40 Tipping
Torque
When you hold an object in your hand, the weight of the object tends to cause a rotation of the forearm with the elbow joint acting as the pivot. The tension force applied by your biceps tries to counteract this rotation.
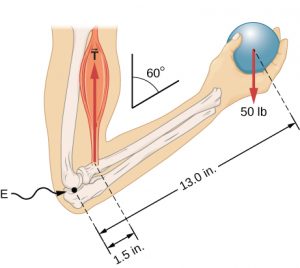
When forces applied to an object tend to cause rotation of the object, we say the force is causing a torque. The size of a torque depends on the size of the force, the direction of the force, and the distance from the pivot point to where the force acts.
Reinforcement Activity
Static Equilibrium
We already know that when an object must have no net force in order for its velocity to remain constant, meaning that it’s translational motion did not change. In similar fashion, on object with constant rotational motion must have zero net torque. Therefore, in order for an object to remain still without rotating all the torques must cancel each other out. If the net torque is not zero the the object will begin to rotate rather than remain still. For example, in our example of the forearm holding the ball, the torque due to biceps tension and torque due to ball weight must be equal, but in opposite directions.
Reinforcement Exercises
Tipping Point
When a body’s center of gravity is above the area formed by the support base the normal force can provide the torque necessary to remain in rotational equilibrium.
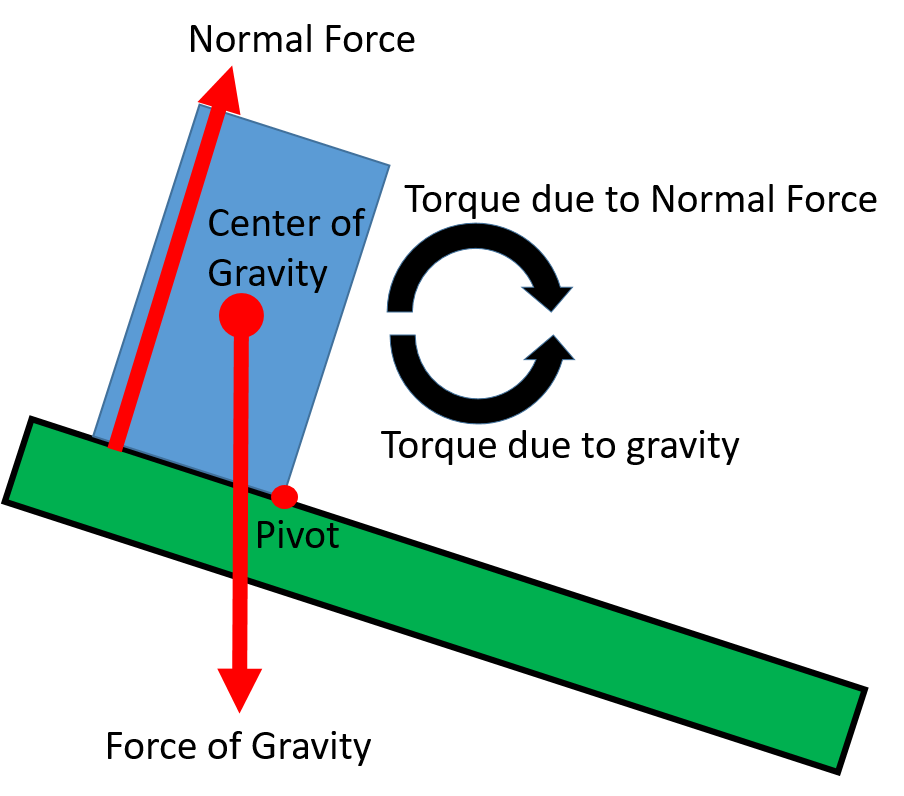
The critical tipping point is reached when the center of gravity passes outside of the support base. Beyond the tipping point, gravity causes rotation away from the support base, so there is no normal force available to cause the torque needed to cancel out the torque caused by gravity. The normal force acting on the pivot point can help support the object’s weight, but it can’t create a torque because it’s not applied at any distance away from the pivot.
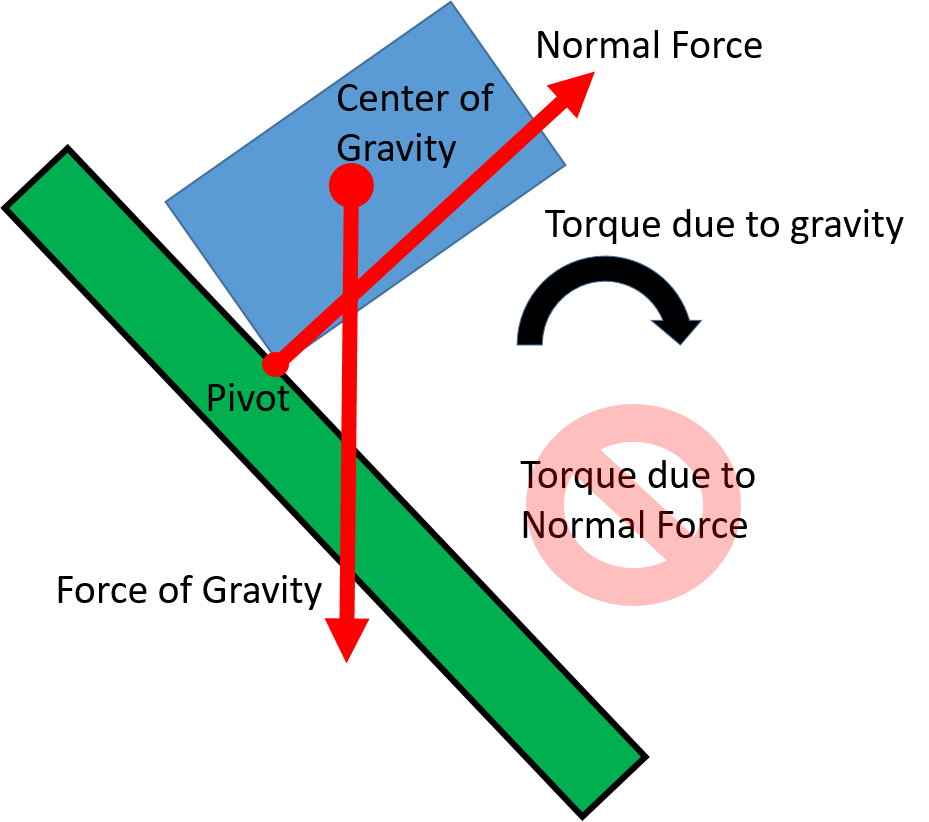
Now with a net torque the object can not be in rotational equilibrium. The object will rotate around the edge of the support base and tip over. We often refer to structures (and bodies) that are relatively resistant to tipping over as having greater stability.
- OpenStax University Physics, University Physics Volume 1. OpenStax CNX. Jul 11, 2018 http://cnx.org/contents/d50f6e32-0fda-46ef-a362-9bd36ca7c97d@10.18. ↵
the force of gravity on on object, typically in reference to the force of gravity caused by Earth or another celestial body
the central point, pin, or shaft on which a mechanism turns or oscillates
the force that is provided by an object in response to being pulled tight by forces acting from opposite ends, typically in reference to a rope, cable or wire
the result of a force applied to an object in such a way that the object would change its rotational speed, except when the torque is balanced by other torques
any interaction that causes objects with mass to change speed and/or direction of motion, except when balanced by other forces. We experience forces as pushes and pulls.
remaining unbalanced torque on an object
a point at which the force of gravity on body or system (weight) may be considered to act. In uniform gravity it is the same as the center of mass.
region defined by lines connecting points of contact with the supporting surface
the outward force supplied by an object in response to being compressed from opposite directions, typically in reference to solid objects.
a state of having not net torque and no change in rotational motion
the point at which an object is displaced from a region of stable equilibrium
attraction between two objects due to their mass as described by Newton's Universal Law of Gravitation

