98 Manipulating Genetic Material
Biotechnology is the use of artificial methods to modify the genetic material of living organisms or cells to produce novel compounds or to perform new functions. Biotechnology has been used for improving livestock and crops since the beginning of agriculture through selective breeding. Since the discovery of the structure of DNA in 1953, and particularly since the development of tools and methods to manipulate DNA in the 1970s, biotechnology has become synonymous with the manipulation of organisms’ DNA at the molecular level. The primary applications of this technology are in medicine (for the production of vaccines and antibiotics) and in agriculture (for the genetic modification of crops). Biotechnology also has many industrial applications, such as fermentation, the treatment of oil spills, and the production of biofuels, as well as many household applications such as the use of enzymes in laundry detergent.
To accomplish the applications described above, biotechnologists must be able to extract, manipulate, and analyze nucleic acids.
Review of Nucleic Acid Structure
To understand the basic techniques used to work with nucleic acids, remember that nucleic acids are macromolecules made of nucleotides (a sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base). The phosphate groups on these molecules each have a net negative charge. An entire set of DNA molecules in the nucleus of eukaryotic organisms is called the genome. DNA has two complementary strands linked by hydrogen bonds between the paired bases.
Unlike DNA in eukaryotic cells, RNA molecules leave the nucleus. Messenger RNA (mRNA) is analyzed most frequently because it represents the protein-coding genes that are being expressed in the cell.
Isolation of Nucleic Acids
To study or manipulate nucleic acids, the DNA must first be extracted from cells. Various techniques are used to extract different types of DNA (Figure 10.2). Most nucleic acid extraction techniques involve steps to break open the cell, and then the use of enzymatic reactions to destroy all undesired macromolecules. Cells are broken open using a detergent solution containing buffering compounds. To prevent degradation and contamination, macromolecules such as proteins and RNA are inactivated using enzymes. The DNA is then brought out of solution using alcohol. The resulting DNA, because it is made up of long polymers, forms a gelatinous mass.
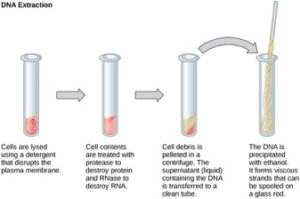
RNA is studied to understand gene expression patterns in cells. RNA is naturally very unstable because enzymes that break down RNA are commonly present in nature. Some are even secreted by our own skin and are very difficult to inactivate. Similar to DNA extraction, RNA extraction involves the use of various buffers and enzymes to inactivate other macromolecules and preserve only the RNA.
Gel Electrophoresis
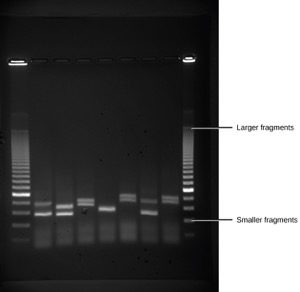
Because nucleic acids are negatively charged ions at neutral or alkaline pH in an aqueous environment, they can be moved by an electric field. Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate charged molecules on the basis of size and charge. The nucleic acids can be separated as whole chromosomes or as fragments. The nucleic acids are loaded into a slot at one end of a gel matrix, an electric current is applied, and negatively charged molecules are pulled toward the opposite end of the gel (the end with the positive electrode). Smaller molecules move through the pores in the gel faster than larger molecules; this difference in the rate of migration separates the fragments on the basis of size. The nucleic acids in a gel matrix are invisible until they are stained with a compound that allows them to be seen, such as a dye. Distinct fragments of nucleic acids appear as bands at specific distances from the top of the gel (the negative electrode end) that are based on their size (Figure 10.3). A mixture of many fragments of varying sizes appear as a long smear, whereas uncut genomic DNA is usually too large to run through the gel and forms a single large band at the top of the gel.
DNA analysis often requires focusing on one or more specific regions of the genome. It also frequently involves situations in which only one or a few copies of a DNA molecule are available for further analysis. These amounts are insufficient for most procedures, such as gel electrophoresis. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique used to rapidly increase the number of copies of specific regions of DNA for further analyses (Figure 10.4). PCR uses a special form of DNA polymerase, the enzyme that replicates DNA, and other short nucleotide sequences called primers that base pair to a specific portion of the DNA being replicated. PCR is used for many purposes in laboratories. These include: 1) the identification of the owner of a DNA sample left at a crime scene; 2) paternity analysis; 3) the comparison of small amounts of ancient DNA with modern organisms; and 4) determining the sequence of nucleotides in a specific region.
References
Unless otherwise noted, images on this page are licensed under CC-BY 4.0 by OpenStax.
OpenStax, Biology. OpenStax CNX. May 27, 2016 http://cnx.org/contents/s8Hh0oOc@9.10:8CA_YwJq@3/Cloning-and-Genetic-Engineerin

