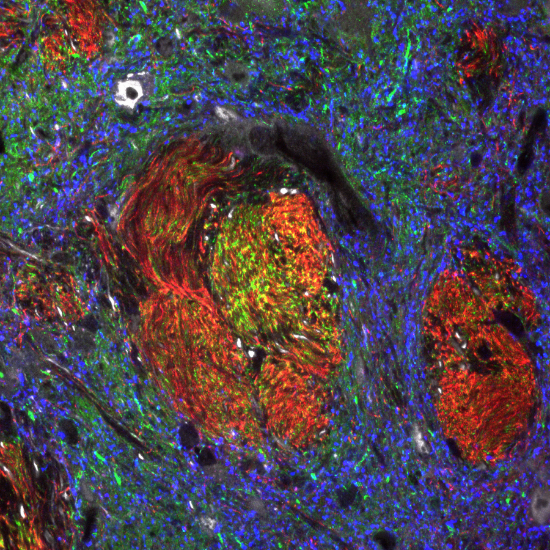
Desert rose by Tarzerind is licensed under CC By SA 4.0General characteristics of neural tissue
Fig. 2.37 is a confocal image of neural tissue. What is particularly nice about this image, and is often absent from images of neural tissue, is that this one shows all of the cells. The typical image of neural tissue uses stains to highlight neurons—the cells specialized at conducting electricity. When only neurons are stained, the glia stay invisible. Glia are majority of cells in the nervous system. While neurons act like electrical wires, glia are responsible for everything else. This includes important tasks like guiding neuronal connections and changing the strength of those connections as we learn. You should see neural tissue is composed of cells, and has very little ECM. While the brain especially has a huge number of blood vessels inside of it, technically they do not run within the neural tissue. Instead, there is a thin blood-brain-barrier separating the brain from the blood vessels. Normally, we wouldn’t call neural tissue avascular, we do so to make a point: neural tissue shares a lot in common with epithelial tissue. By now, we hope you have know why: neural and epithelial tissues share the same lineage.
We dont discuss neural tissue in this book. But we do discuss a number of tissues derived from neural crest cells. These are individual cells that arise during neurulation←, migrate away from other neural tissue, and differentiate into lots of different things. They don’t look like much under the microscope, and their existence is brief. Therefore, they shouldn’t be included in a histology chapter. But you will identify many things they create, including melanocytes, craniofacial bones, the anterior pituitary, taste buds, salivary gland connective tissue, dentin, cementum, pulp, the PDL and alveolar bone. Don’t memorize that whole list, maybe just the tooth and periodontium structures. Then remember that you would be a headless filter-feeder if it weren’t for neural crest cells. In what is called the new head theory, the evolution of neural crest cells gave us vertebrates our paired sensory organs, powerful jaws and the ability to become predators.
3 major embryonic tissues
Gastrulation (a brief introduction)
We are done discussing tissues based on what they look like. Now, lets focus on where they come from. When an embryo implants in the uterus, it is a hollow ball of identical, omnipotent stem cells← that resemble a simple cuboidal epithelium. Soon, some epithelial cells migrate inwards, in an important process called gastrulation←. Now there are two different layers of cells. The layer on the outside becomes the epidermis, oral epithelium and the central nervous system. The layer one on the inside becomes the lining of the gut and other hollow organs. Next, some cells from the outer layer change. They lose contact with neighboring cells, and migrate into the middle. As this happens, they stop looking like epithelial cells and begin to look like mesenchymal stem cells. This produces a third layer of cells in an embryo. These are the three embryonic germ layers are listed below, along with what they are fated to form in the adult:
| 3 embryonic layers | Cell fate |
|---|---|
| Ectoderm | Epithelium of skin and oral mucosa, neural tissue |
| Mesoderm | Connective and muscle tissue |
| Endoderm | Epithelial lining of hollow organs |
We have now sneakily introduced you to two important terms used in embryology. The first is cell lineage, which means where a cell came from (in the past). Now we add cell fate, which means what a cell can become (in the future). Can you think of when we would discuss cell ineage versus when we would discuss cell fate? Here is a hint: timing is everything. If we didn’t think your license exam would include questions on the four major tissue types, we would stick with these three embryonic germ layers. Neural tissue would be a sub-family of ectoderm (you’ll see why later). Epithelia would be divided between ectoderm and endoderm. We’d put connective and muscle tissue together in mesoderm, rather than separate them. We might even add neural crest cells← as a fourth tissue type. But we can see why academia hasn’t changed the way it teaches histology. The confusion that comes with change would not be worth the benefits the average student would gain from grouping cells by lineage rather than appearance. You, however, need to know both the 4 major tissue types and the 3 embryonic germ layers.
< Chapter 1 * navigation * Chapter 3 >
Histology review questions
The study of tissues under a microscope
A group of cells, all the same type, that work together to perform one or more functions.
Hematoxylin and Eosin stain, typically turns proteins pink and DNA purple.
deoxyribonucleic acid is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms.
Ribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid present in all living cells. Its principal role is to act as a messenger carrying instructions from DNA for controlling the synthesis of proteins
Extra-Cellular Matrix: Materials in the body, but outside of cells. A network of macromolecules, such as fibers, enzymes, and glycoproteins, that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells.
The mechanism by which initially equivalent cells in a developing tissue in an embryo assume complex forms and functions.
In the phrase nature vs nurture, nature refers to genetics (heritable traits).
In the phrase nature vs nurture, nurture means environmental factors that occur after fertilization, not DNA inherited from our parents.
The developmental history of a differentiated cell traced back to the embryonic cell from which it arises.
The development of an organism or anatomical or behavioral feature from the earliest stage to maturity.
When one cell begins to look different from another. This process involves limiting cell fate by altering gene transcription to become more specialized.
Undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various cell types, and proliferate to produce more of the same stem cell.
A thin sheet of extracellular matrix between epithelial tissues and the underlying connective tissue of the lamina propria or dermis.
Half of a desmosome, specialized for cell-to-ECM adhesion.
Cell Adhesion Molecules: proteins located on the cell surface involved in binding with other cells or with the extracellular matrix.
Trans-membrane structure specialized for cell-to-cell adhesion.
A type of cell-to-cell contact that prevents diffusion between cells.
Proteins embedded within the plasma membrane, with parts both the inside and outside of the cell.
The top (or apex) side of a cell or tissue, usually facing the lumen.
The side of a cell or tissue oriented away from the lumen or external surface.
The border of every cell, made of a phospholipid bilayer and proteins.
Top-to-bottom polarity, where the apical side of a cell (or tissue) is different from the basolateral side
Hollow center or cavity inside a structure.
The process of cell division, where one cell divides into two identical clones (daughter cells).
DNA molecule packaged into thread-like structures found during mitosis, visible under a light microscope.
Unwound DNA and histone molecules, available for gene transcription.
Without blood vessels
Secreting to a surface of the body, either the outer surface (skin) or inner surface (lumen of a hollow organ).
Secreting to the inside of the body, either blood or ECF.
Without shape
Signaling molecules secreted directly into the blood which travel throughout the body.
An epithelium composed of one layer of flat cells
A single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels, forming the barrier between vessels and tissue and control the flow of substances and fluid into and out of a tissue.
Growth of endothelial cells, creating new blood vessels within a tissue.
A protein that has had sugar residues attached to it in the Golgi apparatus and is often secreted.
An epithelium composed of one layer of square cells
Gel-like substances in the ECM, composed of water held in place by large molecules (proteins, glycoproteins and glycosaminoglycans).
A cyst that forms in the mouth under the tongue.
Epithelia that have one layer of tall cells
Inner Enamel Epithelium: a layer of columnar cells located next to the dental papilla, these pre-ameloblast cells will differentiate into Ameloblasts which are responsible for secretion of enamel during tooth development.
Cells present only during the embryonic period that deposit tooth enamel.
The type or types of cell(s) a stem cell can possibly differentiate into in the future, determined by which genes are methylated and stored around histones, or free to be transcribed.
A two-dimensional sheet that forms a selective barrier.
The mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth. It is a stratified squamous epithelium, named the oral epithelium, and an underlying areolar connective tissue named the lamina propria.
Epithelia that have more than one layer of cells, with the cells at the apical surface having a flat shape.
Having the protein keratin, which lends resistance to abrasion and water loss.
One of a family of tough fibrous structural proteins, the key material making up hair, nails, calluses, and the outer layer of skin.
A terminally differentiated epithelial cell capable of synthesizing large amounts of the protein keratin within its cytoplasm.
The lip, as opposed to adjacent skin or oral mucosa, named for its more reddish appearance than keratinized skin.
A stratified squamous epithelium that does not contain the protein keratin, making it softer and moister than the skin.
An epithelium that has more than one layer of cells, but the layers are not organized into distinct rows.
Unicellular glands, or single epithelial cells, that secrete mucus.
A thin gelatinous secretion composed of primarily of glycoproteins and water.
An adjective used to describe a gelatinous, slimy substance such as loose ground substance or mucus.
rough Endoplasmic Reticulum, an organelle where membrane and secreted proteins are translated by bound ribosomes on the surface of the rER.
Bilateral pairs of blocks of mesoderm that form along the rostral-caudal axis.
A large glycoprotein found in the ECM which binds to integrin proteins on the cell surface, involved in cell adhesion, growth, migration, and differentiation.
A very large glycosaminoglycan distributed widely throughout connective tissue ECM, epithelial, and neural tissues.
The main structural protein in the ECM of connective tissues
A form of collagen, forms a web-like meshwork in ECM.
Thin protein fibers in the ECM, capable of stretching and returning to their original length, made of the protein elastin.
Containing blood vessels
Multipotent cells of a connective tissue that can differentiate into a variety of cell types, including osteoblasts, fibroblasts, chondrocytes, myoblasts, blood cells and adipocytes.
A stem cell found in adult tissues (as opposed to embryonic stem cells found in embryos)
The basic connective tissue cell type capable of secreting ECM components, including fibers and ground substance proteins.
A cell actively producing the components of cartilage extracellular matrix, and may differentiate into a chondrocyte when trapped in the matrix it produced.
A cell of neural crest origin that is part of the outer surface of the dental pulp, and whose biological function is the formation of dentin.
A more differentiated form of a myo-satellite cell that can differentiate into a muscle cell (myofibril)
The cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat.
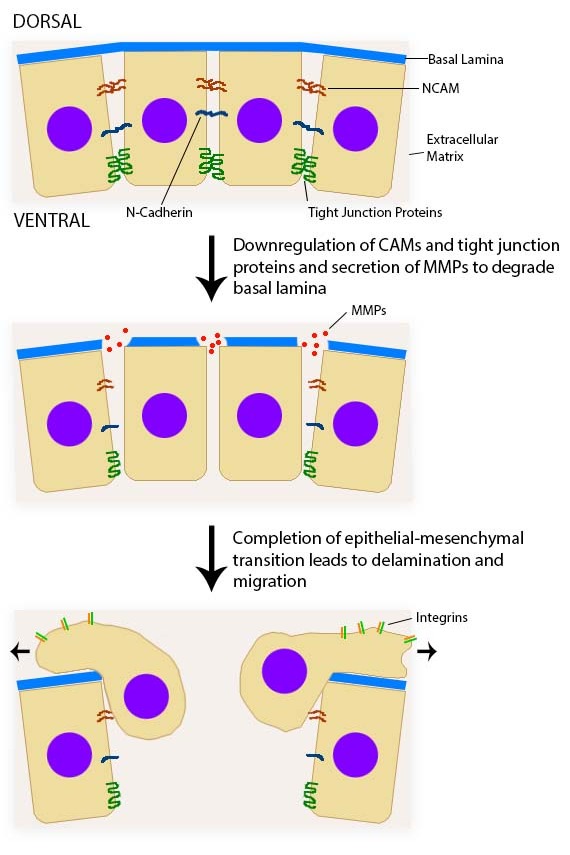
A reversible process that involves the transition from motile mesenchymal cells to planar arrays of polarized epithelial cells.
The ECM proteins elastin and collagen, visible under the light microscope
An embryonic tissue composed of undifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells and mucous ground substance.
Mesenchyme tissue that contains neural crest cell derivatives.
The middle of the three embryonic layers that develop during gastrulaton, mesoderm becomes most of the body's muscle and connective tissues.
A temporary group of cells that arise from the embryonic ectoderm, and in turn give rise to a diverse cell lineage—including melanocytes, cranio-facial cartilage and bone, teeth and periodontal tissue, smooth muscle, peripheral and enteric neurons and glia.
Periodontal Ligament, a group of specialized connective tissue fibers that attach a tooth to alveolar bone.
A loose connective tissue composed of fibroblasts and other cell type, plus ground substance and all three fiber types.
Swelling caused by excess fluid trapped within tissues.
A connective tissue that has fibers that are not arranged in parallel bundles as in dense regular connective tissue. Dense irregular connective tissue consists of mostly collagen fibers. It has less ground substance than loose connective tissue.
The dense irregular connective tissue layer found below the oral mucosa (or mucosa of a hollow organ), homologous to the reticular layer of the dermis.
Th connective tissue layer of the skin, found just deep to the epidermis, composed of areolar CT and dense irregular CT.
A type of connective tissue found in tendons and ligaments that is composed primarily of parallel collagen fibers, secreted by fibroblasts, with very little ground substance.
Artificial patterns or damage to a specimen seen under the microscope caused by the sampling or staining procedure.
A type of connective tissue composed primarily of adipocytes, which store high-energy triglyceride and other lipid molecules.
A firm connective tissue, softer and more flexible than bone composed of chondrocytes and lots of ground substance.
The mature cells found within cartilage tissue.
Lakes, or spaces within cartilage of bone connective tissue where cells reside.
Reorganization or renovation of existing tissues, either physiological or pathological. The process can either change the characteristics of a tissue such as in blood vessel remodeling, or result in the dynamic equilibrium of a tissue such as in bone remodeling.
A hard connective tissue which is mostly ECM, including collagen fibers and a calcium-phosphate crystal.
A differentiated connective tissue cell that secretes bone ECM, including collagen, calcium and phosphate.
A cell that differentiates from a mesenchymal stem cell, and can further differentiate into an osteoblast.
A layer f dense regular connective tissue surrounding bones, also containing osteoblasts, osteo-progenitor cells and some osteoclasts.
A thin membrane covering the inner surface of compact bone and the trabeculae of spongy bone, containing osteoblasts, osteoclasts and osteo-progenitor cells
The terminally differentiated cell type found in mature bone tissue (both compact and spongy), capable of repairing small amounts of damage.
Dense bone tissue composed of osteons, found on the outer edges of bones.
Rod-like mineralized connective tissue structures found in spongy-bone.
Softer bone material composed of thin trabeculae, found deep to compact bone.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum, an organelle where calcium and lipids are stored.
Ca5(PO4)3(OH), the inorganic ECM material composed of calcium, phosphate and hydroxide ions that makes up the bulk of bone tissue.
Damage to a tooth that can happen when decay-causing bacteria make acids that de-mineralize tooth tissues.
A cell derived from bone marrow stem cells capable of demineralizing bone tissue by the secretion of acids and enzymes, releasing calcium into the blood.
Bundles of strong type I collagen that anchor the periosteum to bones by penetrating the outer layers of compact bone tissue
A process in tooth development in which the teeth enter the mouth and become visible.
A general term for peeling or shedding, in humans it refers to the loss of dead epithelial cells or structures (hair, teeth).
Programmed cell death
Osteoblasts and osteoclasts working together to remove old bone tissue and replace it with new bone tissue, necessary for the maintenance of healthy bones.
Formation of bone tissue from a dense connective tissue model
Extracellular matrix material involved in the repair of injured and missing tissues, allows stem cells to migrate into the injured area. It is usually replaced during regeneration.
The embryonic process in which one group of cells directs the development of another group of cells.
The process by which animals and plants grow and change.
The formation of bone tissue from a cartilage model
To state again, or to repeat.
The insoluble (solid) form of a fibrous protein found in blood plasma that contributes to the formation of a blood clot.
A similarity due to shared lineage between a pair of structures or genes in different taxa.
A strong but immovable connective tissue quickly made by fibroblasts, consisting primarily of highly cross-linked collagen fibers.
Inflammation that damages soft tissue and bone that anchors the teeh, including the gingiva plus PDL, cementum or alveolar bone tissue.
A medical procedure in which ground up bone tissue or synthetic bone tissue is placed in an injured site to act as a scaffold, promoting the formation of new bone tissue by the patient's own cells.
Procedures attempting to regenerate (as opposed to replace) lost periodontal structures.
A signaling molecule capable of stimulating cell proliferation, wound healing, and cellular differentiation.
A substance whose non-uniform distribution governs the pattern of tissue development and pattern formation.
The history of the evolution of a species or group, especially in reference to lines of descent and relationships among broad groups of organisms.
A type of connective tissue composed of cells (red and white blood cells) and ECM (plasma)
A type of connective tissue composed of cells (white blood cells) and ECM (lymph).
A soft connective tissue composed of reticular fibers, ground substance, plus fibroblasts and blood cells.
A soft tissue whose cells contains a large amount of actin and myosin proteins, allowing it to change in size (contraction and elongation).
A multi-potent stem cell that can generate more muscle tissue.
When two or more cells, tissues or organs join to become one.
A trans-membrane protein which allows cells to bind to the ECM protein fibronectin, it is involved in cell adhesion, growth, migration, and differentiation.
The main component of the nervous system – both central and peripheral, composed of two types of cells: neurons and glia.
Terminally differentiated and highly specialized cells of neural tissue, capable of firing electrical signals over long distances and releasing chemical signals across discrete locations called synapses.
The numerous and diverse group of cells in neural tissue that provide support for, guide the activity of, and organize the connections between neurons.
The folding process in vertebrate embryos, which includes the transformation of ectoderm into the neural tube.
Terminally differentiated cells derived from neural crest cells that produce one of the three forms of melanin.
A phase early in the embryonic development during which the single-layered blastula is reorganized into a multilayered structure known as the gastrula.
The stratified squamous epithelium of the oral mucosa.
The three layers of cells that arise from gastrulation: endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm.
The branch of biology and medicine concerned with the study of embryos and their development.
he most exterior of the three primary germ layers formed in the gastrula, it gives rise to the epithelial tissue covering the body and the CNS.
The innermost of the body's 3 embryonic tissues that form during gastrulation, it becomes the inner lining of hollow organs.

