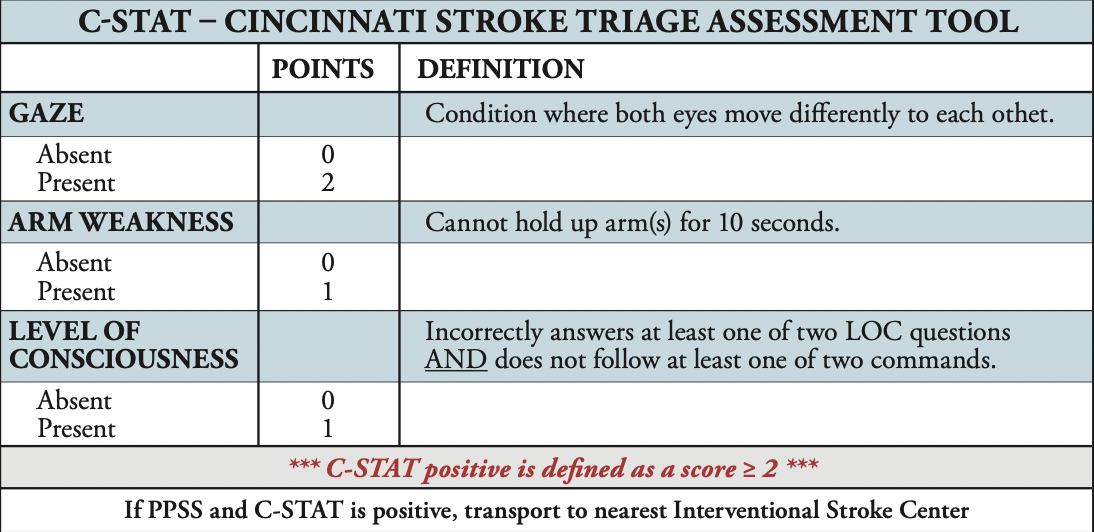
Cerebral Vascular Accident (CVA)/Stroke Recognition
A CVA occurs when there is a blockage or rupture of an artery in the brain. Most strokes originate from an occlusion and are painless. However, some are accompanied with a headache. Patients complaining of severe headaches should be screened for a CVA and the provider should maintain a high index of suspicion for hemorrhagic stroke. Symptom resolution within 24 hours indicates a possible transient ischemic attack (TIA) and is predictive of a CVA in the future. Complete the BFAST assessment score. If positive, proceed to C-STAT and transport as indicated.


|
Stroke assessment |
1 |
2 |
3 (instructor) |
|
Result |
|
|
|
|
Initials |
|
|
|
The original copy of this book resides at openoregon.pressbooks.pub/emslabmanual. If you are reading this work at an alternate web address, it may contain content that has not been vetted by the original authors and physician reviewers.

