37 Supporting the Body
Support Force (Normal Force)
When standing on the ground gravity is pulling you down, but you aren’t falling. In fact you are in static equilibrium so the ground must be providing a supporting force that balances your weight. The ground provides that force in response to compression caused by your weight. When solid objects push back against forces that are deforming them we call that responsive push-back the Normal Force.
Reinforcement Activity
Push your finger down into your palm and feel the resistance from your palm.
That resistance is the normal force.
When you pull your finger away from your palm, the normal force from your palm goes away.
Everyday Example[1]
In the diagram below, we see a person placing a bag of dog food on a table. When the bag of dog food is placed on the table, and the person lets go, how does the table exert the force necessary to balance the weight of the bag? While you wouldn’t see it with your naked eye, the table sags slightly under the load (weight of the bag). This would be noticeable if the load were placed on a thin plywood table, but even a sturdy oak table deforms when a force is applied to it. That resistance to deformation causes a restoring force much like a deformed spring (or a trampoline or diving board). When the load is placed on the table, the table sags until the restoring force becomes as large as the weight of the load, putting the load in equilibrium. The table sags quickly and the sag is slight, so we do not notice it, but it is similar to the sagging of a trampoline or a hammock when you climb on.
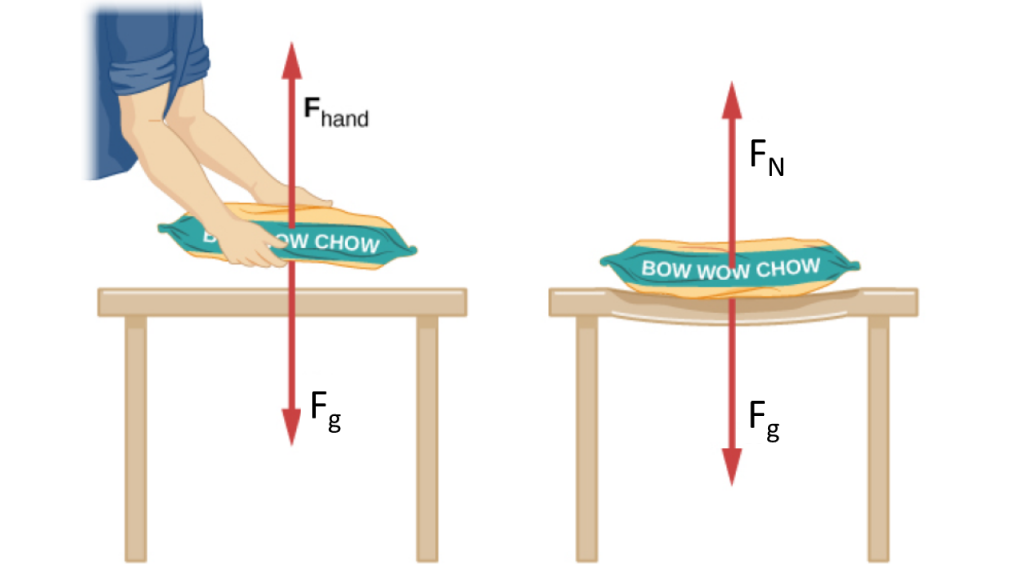
Normal Force and Weight
If you place an object on a table the normal force from the table supports the weight of the object. For this reason normal force is sometimes called support force. However, normal is another word for perpendicular, so we will stick with normal force because it reminds us of the important fact that the normal force always acts at an angle of 90° to the surface. That does not mean the normal force always point vertically, nor is it always equal to an object’s weight. If you push horizontally on the wall, the wall pushes back (keeping your hand from moving through the wall). The force from the wall is a normal force, but it acts horizontally and is not equal to your weight.
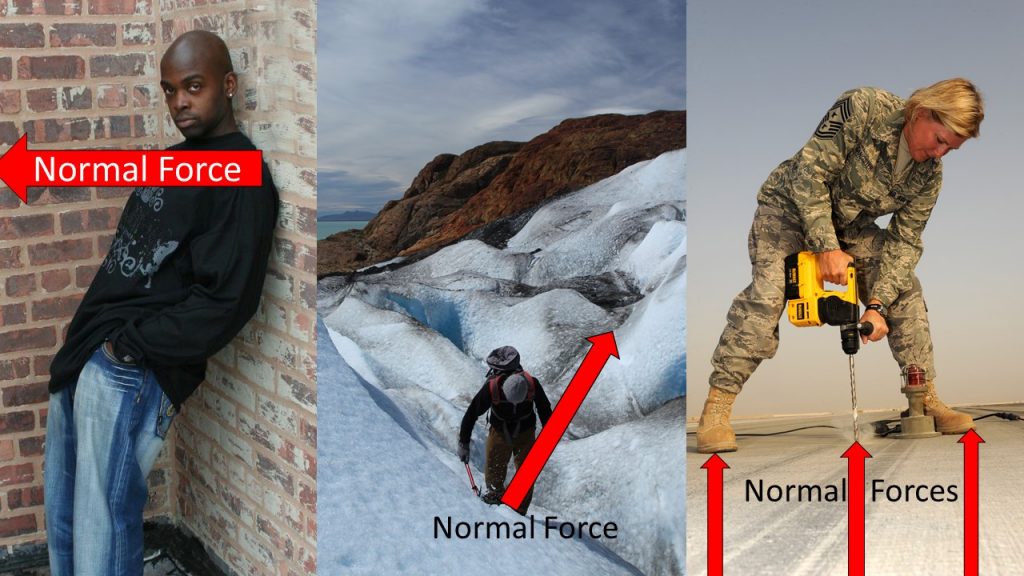

In each situation pictured above the normal force is not equal to body weight. In the left image the normal force is less than body weight, and acting horizontally. In the middle image the normal force is less than body weight and acting at an angle. In the right image the normal force on the drill is more than it’s own weight because Master Sgt. Sangster is also pushing down on the drill. The normal force on Master Sgt. Sangster’s feet is less than her weight because she is also receiving an upward normal force from the drill handle.
Often (N) is used as a symbol for normal force, but we are using N to abbreviate for the SI force unit Newtons, so instead we will use ![]() . The normal force comes up so often students often accidentally begin to refer to normal force as “natural force” instead, so watch out for that possible source of confusion.
. The normal force comes up so often students often accidentally begin to refer to normal force as “natural force” instead, so watch out for that possible source of confusion.
Reinforcement Exercises: Normal Force
- OpenStax University Physics, University Physics Volume 1. OpenStax CNX. Jul 11, 2018 http://cnx.org/contents/d50f6e32-0fda-46ef-a362-9bd36ca7c97d@10.18 ↵
- "Garscon Plancher" by Obiwancho , Wikimedia Commons is licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 ↵
- "U.S. Air Force Chief Master Sgt. Suzan Sangster", Wikimedia Commons is in the Public Domain, ↵
- "Trek on the Viedma Glacier" by Liam Quinn , Wikimedia Commons is licensed under CC BY-SA 2.0 ↵
attraction between two objects due to their mass as described by Newton's Universal Law of Gravitation
the state being in equilibrium (no unbalanced forces or torques) and also having no motion
any interaction that causes objects with mass to change speed and/or direction of motion, except when balanced by other forces. We experience forces as pushes and pulls.
reduction in size caused by application of compressive forces (opposing forces applied inward to the object).
the outward force supplied by an object in response to being compressed from opposite directions, typically in reference to solid objects.
the force of gravity on on object, typically in reference to the force of gravity caused by Earth or another celestial body
a force that tends to move a system back toward the equilibrium position
a state of having no unbalanced forces or torques
at an angle of 90° to a given line, plane, or surface
a system of physical units ( SI units ) based on the meter, kilogram, second, ampere, kelvin, candela, and mole

