Chapter 12 – Healthcare
Learning Outcomes
When you have completed this chapter you should be able to do the following:
- Understand the diverse issues of healthcare practices.
- Explain some of the cultural issues within effective healthcare.
- Explore the variety of healthcare options.
- Discuss how religion, power, ethics, and identity impact healthcare.
- Discuss how culture impacts the ethical implications of healthcare.
The Human Genome Project (1990-2003) identified 20,000-25,000 genes in human DNA making it possible to efficiently tackle more health-related problems than ever before. What the Human Genome Project couldn’t study though was the effect of culture on healthcare. We have learned that effective intercultural communication can mean increased profits or opportunities in many contexts, but in the healthcare setting, effective intercultural communication can impact a patients’ physical or mental well-being (Voelker, 1995), as well as their quality of life. This chapter is designed to introduce the complex issues that culture has on both the providers and receivers of healthcare around the world.
12.1 – Patient and Diversity Issues
The US has one of the most diverse societies in the entire world. There are residents and visitors from almost every place on the planet therefore US healthcare must be approached from a multi-cultural perspective. Doctors face effective communication issues, trying to understand the various cultural and co-cultural issues, and the reality that accessible care might not be available to all patients. Patients face language issues, lack of knowledge of healthcare and treatment options, and historical treatment within healthcare systems.
Language Issues
Healthcare professionals often use medical terminology or jargon. Medical terminology is the scientific language used by doctors to describe specific medical conditions. Examples of medical terminology could be thrombosis for a blood clot and hypertension for high blood pressure. Jargon is often the shorthand used between people practicing the same profession and it might have no meaning outside the profession. Examples of jargon in the healthcare world would be BP for blood pressure, NPO (nil pers os) or nothing by mouth, and c-section for birth by caesarian section.
Another issue is that healthcare providers and patients may both operate out of an ethnocentric framework without realizing it. Cultural beliefs and the ensuing approaches to healthcare are so fundamental to a human being that they are not often overtly communicated, but rather just assumed. For instance, people from different cultures do not always report pain in the same ways, which easily leads to miscommunication in cross-cultural encounters (Lee et al., 1992) and the assumption that some cultures do not feel pain. In working with patients from other cultures, healthcare providers can learn as they go, but this has the potential to be dangerous when dealing with diagnosis and treatment of issues.

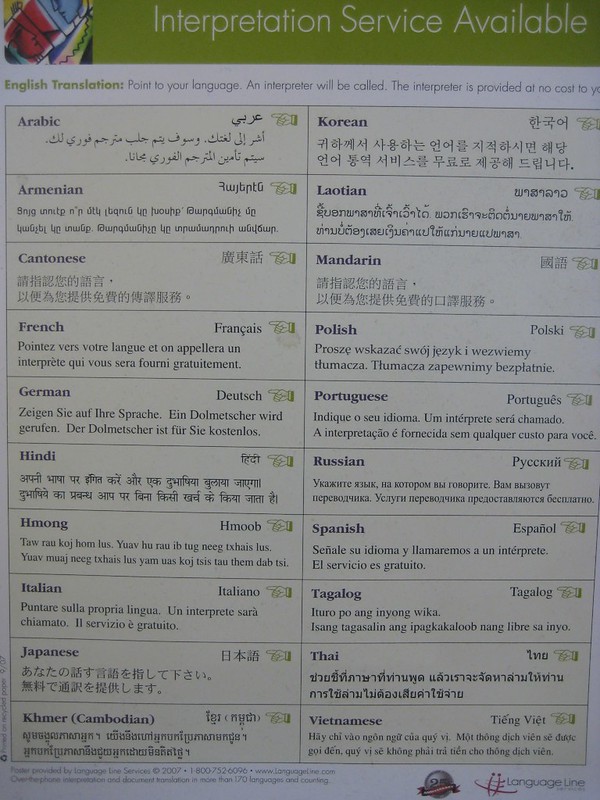
Today 60 million US Americans (nearly 1 in 5) speak a language other than English at home and of that 60 million, 25 million self-identify as not speaking well (CM Elearning, 2022). Finding adequate translators and interpreters who are familiar with medical terminology is difficult. There is plenty of evidence that gaps in translation can lead to adverse outcomes, but one thing is even more clear, patients can’t make decisions about treatment without a competent medical translator. As more of the patient’s family and friends’ attempt to translate, there is more potential for harm than good.
And lastly, treating patients is not always a matter of communication just between doctors and patients. Most cultures have laws regarding healthcare issues and practices. In the United States the judicial issue of informed consent requires that all patients receive full information enabling them to freely make decision about their own health care (Gostin, 1995). This might make sense to you, but in some family-centered cultures, this might be a problem. In this case, families and extended families may expect to be actively involved by providing input and support on treatment decisions.
Historical Treatment of Cultural Groups
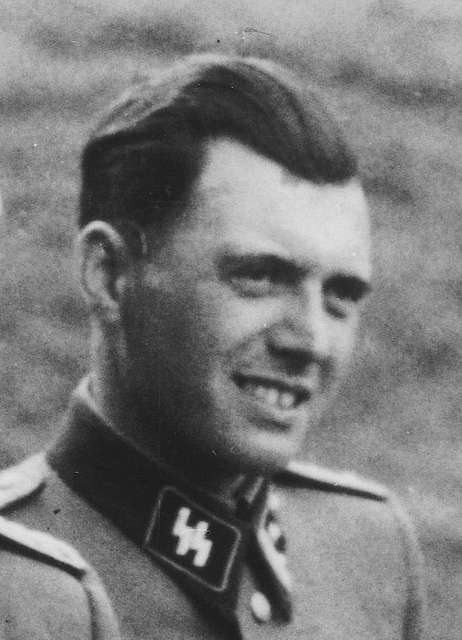
Widespread stereotypes and prejudice directed toward different cultural groups have fostered differential treatment for some groups—especially racial and ethnic minorities. Some historical examples that you might be familiar with are Josef Mengele, the SS physician at Auschwitz, Germany who conducted experiments on Holocaust prisoners that included giving prisoners infections to watch the progression of the disease and spraying them with chemicals to test possible chemical warfare solutions.

In the 1930s and 1940s, Japan’s Imperial Army Unit 731 conducted biological warfare and medical testing on Chinese civilians. As many as 200,000 people were impacted. There were also the Asian “comfort women” of World War II. The term comfort woman is a euphemism for women that were captured and forced to work in brothels. Many experienced great cruelties without access to medical care.

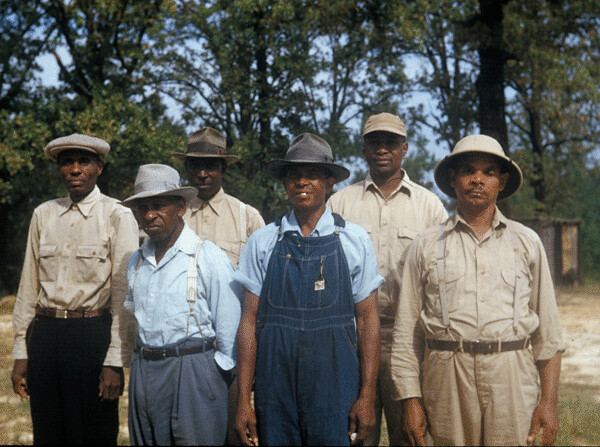
Of course, in the United States, there was the Tuskegee Syphilis Project that lasted for 40 years (1932-1972) in which researchers conducted a study on the health effects of untreated syphilis. African American men who enrolled in the “project” were told that they were being treated for “bad blood.” During the same time, the US was also doing experiments with syphilis in Guatemala on prisoners and individuals with mental illness. Based on both recent and historical atrocities, it is not surprising that some cultural groups are suspicious of healthcare.

Prejudicial ideologies or sets of ideas based on stereotypes, can cause significant barriers to intercultural communication, and may influence the quality of care that patients receive. Patients may enter the healthcare system with their own prejudices based on historical events, distrust of doctors, distrust of certain treatments, and more. Professional healthcare workers may lack an understanding of healthcare provided outside of the traditional western system and that are a part of cultural traditions other than their own.
12.2 – Cultural Differences in Healthcare Concepts
Health is a cultural concept. Culture frames and shapes how we perceive the world, and our experiences, hence different cultures bring different perspectives on health. Most cultures fall somewhere within the individualism and collectivism continuum. Verbal communication styles that directly affect health care are traits like direct/indirect communication, high/low context, and honesty versus harmony. Nonverbal communication styles would include high and low contact. Healthcare is also heavily impacted by the cultural view of power relationships.

Culture helps to define what patients and healthcare providers believe about the causes of illness, which diseases are stigmatized and why, how illness and pain are experienced and expressed, where patients seek help and ask for help, and the acceptance of a diagnosis (Mayhew, 2018). Please remember that as significant as culture can be, within any given culture, there will be variations among individual members.
Belief Systems
The healthcare process is often represented through different worldviews that we commonly call Eastern and Western medicine. Eastern medicine describes a disease as a signal that the body is out of balance. Instead of viewing illness as something to cure, Eastern medicine uses natural plants to work with the natural process of the body. Western medicine relies on the scientific method to understand what causes illness. For many, human beings are just like “machines” that need fixing or tuning to “eradicate the enemy” (Todd, 1999).
In the US, and other nations that practice Western medicine, the dominant healthcare model is based on biomedical science. According to the biomedical model, doctors look for physical signs of what is wrong. Once the symptom is identified, things like drugs and procedures are used to get rid of the problem. Providers who operate from a biomedical model, might communicate in ways that are efficient and logical. This approach uses relatively little time, and providers might see many patients in a day.
In nations that practice Eastern medicine, the dominant healthcare model is biopsychosocial. The biopsychosocial model acknowledges that illness is not always just a physical thing. Disease and illness are often influenced by environment and social factors as well as emotions, stress, and lived experiences. Patients and providers may care deeply about communication and the “bigger picture” which often means spending significant amounts of time working through the illness together.

Alternative Medicine
Healthcare provided outside the traditional Western medical system to Westerners is often referred to as “alternative medicine” whether they fall within the Eastern medical system or not. Alternative medicine can mean returning to traditional cultural medicinal practices such as herbal remedies and sweat lodges, or it can also mean seeking out medical practices that are part of other cultural traditions rather than your own such as acupuncture and cupping.
Alternative medicine generally falls into four broad categories:
- The first is referred to as mind-body medicine which focuses on using the mind to influence the body. These types of approaches might include patient support-group therapy, meditation, and prayer.

- The second is biologically based practices which refers to the use of products found in nature. These types of approaches include the use of herbal therapies, dietary supplements, and other natural products.

- The third category would be manipulative and body-based practices. This approach refers to the use of massage or chiropractic manipulation to promote health.
- And the last type is referred to as energy medicine which could include acupuncture, Reiki, and certain types of massage.

Social Implications of Illness
The ways that a culture perceives health is influenced by different things within a culture. Social implications can be defined broadly such as climate and environmental factors, but there can also be more specific factors such as emotional, economic, family, and community factors that impact patients.
Diseases often carry their own emotional stigma within a culture. HIV, cancer, alcoholism, drug addiction, and mental illness can cause both patients and family members to feel shameful and withdraw from treatment and cultural interaction.
In countries without universal or nationalized healthcare systems, health costs can economically devastate families, cause family members with employer provided insurance to be underemployed to avoid losing insurance, or impact credit ratings and job opportunities. Poor people can feel that they have no control over health problems and fatalistically make bad choices.
The impact of disease on the families of patients is often unrecognized and underestimated. Family members are often care givers as well as economic providers. Much has been studied about quality of life issues for family members and chronic illnesses cross cultural boundaries although in some families’ relationships can grow stronger as members work together.
Much has also been studied about community interaction as well. Community interaction can range from “drifting away” to ostracism and fear of stranger’s reactions to community organization of support.
12.3 – Religion and Healthcare
When people become ill, and the treatment isn’t effective, some people are driven to seek answers to questions from sources outside of the science-based medicine process. The role of religion and spirituality in healthcare raises several issues about ethical ways to incorporate healthcare practices into existing beliefs. Some providers worry about religious freedom issues, while others may not be aware of the diversity of religious beliefs surrounding health care.

Religious beliefs can impact concerns about modesty and being treated by someone of the opposite sex. Some patients will refuse to consume certain foods or eat at certain times or even take medications that are produced using problematic processes. Pain medications may be welcomed or shunned because of beliefs. Healthcare providers may also be asked to minimize actions that might disturb the sick person. Washing, fasting, jewelry might have to be negotiated with providers. Other points of negotiation might be blood and organ donations, transplants, withholding or providing life-sustaining therapy, and the burial of amputated limbs. Family and faith community members might expect to keep company with a dying patient, and for some the bodies of the dead may have to be buried or cremated as soon as possible. And it cannot be stressed enough that rituals and prayers occur in a variety of different ways, but they are all viewed as a necessary part of the healthcare process.
Learn a bit more!
While religious and spiritual beliefs may vary, there are strategies for helping healthcare professionals serve religious patients. The following is a compilation put together from lists provided by the Agency for Healthcare Research (2015), the US Health Resources & Services Administration (ret. 8/10/19), the University of Pennsylvania Medical System (2008), the University of Washington Medical Center (1997), and the Canadian Paediatric Society (2019).
- Help patients feel comfortable at the facility.
- Establish a relationship with patients by supporting or encouraging religious beliefs.
- Provide health information in ways the patient accepts.
- Maintain good communication with patients
- What do you call your illness and what do you think caused it?
- Is there anything I should know about your culture, beliefs, or religious practices that would help me take better care of you?
- Do any traditional healers advise you about your health?
- Do you have any dietary restrictions that we should consider as we develop a food plan?
- Your condition is very serious. Some people like to know everything that is going on with their illness, whereas others may want to know what is most important but not necessarily all the details. How much do you want to know? Is there anyone else you would like me to talk to about your condition?
- Show patients respect by viewing religious and spiritual support as part of the healthcare plan.
- Be ready for when religious and spiritual support are not available.
12.4 – Power and Ethics in Healthcare
Healthcare is ripe with imbalances in power. Providers and patients are not equal in medical knowledge, nor can patients access treatment procedures without referral from a provider. Patients may encounter many healthcare workers within a short amount of time without knowing why or how they are related to treatment. Questions may be seen as a challenge to authority.
In the United States, healthcare is a business. It’s a HUGE business. Deloitt.com (ret. 8/11/19) estimates an annual growth rate of 5.4% between 2017 and 2022. In dollars this is 7.077 trillion in 2015 to 8.734 trillion in 2022. The insurance industry drives MOST healthcare decisions in the US. Costs impact how the US thinks about medical resources and their distribution. For people who come from other healthcare systems, the private healthcare system as practiced in the United States can be confusing or downright inaccessible.
Ethics
The insurance industry and the fear of malpractice suits guides many decisions regarding medical ethics in the United States. Some healthcare organizations use ethics committees staffed by healthcare professionals, religious leaders, social workers, and governmental agencies to help make decisions about medical ethics. Such committees could debate about providing or discontinuing care for terminally ill patients and the possible funding of drug rehabilitation programs for a long-term drug addict. If there are value-laden or value-dependent questions that go beyond what medical science can address, but there is a need for a decision to be made, the issue is most often referred to an ethics committee (Aulisio, 2016).

In the US, the ethics committee rose into prominence during the 1962 through 1990 time period (Aulisio, 2016). In Eastern and Central Europe, ethics committees were the result of fundamental political and societal change during 1989-1990. Whereas in Western Europe, ethics committees were common at the local level, but didn’t become nationalized until the early 2000s (Steinkamp et. al, 2007).
Some medical procedures are very controversial, even among members of the same culture. In the United States, abortion, and euthanasia, or assisting terminally ill people in committing suicide, are two prime examples. As a state, Oregon is often required to defend its ‘Death with Dignity Law’ from interest group lawsuits.
12.5 – Information-Sharing, and Identity
Knowing the appropriate way to communicate with families and patients in an intercultural context can be incredibly complex. In some cultures, the family is involved in the healthcare and medical treatment of its members. In other cultures, medical information is confidential and only given to the patient. Some patients may not want their families involved in their care if they have had a miscarriage, are suffering from certain types of cancer, or are depressed. All patients will act within a framework of cultural values.
Information Sharing
In general, healthcare providers will give information regarding patient health in four general frameworks.
- Strict Paternalism – reflects a physician’s decision to provide misinformation to the patient when he or she believes it is in the best interests of the patient.
- Benevolent Deception – occurs when the physician chooses to communicate only part of a patient’s diagnosis.
- Contractual Honesty – refers to the practice of telling the patient only what he or she wants to hear or to know.
- Unmitigated Honesty – refers to when a physician chooses to communicate the entire diagnosis to a patient. (Martin & Nakayama, 2007)
In the United States, unmitigated honesty is the only one of these options that is legal for adults. When seen as too difficult or frustrating, cultural, and legal differences between provider and patient can contribute to a patient’s inability to understand the provider’s directions. Communication problems resulting from conflicting identities and perceptions can be overcome with sensitivity and adaptation (Brown & School, 2006).

Identity
Both patients and providers are concerned about their cultural identities. Communication Theory of Identity (Hecht, 2009) explains that people make assumptions about each other based on their backgrounds. The premise behind this theory can help to explain how misunderstandings occur in the intercultural healthcare setting (School, Wilson, & Hughes, 2011). Individuals use their identities to affiliate themselves with groups and cultures. The extent to which people identify with specific groups and cultures varies based on the dimensions of salience and intensity (Hecht et al., 1993).
Identity salience refers to the fact that people view their cultural identity as an important part of who they are, while identity intensity refers to the level of importance that people place on their cultural identity (Brown, 2006). When people from different cultures interact, they communicate according to the ways that people from their culture communicate, and by doing so, enact their identity with particular groups.

Hecht (1993) asserted that there are four frames that may overlap and occur in the same communicative interaction: personal, enactment, relational, and communal. Each identity frame has its own set of assumptions concerning how the intercultural provider-patient interaction negotiates identity (Brown, 2006). In a 2017 study on intercultural healthcare communication through the eyes of patients in the Netherlands, Patternotte et. al, found that a doctor’s cultural background was not important if the doctor was a professional, but noted that all of the patients had already lived in the Netherlands for a significant amount of time. Some patients did have a clear preference for a doctor of a particular gender. Many patients felt that a competent doctor needed to be accessible, have enough time, treat them as unique people, and ask about cultural habits. Respect for cultural identity was an integral part of communication skills in a healthcare setting.

12.6 – Conclusion
Communication is vitally important to the competent functioning of healthcare services. Patients and providers may not be satisfied with their healthcare interactions when they do not communicate effectively with one another. Although this chapter has just skimmed the surface of a vast and complicated topic, a knowledge of intercultural communication theories and skills can be the beginning of competence and success in the healthcare arena.
Key Terms
- Medical Terminology
- Eastern Medicine
- Biopsychosocial Model
- Biologically Based Practices
- Strict Paternalism
- Unmitigated Honesty
- Communication Theory of Identity
- Jargon
- Western medicine
- Alternative medicine
- Body-Based Practices
- Benevolent Perception
- Euthanasia
- Identity intensity
- Prejudicial ideology
- Biomedical Model
- Mind-body Medicine
- Energy Medicine
- Contractual Honesty
- Identity Salience
Reflection Questions
- Why might people in the United States seek out alternative forms of health care such as acupuncture?
- How might intercultural communication misunderstandings arise between patients, their families, and health care professionals? Provide an example.
- What medical jargon have you encountered in your interactions with health care professionals? Did it effect your communication? If so, how?
- What are some examples of power imbalances in the health care interaction?
- If you were suffering from a disease, which ethical framework (strict paternalism, benevolent deception, contractual honesty, or unmitigated honesty) would you want your health care professional to use when communicating with you and your family? Why?
The scientific language used by doctors to describe specific medical conditions.
An occupation-specific language used by people in a particular profession.
Sets of ideas or values based on stereotypes.
Uses natural plants to work with the natural process of the body.
Relies on the scientific method to understand what causes illness.
Doctors look for physical signs of what is wrong using scientific methods.
Acknowledges that illness is not always just a physical thing.
Can mean returning to traditional cultural medicinal practices such as herbal remedies and sweat lodges, or it can also mean seeking out medical practices that are part of other cultural traditions rather than your own such as acupuncture and cupping.
Focuses on using the mind to influence the body.
Refers to the use of products and practices found in nature.
Refers to the use of massage or chiropractic manipulation to promote health.
Could include acupuncture, Reiki, and certain types of massage.
Assisting terminally ill people in committing suicide.
Reflects a physician’s decision to provide misinformation to the patient when he or she believes it is in the best interests of the patient.
Occurs when the physician chooses to communicate only part of a patient’s diagnosis.
Refers to the practice of telling the patient only what he or she wants to hear or to know.
Refers to when a physician chooses to communicate the entire diagnosis to a patient.
People make assumptions about each other based on their backgrounds.
The fact that people view their cultural identity as an important part of who they are.
The level of importance that people place on their cultural identity.

