39.5 – Bilateral Monopoly
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Explain how firms determine wages and employment when a specific labor market combines a union and a monopsony
What happens when there is market power on both sides of the labor market, in other words, when a union meets a monopsony? Economists call such a situation a bilateral monopoly.
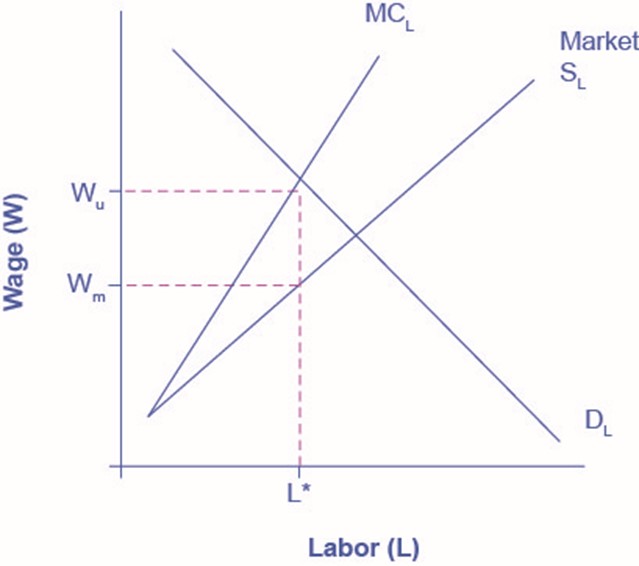
As Figure 1 shows, a monopsony wants to reduce wages as well as employment, Wm and L* in the figure. A union wants to increase wages, but at the cost of lower employment, Wu and L* in the figure. Since both sides want to reduce employment, we can be sure that the outcome will be lower employment compared to a competitive labor market. What happens to the wage, though, is based on the monopsonist’s relative bargaining power compared to the union. The actual outcome is indeterminate in the graph, but it will be closer to Wu if the union has more power and closer to Wm if the monopsonist has more power.

