51 Brittle Bones
Brittle materials have a small plastic region and they begin to fail toward fracture] or rupture almost immediately after being stressed beyond their elastic limit. Bone, cast iron, ceramic, and concrete are examples of brittle materials. Materials that have relatively large plastic regions under tensile stress are known as ductile. Examples of ductile materials include aluminum and copper. The following figure shows how brittle and ductile materials change shape under stress. Even the cartilage that makes up tendons and ligaments is relatively brittle because it behaves less like example (c) and more like examples (a) and (b). Luckily, those tissues have adapted to allow the deformation required for mobility by, which is the purpose of the toe region of their stress vs. strain curves.
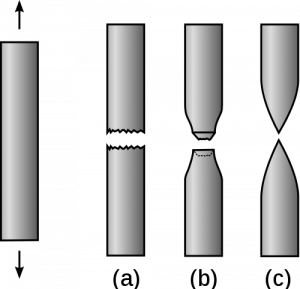
Materials that are very malleablecan undergo significant plastic deformation under compressive stress, as apposed to tensile stress. Very malleable materials can be pounded into thin sheets. Gold is the most malleable metal.[1]
Reinforcement Exercises
the sudden and complete failure of a material under stress
the range of values for stress and strain values over which a material returns to its original shape after deformation
a physical quantity that expresses the internal forces that neighboring particles of material exert on each other
reduction in size caused by application of compressive forces (opposing forces applied inward to the object).
the force that is provided by an object in response to being pulled tight by forces acting from opposite ends, typically in reference to a rope, cable or wire

