3.3 GRAMMAR: Verbs — It’s All about Time, Attitude, and Relationships
You probably have been studying the different verb tenses for several years. So this is just a review. If you feel you need more instruction or practice, please speak with your teacher.
Present tense
 This verb tense …
This verb tense …
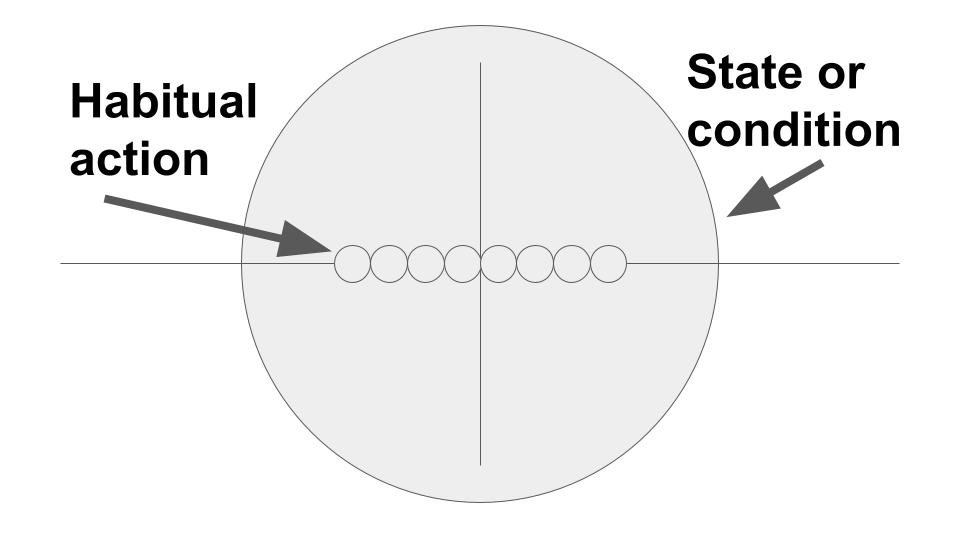
- shows present state or condition: Brenda is happy.
- shows a general fact or something that is always true: Hot air rises.
- shows habitual action: Many people drink coffee every morning with breakfast.
- is used in research writing to report what others have said or done: In this article, Darwin presents evidence for the development of life.
- is used for definitions/explanations: Picture B replaces Picture A as shown on page 2.
- shows future possibility in conditional and time clauses: Gary will pay you $50.00 if he likes your work.
- is used to show future events that are considered certain to happen: The plane leaves at 10:15 tonight.
If you see a frequency adverb, use the present tense. Some examples of frequency adverbs are: always, frequently, generally, never, occasionally, often, rarely, seldom, sometimes, usually. Example: Students often have difficulty deciding on a major.
Present progressive/continuous tense
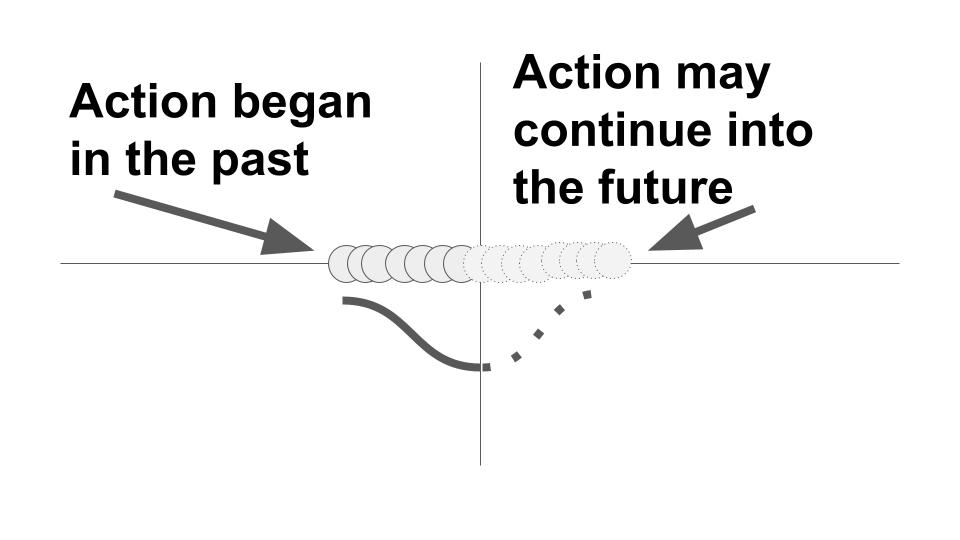 This tense shows action as a process that is incomplete now but will end. With an adverb of frequency, this tense can show habitual action and in certain situations it can show future action.
This tense shows action as a process that is incomplete now but will end. With an adverb of frequency, this tense can show habitual action and in certain situations it can show future action.
- Our dog is chasing your cat. (action now in progress)
- The dog is usually chasing the cat. (habitual action)
- Our dog is coming home from the animal hospital tomorrow. (a future event that you are looking forward to now)
Clues such as the following are often used with the present progressive/continuous tense: Look! Listen! Right now, this period, today, this week, at the present time, currently, at this moment, for the time being, temporarily. Example: Thinh is taking an art workshop this term.
Past tense
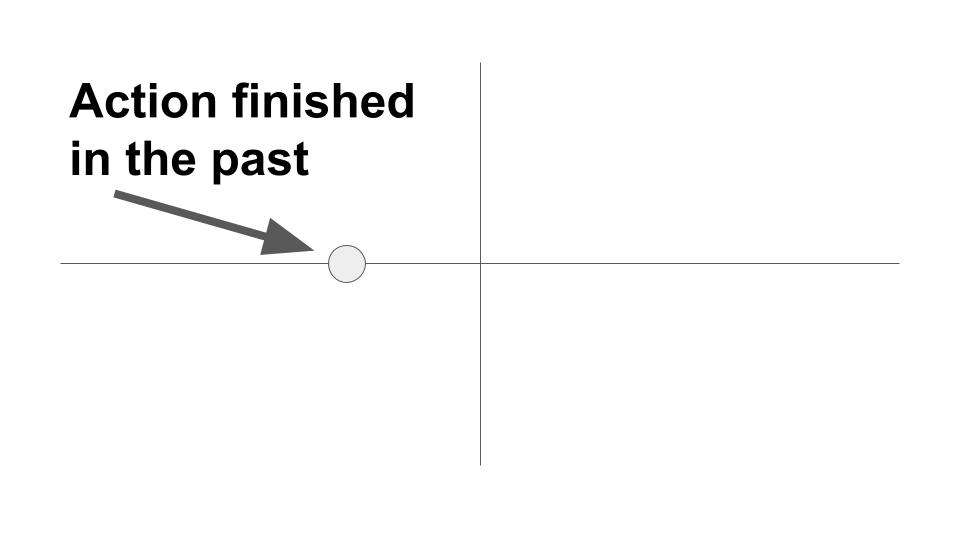 This tense is used for events that happened at a specific time in the past. Use the past tense for a single event or for events that took place over a period of time if that period is finished. This tense is used to tell a story, discuss history, or for repeated/habitual actions that no longer occur.
This tense is used for events that happened at a specific time in the past. Use the past tense for a single event or for events that took place over a period of time if that period is finished. This tense is used to tell a story, discuss history, or for repeated/habitual actions that no longer occur.
- I called a Lyft driver at 2:30 this afternoon. (single event, finished)
- Our neighbor’s dog barked at the neighbor’s cat every night last week. (repeated action, finished)
The past tense is used to express a completed action that took place at a specified time in the past. The specified time is either stated or implied. Example: Our friends arrived late for the concert last night.
Past progressive/continuous tense
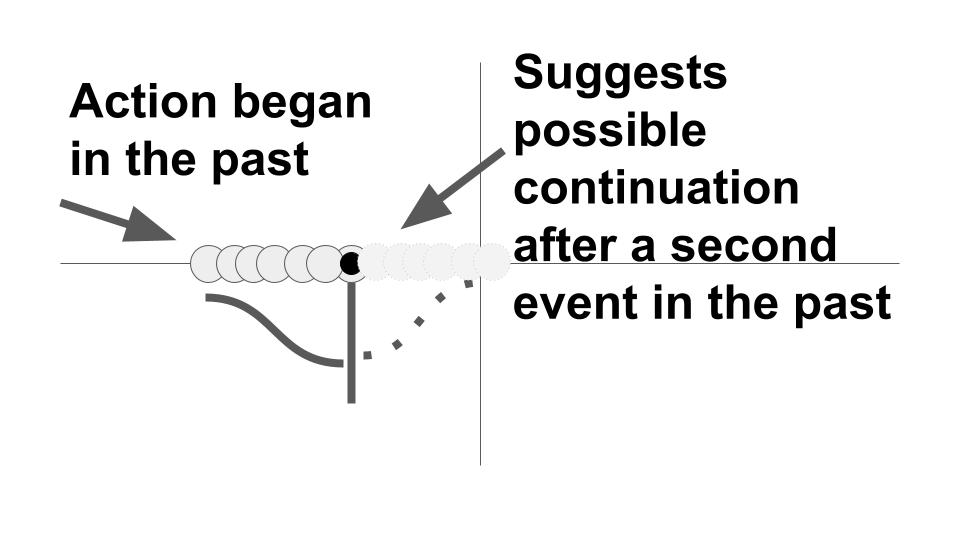 This verb tense is used:
This verb tense is used:
- to show duration, with emphasis on the length of time, of an act that is no longer going on: We were waiting for that plane to arrive for six hours before it came.
- for an action in the past that was not completed in the time period mentioned: They were shopping for a new car yesterday. (They didn’t find one.)
- for an action that was going on at a time in the past when something else happened: While Juan and I were watching television, lightning struck the roof of the garage.
The past continuous tense is used in sentences with the two past actions to show that, while one action was going on, another action occurred. The past continuous describes the longer action; the past tense describes the shorter action. While and as are often used with the past continuous form. Example: While the farmers were planting crops, a windstorm struck.
Future tense
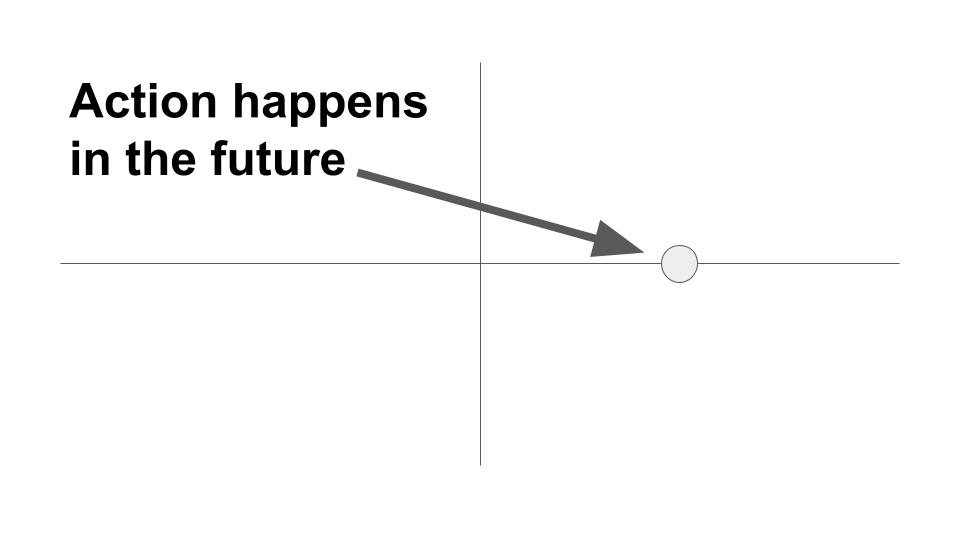 This tense is used to show future events: The art class will visit the museum tomorrow. (This tense is often used when the decision is newly made or when someone in authority gives an order.)
This tense is used to show future events: The art class will visit the museum tomorrow. (This tense is often used when the decision is newly made or when someone in authority gives an order.)
The future tense is used to express an action that will occur at some time in the future. Sentences in future time often contain time clauses, beginning with such words as when, after, before, as soon as, until and while. Example: The writers of the TV show will consult the guest star before they finish the story.
Future progressive/continuous tense
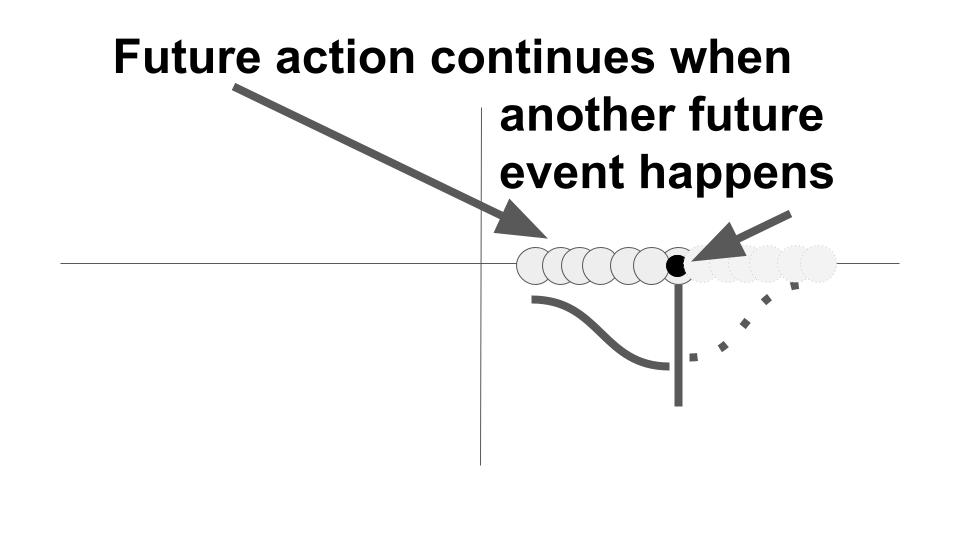 Use this tense to emphasize duration, intention, or a temporary condition in the future.
Use this tense to emphasize duration, intention, or a temporary condition in the future.
- Sometimes I think I will be studying English for the rest of my life.
- I will mail that package for you since I will be walking by the post office this afternoon.
- Our salesman will be visiting you soon to take your order.
The future progressive/continuous tense is used to describe an action that will be in process at a particular time in the future, often in relation to another action. Example: Mai can’t play soccer next Sunday because she will be working.
Present perfect tense
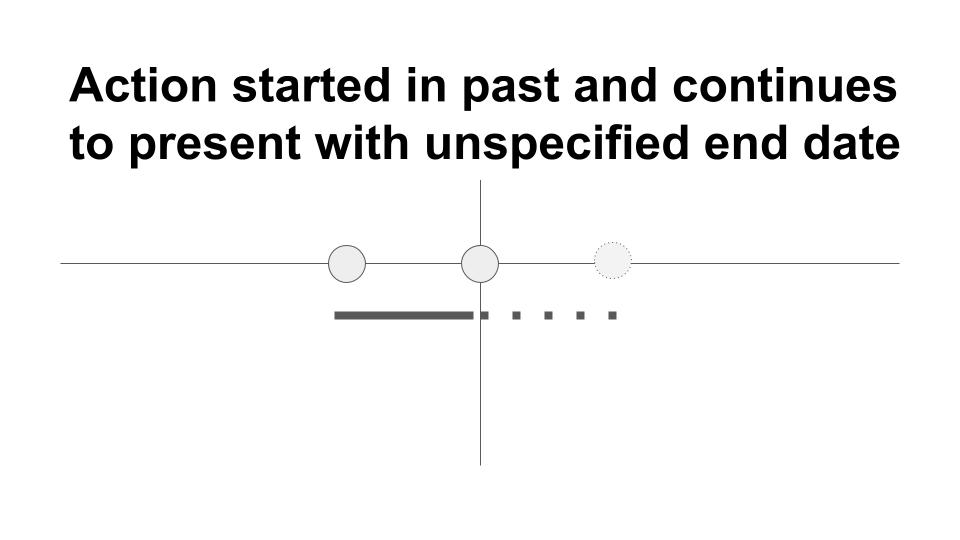 This tense is used:
This tense is used:
- to show an action that began in the past and is still going on: I have not finished that homework assignment yet.
- to show an action that began in the past and was finished at an indefinite time but is
closely related to the present and/or future: Benjamin and Irving have recently announced their engagement. (They are still engaged.)
Words often used to show continued action from the past to the present (present perfect tense) are: since, for, up to the present, until now, so far, for the past hour, for the past few days, in a long time, for a short time, in quite a while, all day, all week, lately. Example: Mbacke and Amari have worked together as business partners for 12 years.
Present perfect tense can also be used for action completed at some point from the past to the present. The intention is simply to state an action took place one or more times; often it is implied that the action may occur again in the future. Words commonly used are: many times, several times, once, twice, three times (etc.), ever, finally, just, already, recently. The words not, never, still and yet are used with the negative. Example: City workers have just repaired one of the damaged bridges.
Present perfect progressive/continuous tense
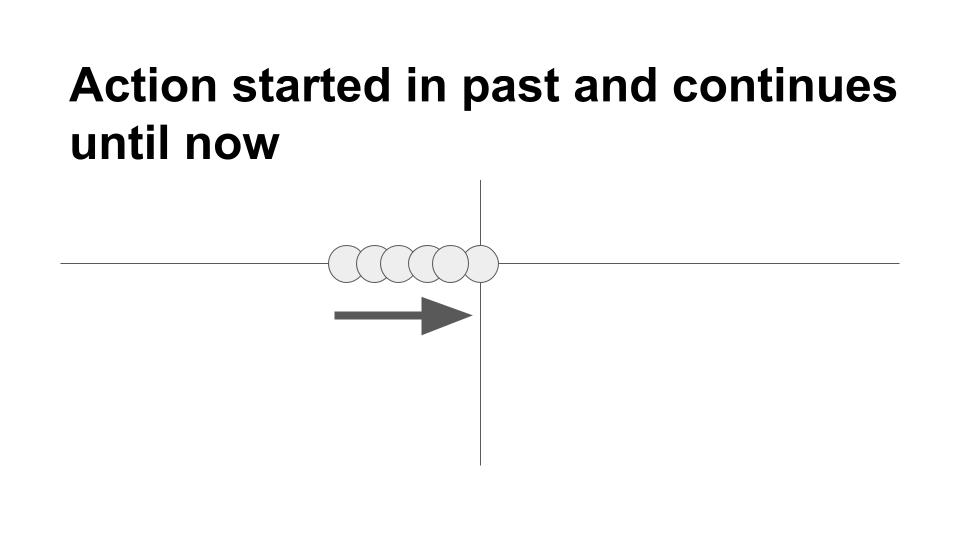 This tense is used to show incompleteness or indefiniteness very close to the present time, often contrasted with now. It shows that the activity is very recent.
This tense is used to show incompleteness or indefiniteness very close to the present time, often contrasted with now. It shows that the activity is very recent.
- Raksha has been asking about you.
- Ms. Goldstein has been trying to call her doctor all morning.
Length of time is mentioned or implied with the present perfect continuous tense. Example: Because of poor sales, corporate profit has been decreasing lately.
Past perfect tense
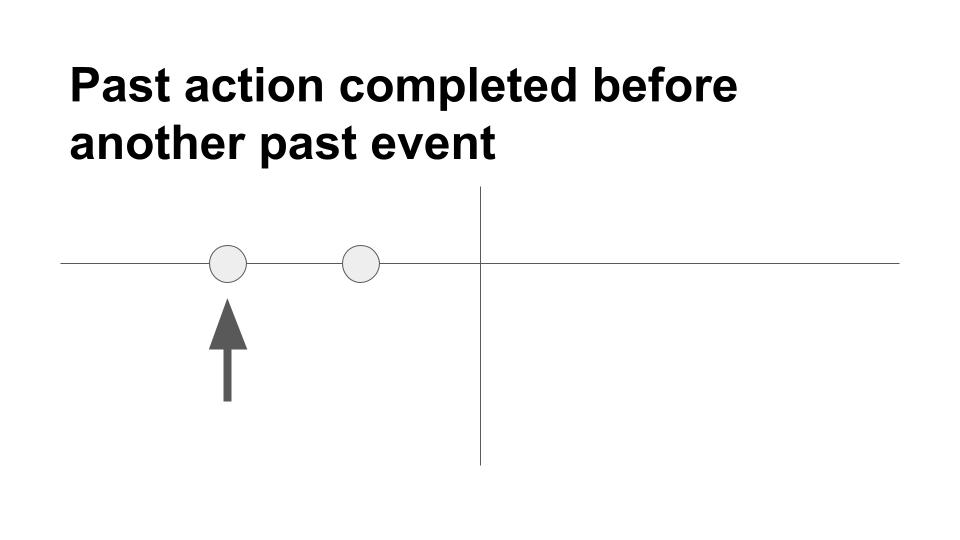 This tense is used to show action in the past that happened before some other action in the past (shown by a past tense verb): Before she came to PCC, Laura had taught in Japan for two years.
This tense is used to show action in the past that happened before some other action in the past (shown by a past tense verb): Before she came to PCC, Laura had taught in Japan for two years.
The past perfect tense is used in sentences with two past actions to show that one of the actions was completed before the other action. Use the past perfect tense for the first completed action, and use the past tense for the second completed action. Example: Vincent suddenly realized that he had seen the film. Sometimes you’ll see these words used with the past perfect tense: before, many times, several times, once, twice, ever, already, just, by the time, still, yet. Example: Before America gained independence, it had been a British colony.
Past perfect progressive/continuous tense
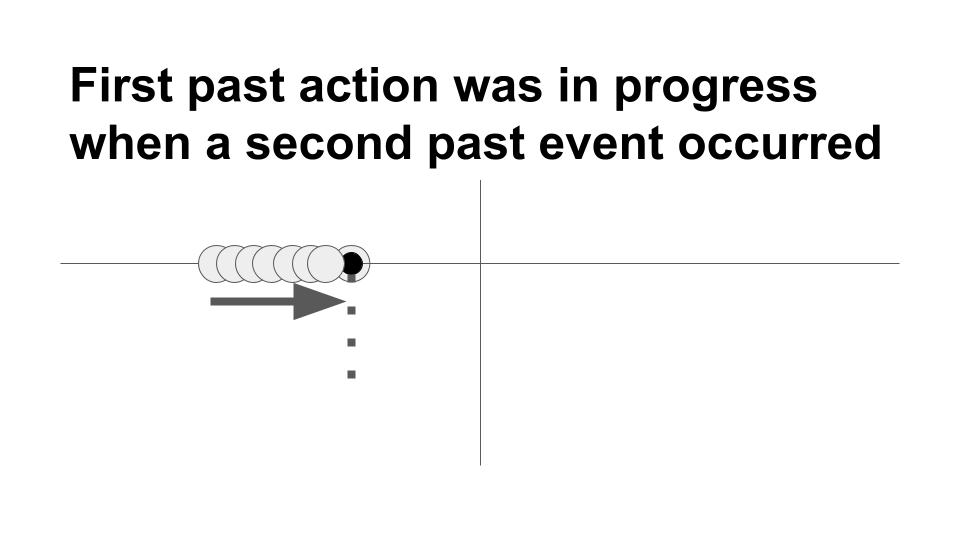 This tense is used to show that:
This tense is used to show that:
- an action in the remote past was temporary, or
- the time it lasted is important, or
- that an action was going on when something else happened.
For example:
- Susana had been looking for a new roommate for six weeks before she finally found one. (temporary)
- Women had been demanding the right to vote for many years before they finally got it. (length of time is important)
- Many people had been swimming in the ocean when the shark was sighted. (the actions going on when something else happened)
- How long had you been looking for a roommate before you finally found one? (yes, we can use this tense in a question)
The past perfect continuous tense is used in sentences with two past actions to emphasize the fact that the first action had been continuous before the second action took place. Length of time is mentioned or implied with the past perfect continuous tense. Example: Vy and Tomas had been talking on Zoom for several minutes when their internet suddenly stopped working.
Future perfect tense
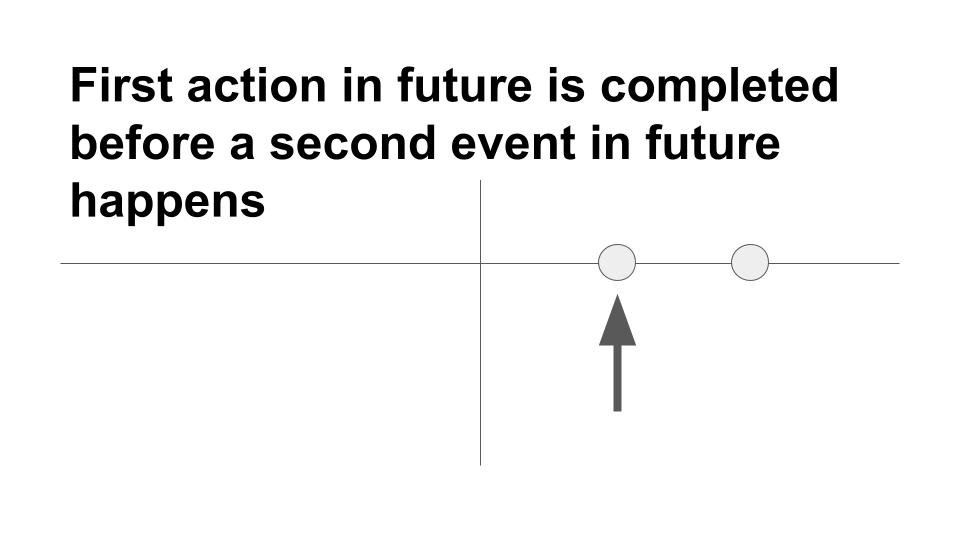 This tense is used to show an action that will be completed in the future. Example: By the end of the winter season, more tourists will have visited Mt. Hood than ever before.
This tense is used to show an action that will be completed in the future. Example: By the end of the winter season, more tourists will have visited Mt. Hood than ever before.
The future perfect tense is used to describe an action that will have been completed by a certain time in the future, often in relation to another action. Example: Although the incident is disturbing to you now, in a few months you will have forgotten all about it.
Future perfect progressive/continuous tense
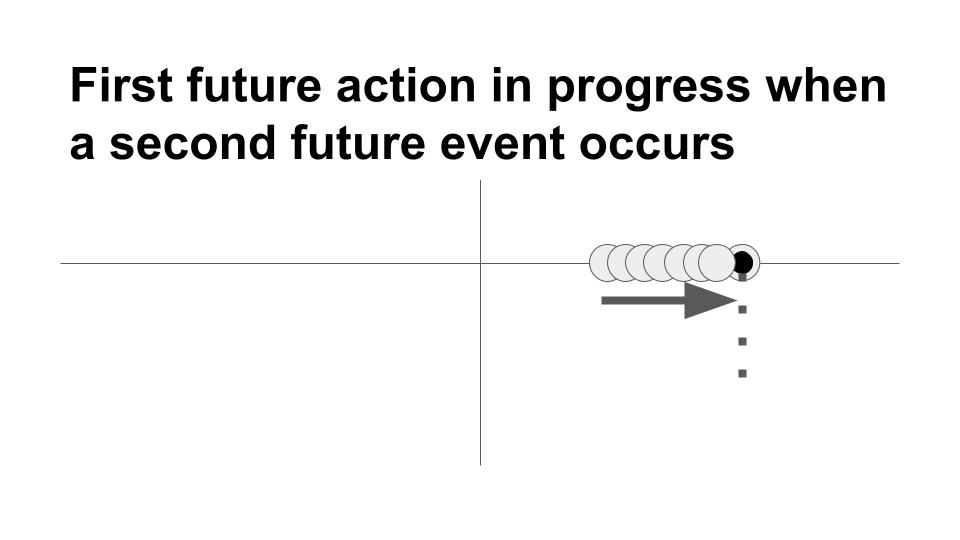 Use this tense to combine the ideas of completeness and duration of time in the future. For example:
Use this tense to combine the ideas of completeness and duration of time in the future. For example:
- Soon he will have been studying at PCC for six months.
- The hikers started out at sunrise this morning; by 8:00 they will have been walking for three hours.
The future perfect progressive/continuous tense is used to describe an action in the future which will have been going on up to a certain designated time or in relation to another action. The length of time is often mentioned with future perfect continuous action. Example: Ignacio will have been writing letters for a few hours when his wife returns.
Comparison of the 12 verb tenses
Look at how the 12 verb tenses change the time, attitude, and relationships … when eating pizza!
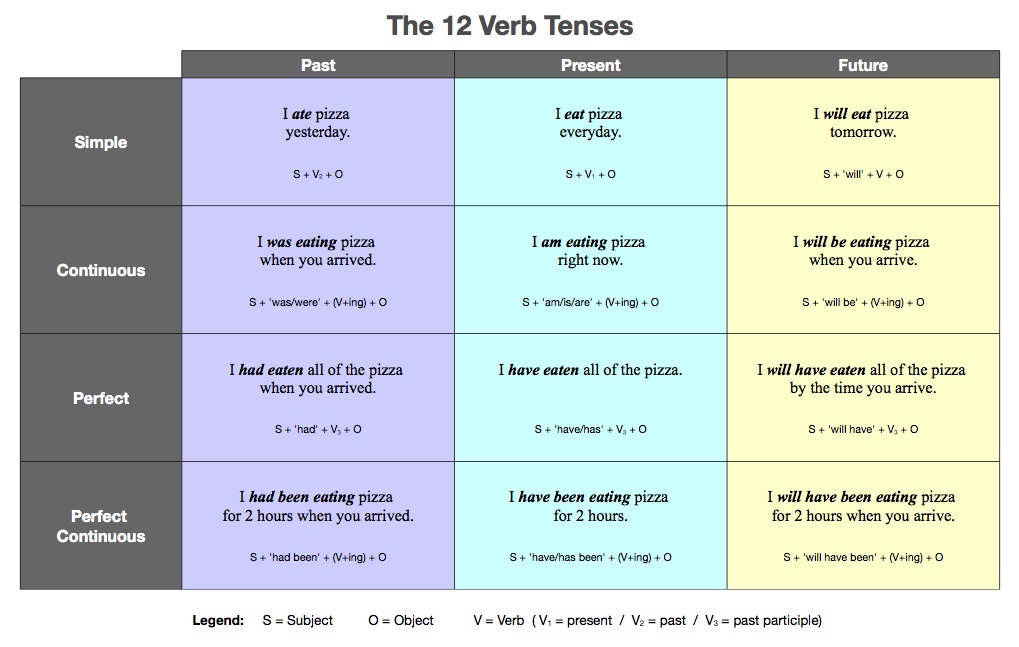
Where to get more information
If you want more instruction and examples, here is a verb tense review handout.
You might also be interested in some of the videos in this SmrtEnglish video playlist (look for the ones about verbs!).
Practice
Now practice with this exercise; it is not graded, and you may repeat it as many times as you wish:
QUIZ
1. We walked in the opposite direction as soon as we realized that we __________________ the wrong path.
- had taken
- were taken
- have taken
- took
2. Masaya couldn’t come to the telephone when Miss Tsuji called him because he __________________ in the laboratory.
- was working
- worked
- has been working
- had been working
3. The deficit __________________ so large, we will probably have to pay additional taxes.
- grows
- was growing
- has growed
- is growing
4. What a lovely night! The moon __________________ brightly.
- shines
- is shining
- shined
- was been shining
5. By next October that couple __________________ together for 25 years.
- will be performed
- will have been performing
- have performed
- will perform
6. By this time next week, the winners __________________ their awards.
- will be received
- will have receive
- will have received
- will have been receiving
7. For some time, Jeff ___________________________his paintings to the Perison Art Gallery.
- is selling
- has selled
- has been selling
- was sold
8. If they __________________ everyone can have a chance to speak.
- took turns answering
- take turns answering
- are take turns answering
- would take turns answering
9. Matthew __________________ her, but he changed his mind.
- was planned to call
- would have call
- would call
- was going to call
10. Last month I read a book about the ethics of a primitive society. This month __________________ a recently published historical novel.
- I’ve reading
- I’d been reading
- I was reading
- I’m reading
Some text has been adapted from a grammar packet prepared by ESOL instructors at the Rock Creek campus of Portland Community College.
The grammar chart about eating pizza has many incarnations on the internet and is believed to be in the public domain.

