The Endomembrane System
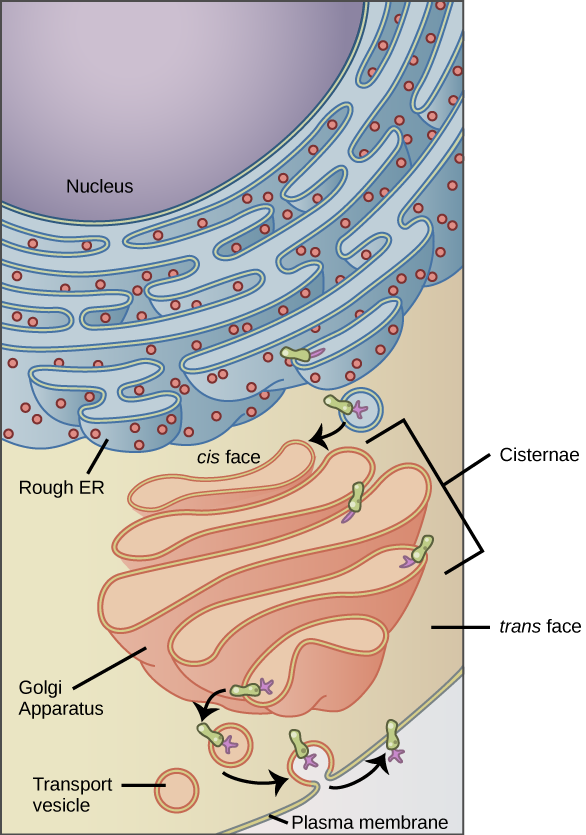
The endomembrane system (endo = within) is a group of membranes and organelles (see Figure 1) in eukaryotic cells that work together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins. It includes the nuclear envelope, lysosomes, and vesicles, the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus, which we will cover shortly. Although not technically within the cell, the plasma membrane is included in the endomembrane system because, as you will see, it interacts with the other endomembranous organelles. None of the organelles that make up the endomembrane system are found in prokaryotes with the exception of the plasma membrane.
References
Unless otherwise noted, images on this page are licensed under CC-BY 4.0 by OpenStax.
Text adapted from: OpenStax, Concepts of Biology. OpenStax CNX. May 18, 2016 http://cnx.org/contents/b3c1e1d2-839c-42b0-a314-e119a8aafbdd@9.10

