Capillary Blood Glucose (CBG)
Assessing blood glucose should be a part of every patient with altered mentation. Concerning findings for EMS professionals include readings below 60 mg/dL, and above 500-600 mg/dL. Be familiar with the Glucometer specs supplied by your service. Sometimes you might get a reading of “LO” or “HI”, the manufacturer specs will give the ranges of blood sugar levels that fall into those categories (usually under 20 mg/dL or over 500 mg/dL)
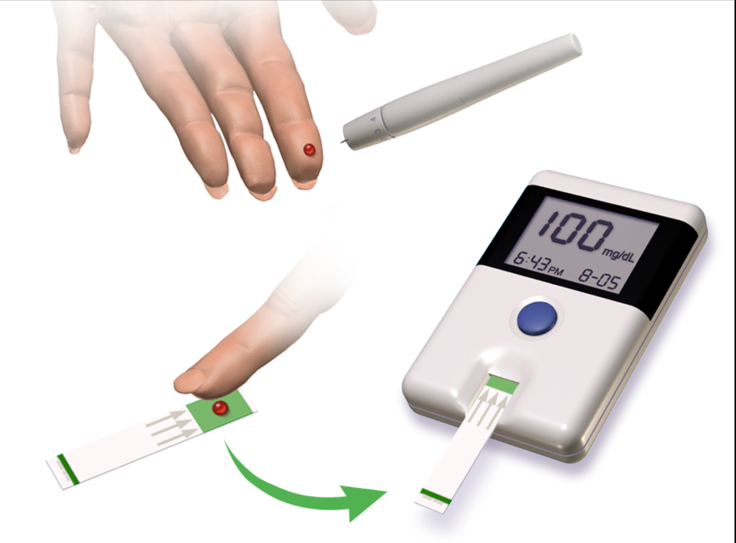
To take a CBG:
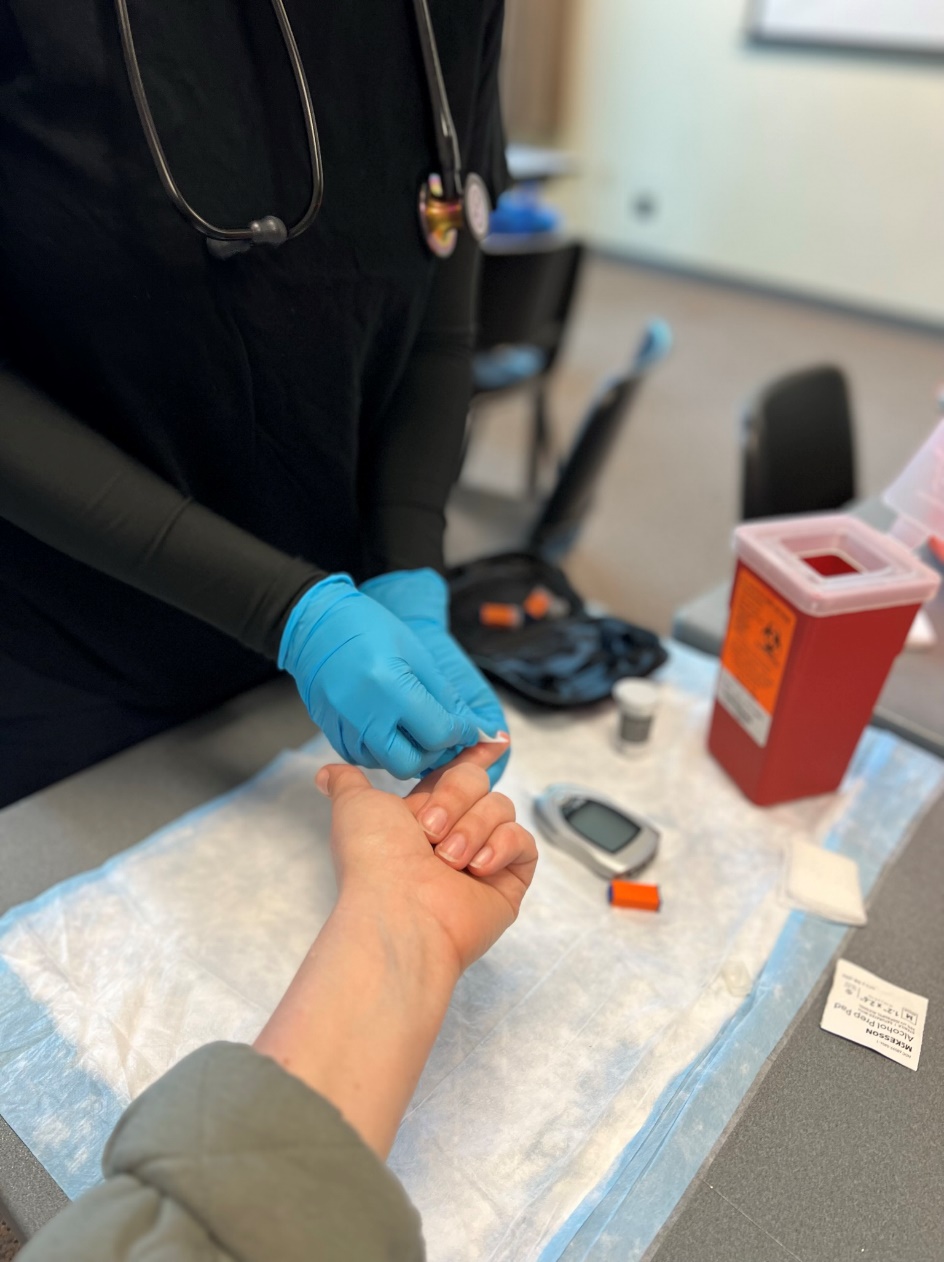
- Ensure proper PPE. Have a sharps container handy.
- Identify a finger of choice – ideally off to the side of the distal tip as it tends to hurt less.
- Clean the site using an alcohol pad & let it dry.
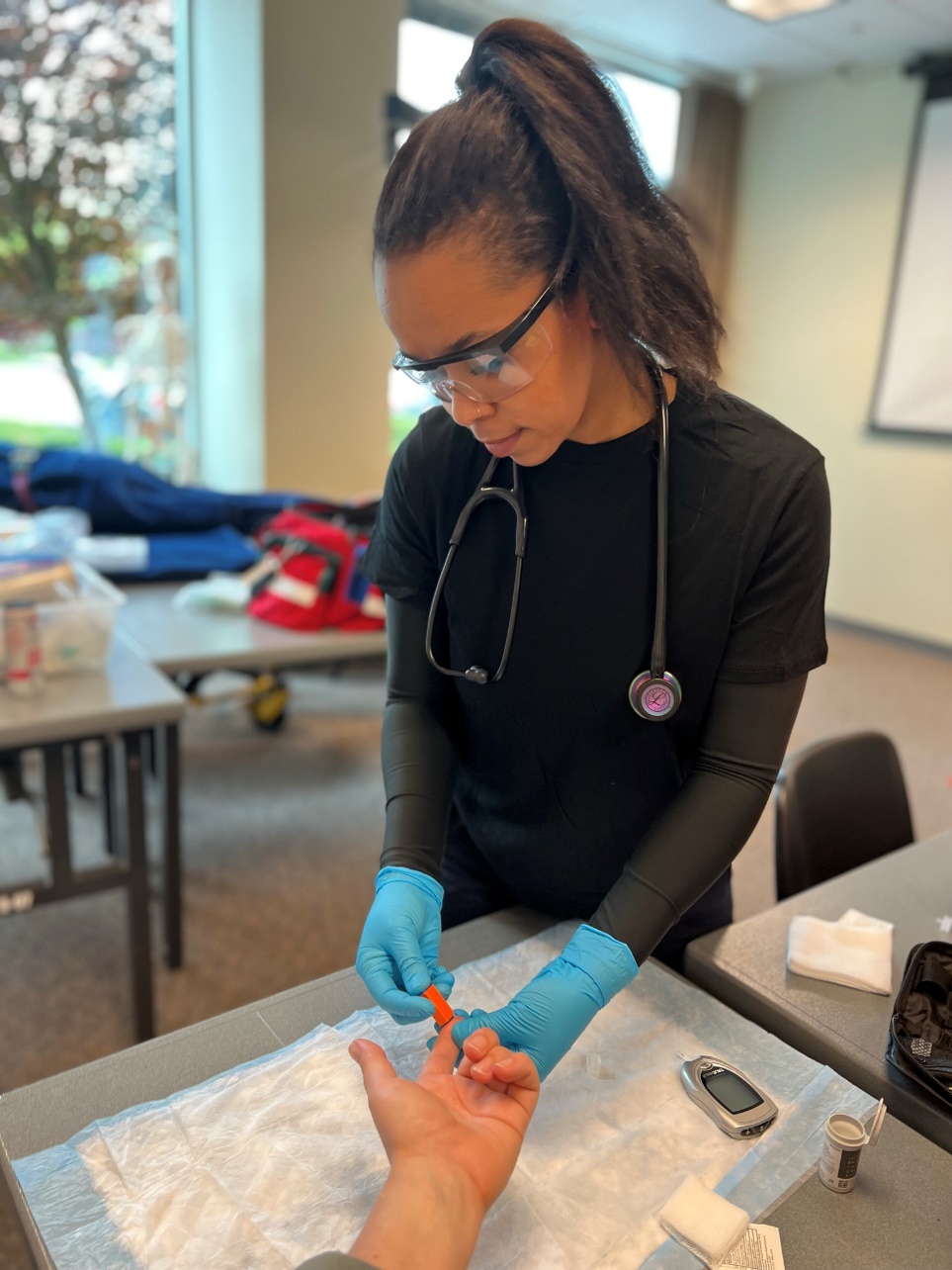
- Insert test strip into monitor.
- Communicate to your patient that they will feel a “poke”.
- Use your department approved lancet to puncture the site and draw blood.
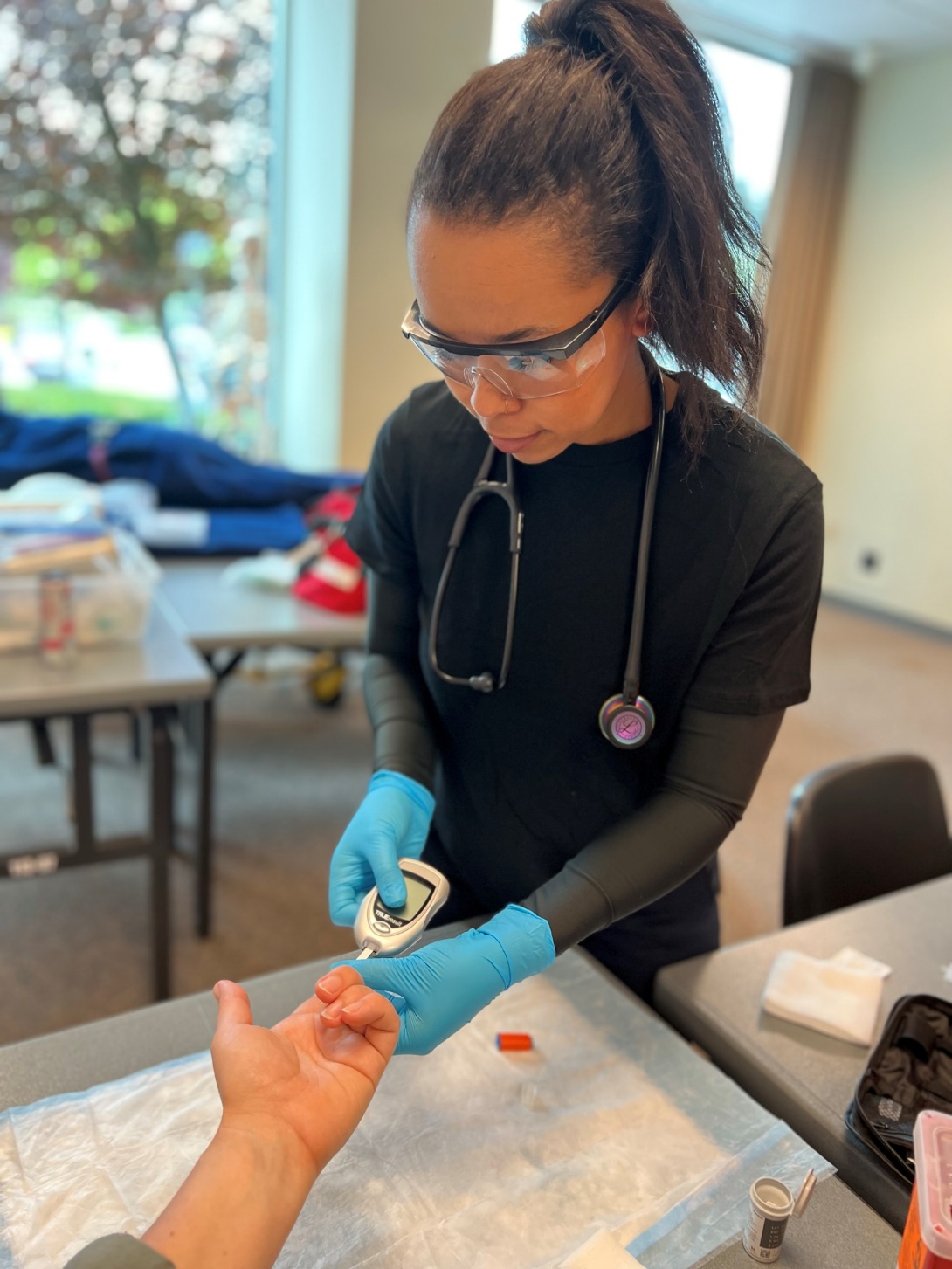
- With the test strip inserted, bring the end of the test strip to the blood, and allow it to “soak up” into the strip.
- You should have a reading within 10 seconds – record the reading.
- Control bleeding as necessary use gauze and direct pressure.
*On rare occasion the patient’s fingers are so calloused that the lancet does not penetrate deep enough to obtain a blood sample, the patient’s ear lobe might be a good alternative to get blood sample with lancet
| CBG | 1 | 2 | 3 (instructor) |
| CBG Reading mg/DL | |||
| Initials |
The original copy of this book resides at openoregon.pressbooks.pub/emslabmanual. If you are reading this work at an alternate web address, it may contain content that has not been vetted by the original authors and physician reviewers.

