9.2 Conflict Management Strategies
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Compare and contrast the five styles of conflict management.
- Describe the four steps in the STLC conflict model.
Would you describe yourself as someone who prefers to avoid conflict? Do you like to get your way? Are you good at working with someone to reach a solution that is mutually beneficial? Odds are that you have been in situations where you could answer yes to each of these questions, which underscores the important role context plays in conflict and conflict management styles in particular. The way we view and deal with conflict is learned and contextual. Research does show that there is intergenerational transmission of traits related to conflict management. As children, we test out different conflict resolution styles we observe in our families with our parents and siblings. Later, as we enter adolescence and begin developing platonic and romantic relationships outside the family, we begin testing what we’ve learned from our parents in other settings. If a child has observed and used negative conflict management styles with siblings or parents, he or she is likely to exhibit those behaviors with non–family members (Reese-Weber & Bartle-Haring, 1998).
There has been much research done on different types of conflict management styles, which are communication strategies that attempt to avoid, address, or resolve a conflict. Keep in mind that we don’t always consciously choose a style. We may instead be caught up in emotion and become reactionary. The strategies for more effectively managing conflict that will be discussed later may allow you to slow down the reaction process, become more aware of it, and intervene in the process to improve your communication. A powerful tool to mitigate conflict is information exchange. Asking for more information before you react to a conflict-triggering event is a good way to add a buffer between the trigger and your reaction. This can be accomplished through the practice of perception checking that you learned about in chapter 6 on perception. Another key element is whether or not a communicator is oriented toward self-centered or other-centered goals. For example, if your goal is to “win” or make the other person “lose,” you show a high concern for self and a low concern for other. If your goal is to facilitate a “win/win” resolution or outcome, you show a high concern for self and other. In general, strategies that facilitate information exchange and include concern for mutual goals will be more successful at managing conflict (Sillars, 1980).
Five Styles of Conflict Management
The five strategies for managing conflict we will discuss are competing, avoiding, accommodating, compromising, and collaborating. Each of these conflict styles accounts for the concern we place on self versus other (Figure 9.4).
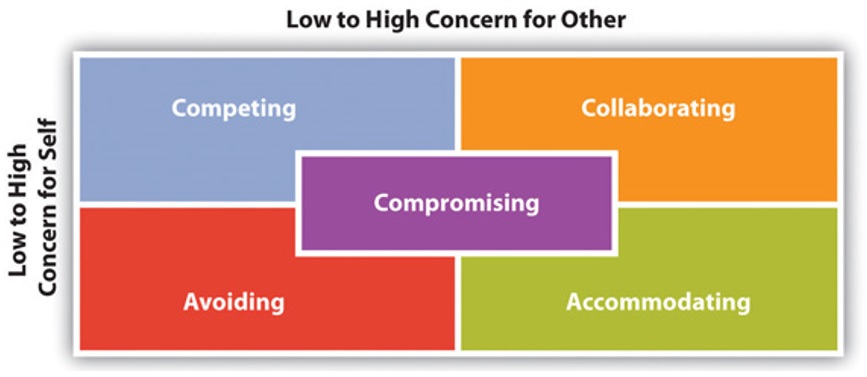
In order to better understand the elements of the five styles of conflict management, we will apply each to the follow scenario:
Rosa and D’Shaun have been partners for seventeen years. Rosa is growing frustrated because D’Shaun continues to give money to their teenage daughter, Casey, even though they decided to keep the teen on a fixed allowance to try to teach her more responsibility. While conflicts regarding money and child rearing are very common, we will see the numerous ways that Rosa and D’Shaun could address this problem.
Competing
The competing style indicates a high concern for self and a low concern for other. When we compete, we are striving to “win” the conflict, potentially at the expense or “loss” of the other person. One way we may gauge our win is by being granted or taking concessions from the other person. For example, if D’Shaun gives Casey extra money behind Rosa’s back, he is taking an indirect competitive route resulting in a “win” for him because he got his way. The competing style also involves the use of power, which can be noncoercive or coercive (Sillars, 1980). Noncoercive strategies include requesting and persuading. When requesting, we suggest the conflict partner change a behavior. Requesting doesn’t require a high level of information exchange. When we persuade, however, we give our conflict partner reasons to support our request or suggestion, meaning there is more information exchange, which may make persuading more effective than requesting. Rosa could try to persuade D’Shaun to stop giving Casey extra allowance money by bringing up their fixed budget or reminding him that they are saving for a summer vacation. Coercive strategies violate standard guidelines for ethical communication and may include aggressive communication directed at rousing your partner’s emotions through insults, profanity, and yelling, or through threats of punishment if you do not get your way. If Rosa is the primary income earner in the family, she could use that power to threaten to take D’Shaun’s ATM card away if he continues giving Casey money. In all these scenarios, the “win” that could result is only short term and can lead to conflict escalation. Interpersonal conflict is rarely isolated, meaning there can be ripple effects that connect the current conflict to previous and future conflicts. D’Shaun’s behind-the-scenes money giving or Rosa’s confiscation of the ATM card could lead to built-up negative emotions that could further test their relationship.
Competing has been linked to aggression, although the two are not always paired. If assertiveness does not work, there is a chance it could escalate to hostility. There is a pattern of verbal escalation: requests, demands, complaints, angry statements, threats, harassment, and verbal abuse (Johnson & Roloff, 2000). Aggressive communication can become patterned, which can create a volatile and hostile environment. The reality television show The Bad Girls Club is a prime example of a chronically hostile and aggressive environment. If you do a Google video search for clips from the show, you will see yelling, screaming, verbal threats, and some examples of physical violence. The producers of the show choose houseguests who have histories of aggression, and when the “bad girls” are placed in a house together, they fall into typical patterns, which creates dramatic television moments. Obviously, living in this type of volatile environment would create stressors in any relationship, so it’s important to monitor the use of competing as a conflict resolution strategy to ensure that it does not lapse into aggression.
The competing style of conflict management is not the same thing as having a competitive personality. Competition in relationships isn’t always negative, and people who enjoy engaging in competition may not always do so at the expense of another person’s goals. In fact, research has shown that some couples engage in competitive shared activities like sports or games to maintain and enrich their relationship (Dindia & Baxter, 1987). And although we may think that competitiveness is gendered, research has often shown that women are just as competitive as men (Messman & Mikesell, 2000).
Avoiding
The avoiding style of conflict management often indicates a low concern for self and a low concern for other, and no direct communication about the conflict takes place. However, as we will discuss later, in some cultures that emphasize group harmony over individual interests, and even in some situations in the United States, avoiding a conflict can indicate a high level of concern for the other. In general, avoiding doesn’t mean that there is no communication about the conflict. Remember, you cannot not communicate. Even when we try to avoid conflict, we may intentionally or unintentionally give our feelings away through our verbal and nonverbal communication. Rosa’s sarcastic tone as she tells D’Shaun that he’s “Soooo good with money!” and his subsequent eye roll both bring the conflict to the surface without specifically addressing it. The avoiding style is either passive or indirect, meaning there is little information exchange, which may make this strategy less effective than others. We may decide to avoid conflict for many different reasons, some of which are better than others. If you view the conflict as having little importance to you, it may be better to ignore it. If the person you’re having conflict with will only be working in your office for a week, you may perceive a conflict to be temporary and choose to avoid it and hope that it will solve itself. If you are not emotionally invested in the conflict, you may be able to reframe your perspective and see the situation in a different way, therefore resolving the issue. In all these cases, avoiding doesn’t really require an investment of time, emotion, or communication skill, so there is not much at stake to lose.
Avoidance is not always an easy conflict management choice, because sometimes the person we have conflict with isn’t a temp in our office or a weekend houseguest. While it may be easy to tolerate a problem when you’re not personally invested in it or view it as temporary, when faced with a situation like Rosa and D’Shaun’s, avoidance would just make the problem worse. For example, avoidance could first manifest as changing the subject, then progress from avoiding the issue to avoiding the person altogether, to even ending the relationship.
Indirect strategies of hinting and joking also fall under the avoiding style. While these indirect avoidance strategies may lead to a buildup of frustration or even anger, they allow us to vent a little of our built-up steam and may make a conflict situation more bearable. When we hint, we drop clues that we hope our partner will find and piece together to see the problem and hopefully change, thereby solving the problem without any direct communication. For the most part, the person dropping the hints overestimates their partner’s detective abilities. For example, when Rosa leaves the bank statement on the kitchen table in hopes that D’Shaun will realize how much extra money he is giving Casey, D’Shaun may simply ignore it or even get irritated with Rosa for not putting the statement with all the other mail. We also overestimate our partner’s ability to decode the jokes we make about a conflict situation. It is more likely that the receiver of the jokes will think you’re genuinely trying to be funny or feel provoked or insulted than realize the conflict situation that you are referencing. So, more frustration may develop when the hints and jokes are not decoded, which often leads to a more extreme form of hinting/joking: passive-aggressive behavior.
Passive-aggressive behavior is a way of dealing with conflict in which one person indirectly communicates their negative thoughts or feelings through nonverbal behaviors, such as not completing a task. For example, Rosa may wait a few days to deposit money into the bank so D’Shaun can’t withdraw it to give to Casey, or D’Shaun may cancel plans for a romantic dinner because he feels like Rosa is questioning his responsibility with money. Although passive-aggressive behavior can feel rewarding in the moment, it is one of the most unproductive ways to deal with conflict. These behaviors may create additional conflicts and may lead to a cycle of passive-aggressiveness in which the other partner begins to exhibit these behaviors as well, while never actually addressing the conflict that originated the behavior. In most avoidance situations, both parties lose. However, as noted above, avoidance can be the most appropriate strategy in some situations—for example, when the conflict is temporary, when the stakes are low or there is little personal investment, or when there is the potential for violence or retaliation.
Accommodating
The accommodating conflict management style indicates a low concern for self and a high concern for other and is often viewed as passive or submissive, in that someone complies with or obliges another without providing personal input. The context for and motivation behind accommodating play an important role in whether or not it is an appropriate strategy. Accommodating can be appropriate when there is little chance that our own goals can be achieved, when we don’t have much to lose by accommodating, when we feel we are wrong, or when advocating for our own needs could negatively affect the relationship (Isenhart & Spangle, 2000). The occasional accommodation can be useful in maintaining a relationship—remember earlier we discussed putting another’s needs before your own as a way to achieve relational goals. For example, Rosa may say, “It’s OK that you gave Casey some extra money; she did have to spend more on gas this week since the prices went up.” However, being a team player can slip into being a pushover, which people generally do not appreciate. If Rosa keeps telling D’Shaun, “It’s OK this time,” they may find themselves short on spending money at the end of the month. At that point, Rosa and D’Shaun’s conflict may escalate as they question each other’s motives, or the conflict may spread if they direct their frustration at Casey and blame it on her irresponsibility.
Research has shown that the accommodating style is more likely to occur when there are time restraints and less likely to occur when someone does not want to appear weak (Cai & Fink, 2002). If you’re standing outside the movie theatre and two movies are starting, you may say, “Let’s just have it your way,” so you don’t miss the beginning. If you’re a new manager at an electronics store and an employee wants to take Sunday off to watch a football game, you may say no to set an example for the other employees. As with avoiding, there are certain cultural influences we will discuss later that make accommodating a more effective strategy.
Compromising
The compromising style shows a moderate concern for self and other and may indicate that there is a low investment in the conflict and/or the relationship (Figure 9.5). Even though we often hear that the best way to handle a conflict is to compromise, the compromising style isn’t a win/win solution; it is a partial win/lose. In essence, when we compromise, we give up some or most of what we want. It’s true that the conflict gets resolved temporarily, but lingering thoughts of what you gave up could lead to a future conflict. Compromising may be a good strategy when there are time limitations or when prolonging a conflict may lead to relationship deterioration. Compromise may also be good when both parties have equal power or when other resolution strategies have not worked (Macintosh & Stevens, 2008).

A negative of compromising is that it may be used as an easy way out of a conflict. The compromising style is most effective when both parties find the solution agreeable. Rosa and D’Shaun could decide that Casey’s allowance does need to be increased and could each give ten more dollars a week by committing to taking their lunch to work twice a week instead of eating out. They are both giving up something, and if neither of them have a problem with taking their lunch to work, then the compromise was equitable. If the couple agrees that the twenty extra dollars a week should come out of D’Shaun’s golf budget, the compromise isn’t as equitable, and D’Shaun, although he agreed to the compromise, may end up with feelings of resentment. Wouldn’t it be better to both win?
Collaborating
The collaborating style involves a high degree of concern for self and other and usually indicates investment in the conflict situation and the relationship. Although the collaborating style takes the most work in terms of communication competence, it ultimately leads to a win/win situation in which neither party has to make concessions because a mutually beneficial solution is discovered or created. The obvious advantage is that both parties are satisfied, which could lead to positive problem solving in the future and strengthen the overall relationship. For example, Rosa and D’Shaun may agree that Casey’s allowance needs to be increased and may decide to give her twenty more dollars a week in exchange for her babysitting her little brother one night a week. In this case, they didn’t make the conflict personal but focused on the situation and came up with a solution that may end up saving them money. The disadvantage is that this style is often time consuming, and only one person may be willing to use this approach while the other person is eager to compete to meet their goals or willing to accommodate.
Here are some tips for collaborating and achieving a win/win outcome (Hargie, 2011):
- Do not view the conflict as a contest you are trying to win.
- Remain flexible and realize there are solutions yet to be discovered.
- Distinguish the people from the problem (don’t make it personal).
- Determine what the underlying needs are that are driving the other person’s demands (needs can still be met through different demands).
- Identify areas of common ground or shared interests that you can work from to develop solutions.
- Ask questions to allow them to clarify and to help you understand their perspective.
- Listen carefully and provide verbal and nonverbal feedback.
STLC Conflict Model
Cahn and Abigail (2014) created a very simple model when thinking about how we communicate during conflict. They called the model the STLC Conflict Model because it stands for stop, think, listen, and then communicate (Figure 9.6).

Stop
The first thing an individual needs to do when interacting with another person during conflict is to take the time to be present within the conflict itself. Too often, people engaged in a conflict say whatever enters their mind before they’ve really had a chance to process the message and think of the best strategies to use to send that message. Others end up talking past one another during a conflict because they simply are not paying attention to each other and the competing needs within the conflict. Communication problems often occur during conflict because people tend to react to conflict situations when they arise instead of being mindful and present during the conflict itself. For this reason, it’s always important to take a breath during a conflict and first stop.
Sometimes these “time outs” need to be physical. Maybe you need to leave the room and go for a brief walk to calm down, or maybe you just need to get a glass of water. Whatever you need to do, it’s important to take this break. This break helps you to be proactive rather than reactive (Cahn & Abigail, 2014).
Think
Once you’ve stopped, you now have the ability to really think about what you are communicating. You want to think through the conflict itself. What is the conflict really about? Often people engage in conflicts about superficial items when there are truly much deeper issues that are being avoided. You also want to consider what possible causes led to the conflict and what possible courses of action you think are possible to conclude the conflict. Cahn and Abigail argue that there are four possible outcomes that can occur: do nothing, change yourself, change the other person, or change the situation.
First, you can simply sit back and avoid the conflict. Maybe you’re engaging in a conflict about politics with a family member, and this conflict is actually just going to make everyone mad. For this reason, you opt just to stop the conflict and change topics to avoid making people upset.
Second, we can change ourselves. Often, we are at fault and start conflicts. We may not even realize how our behavior caused the conflict until we take a step back and really analyze what is happening. When it comes to being at fault, it’s very important to admit that you’ve done wrong. Nothing is worse (and can stoke a conflict more) than when someone refuses to see their part in the conflict.
Third, we can attempt to change the other person. Let’s face it, changing someone else is easier said than done. Just ask your parents/guardians! All of our parents/guardians have attempted to change our behaviors at one point or another, and changing people is very hard. Even with the powers of punishment and reinforcement, a lot of the time change only lasts as long as the punishment or the reinforcer is active.
Lastly, we can just change the situation. Having a conflict with your roommates? Move out. Having a conflict with your boss? Find a new job. Having a conflict with a professor? Drop the course. Admittedly, changing the situation is not necessarily the first choice people should take when thinking about possibilities, but often it’s the best decision for long-term happiness. In essence, some conflicts will not be settled between people. When these conflicts arise, you can try and change yourself, hope the other person will change (they probably won’t, though), or just get out of it altogether.
Listen
The third step in the STLC model is listen. Humans are not always the best listeners. Listening is a skill. Unfortunately, during a conflict situation, this is a skill that is desperately needed and often forgotten. When we feel defensive during a conflict, our listening becomes spotty at best because we start to focus on ourselves and protecting ourselves instead of trying to be empathic and seeing the conflict through the other person’s eyes.
One mistake some people make is to think they’re listening, but in reality, they’re listening for flaws in the other person’s argument. We often use this type of selective listening as a way to devalue the other person’s stance. In essence, we will hear one small flaw with what the other person is saying and then use that flaw to demonstrate that obviously everything else must be wrong as well.
The goal of listening must be to suspend your judgment and really attempt to be present enough to accurately interpret the message being sent by the other person. When we listen in this highly empathic way, we are often able to see things from the other person’s point-of-view, which could help us come to a better-negotiated outcome in the long run.
Communicate
Lastly, but certainly not least, we communicate with the other person. Notice that Cahn and Abigail (2014) put communication as the last part of the STLC model because it’s the hardest one to do effectively during a conflict if the first three are not done correctly. When we communicate during a conflict, we must be hyper-aware of our nonverbal behavior (eye movement, gestures, posture, etc.). Nothing will kill a message faster than when it’s accompanied by bad nonverbal behavior. For example, rolling one’s eyes while another person is speaking is not an effective way to engage in conflict.
During a conflict, it’s important to be assertive and stand up for your ideas without becoming verbally aggressive. Conversely, you have to be open to someone else’s use of assertiveness as well without having to tolerate verbal aggression. We often end up using mediators to help call people on the carpet when they communicate in a fashion that is verbally aggressive or does not further the conflict itself.
Summary
- Interpersonal conflict is an inevitable part of relationships that, although not always negative, can take an emotional toll on relational partners unless they develop skills and strategies for managing conflict.
- Although there is no absolute right or wrong way to handle a conflict, there are five predominant styles of conflict management, which are competing, avoiding, accommodating, compromising, and collaborating.
- In the STLC model of conflict the steps in conflict are: Stop, Think, Listen, and Communicate.
Discussion Questions
- Of the five conflict management strategies, is there one that you use more often than others? Why or why not? Do you think people are predisposed to one style over the others? Why or why not?
- Review the example of D’Shaun and Rosa. If you were in their situation, what do you think the best style to use would be and why?
- Discuss an example of a conflict you’ve experienced. How could you have used the STLC Conflict Model to help you resolve this conflict positively.
Remix/Revisions featured in this section
- Small editing revisions to tailor the content to the Psychology of Human Relations course.
- Remix of Employment Legislation (Introduction to Business – Lumen Learning) and EEO Best Practices, EEO Complaints (Human Resources Management – Lumen Learning) added to Introduction to Social Diversity in the Workplace (Organizational Behavior and Human Relations – Lumen Learning).
- Added images and provided links to locations of images and CC licenses.
- Added doi links to references to comply with APA 7thedition formatting reference manual.
Attributions
CC Licensed Content, Original
Modification, adaptation, and original content. Provided by: Stevy Scarbrough. License: CC-BY-NC-SA
CC Licensed Content Shared Previously
Communication in the Real World. Authored by: University of Minnesota. Located at: https://open.lib.umn.edu/communication/chapter/6-2-conflict-and-interpersonal-communication/ License: CC-BY-NC-SA 4.0
CC Licensed Content Shared Previously
Conflict Management Authored by: Laura Westmaas. Published by: Open Library Located at: https://ecampusontario.pressbooks.pub/conflictmanagement/ License: CC BY 4.0
References
Cahn D. D., & Abigail, R. A. (2014). Managing conflict through communication (5th ed.). Pearson Education.
Cid, D., & Fink, E. (2010). Conflict style differences between individualists and collectivists. Communication Monographs, 69(1), 67-87. https://doi.org/10.1080/03637750216536
Dindia, K., & Baxter, L. A. (1987). Strategies for Maintaining and Repairing Marital Relationships. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships, 4(2), 143–158. https://doi.org/10.1177/0265407587042003
Hargie, O. (2011). Skilled Interpersonal Interaction: Research, Theory, and Practice. Routledge.
Isenhart, M. W., & Spangle, M. (2000). Collaborative Approaches to Resolving Conflict. Sage.
Johnson, K. L., & Roloff, M. E. (2000). Correlates of the perceived resolvability and relational consequences of serial arguing in dating relationships: Argumentative features and the use of coping strategies. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships, 17(4-5), 676-686. https://doi.org/10.1177/0265407500174011
Macintosh, G., & Stevens, C. (2008). Personality, motives, and conflict strategies in everyday service encounters. International Journal of Conflict Management, 19(2), 112-131. https://doi.org/10.1108/10444060810856067
Messman, S. J., & Mikesell, R. L. (2009). Competition and interpersonal conflict in dating relationships. Communication Reports, 13(1), 21-34. https://doi.org/10.1080/08934210009367720
Rahim, M. A. (1983). A measure of styles of handling interpersonal conflict. The Academy of Management Journal, 26(2), 368-379. https://doi.org/10.2307/255985
Reese-Weber, M., & Bartle-Haring, S. (1998). Conflict resolution styles in family subsystems and adolescent romantic relationships. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 27(6), 735–752. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022861832406
Sillars, A. (1980). Attributions and communication in roommate conflicts. Communication Monographs, 47(3), 180-200. https://doi.org/10.1080/03637758009376031

