Genetic Engineering
Gene Targeting
Although classical methods of studying the function of genes began with a given phenotype and determined the genetic basis of that phenotype, modern techniques allow researchers to start at the DNA sequence level and ask: “What does this gene or DNA element do?” This technique, called reverse genetics, has resulted in reversing the classic genetic methodology. This method would be similar to damaging a body part to determine its function. An insect that loses a wing cannot fly, which means that the function of the wing is flight. The classical genetic method would compare insects that cannot fly with insects that can fly, and observe that the non-flying insects have lost wings. Similarly, mutating or deleting genes provides researchers with clues about gene function. The methods used to disable gene function are collectively called gene targeting. Gene targeting is the use of recombinant DNA vectors to alter the expression of a particular gene, either by introducing mutations in a gene, or by eliminating the expression of a certain gene by deleting a part or all of the gene sequence from the genome of an organism.
Genetic Diagnosis and Gene Therapy
The process of testing for suspected genetic defects before administering treatment is called genetic diagnosis by genetic testing. Depending on the inheritance patterns of a disease-causing gene, family members are advised to undergo genetic testing. For example, women diagnosed with breast cancer are usually advised to have a biopsy so that the medical team can determine the genetic basis of cancer development. Treatment plans are based on the findings of genetic tests that determine the type of cancer. If the cancer is caused by inherited gene mutations, other female relatives are also advised to undergo genetic testing and periodic screening for breast cancer. Genetic testing is also offered for fetuses (or embryos with in vitro fertilization) to determine the presence or absence of disease-causing genes in families with specific debilitating diseases.
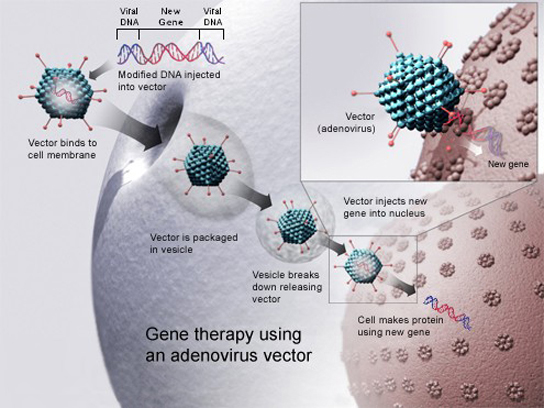
Gene therapy is a genetic engineering technique used to cure disease. In its simplest form, it involves the introduction of a good gene at a random location in the genome to aid the cure of a disease that is caused by a mutated gene. The good gene is usually introduced into diseased cells as part of a vector transmitted by a virus that can infect the host cell and deliver the foreign DNA (Figure 1). More advanced forms of gene therapy try to correct the mutation at the original site in the genome, such as is the case with treatment of severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID).
Production of Vaccines, Antibiotics, and Hormones
Traditional vaccination strategies use weakened or inactive forms of microorganisms to mount the initial immune response. Modern techniques use the genes of microorganisms cloned into vectors to mass produce the desired antigen. The antigen is then introduced into the body to stimulate the primary immune response and trigger immune memory. Genes cloned from the influenza virus have been used to combat the constantly changing strains of this virus.
Antibiotics are a biotechnological product. They are naturally produced by microorganisms, such as fungi, to attain an advantage over bacterial populations. Antibiotics are produced on a large scale by cultivating and manipulating fungal cells.
Recombinant DNA technology was used to produce large-scale quantities of human insulin in E. coli as early as 1978. Previously, it was only possible to treat diabetes with pig insulin, which caused allergic reactions in humans because of differences in the gene product. Currently, the vast majority of diabetes suffers who inject insulin do so with insulin produced by bacteria.
Human growth hormone (HGH) is used to treat growth disorders in children. The HGH gene was cloned from a cDNA library and inserted into E. coli cells by cloning it into a bacterial vector. Bacterial HGH can be used in humans to reduce symptoms of various growth disorders.
Transgenic Animals
Although several recombinant proteins used in medicine are successfully produced in bacteria, some proteins require a eukaryotic animal host for proper processing. For this reason, the desired genes are cloned and expressed in animals, such as sheep, goats, chickens, and mice. Animals that have been modified to express recombinant DNA are called transgenic animals. Several human proteins are expressed in the milk of transgenic sheep and goats, and some are expressed in the eggs of chickens. Mice have been used extensively for expressing and studying the effects of recombinant genes and mutations.
Transgenic Plants
Manipulating the DNA of plants (i.e., creating GMOs) has helped to create desirable traits, such as disease resistance, herbicide and pesticide resistance, better nutritional value, and better shelf-life (Figure 3). Plants are the most important source of food for the human population. Farmers developed ways to select for plant varieties with desirable traits long before modern-day biotechnology practices were established.

Plants that have received recombinant DNA from other species are called transgenic plants. Because they are not natural, transgenic plants and other GMOs are closely monitored by government agencies to ensure that they are fit for human consumption and do not endanger other plant and animal life. Because foreign genes can spread to other species in the environment, extensive testing is required to ensure ecological stability. Staples like corn, potatoes, and tomatoes were the first crop plants to be genetically engineered.
Transformation of Plants Using Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Gene transfer occurs naturally between species in microbial populations. Many viruses that cause human diseases, such as cancer, act by incorporating their DNA into the human genome. In plants, tumors caused by the bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens occur by transfer of DNA from the bacterium to the plant. Although the tumors do not kill the plants, they make the plants stunted and more susceptible to harsh environmental conditions. Many plants, such as walnuts, grapes, nut trees, and beets, are affected by A. tumefaciens. The artificial introduction of DNA into plant cells is more challenging than in animal cells because of the thick plant cell wall.

Researchers used the natural transfer of DNA from Agrobacterium to a plant host to introduce DNA fragments of their choice into plant hosts. In nature, the disease-causing A. tumefaciens have a set of plasmids, called the Ti plasmids (tumor-inducing plasmids), that contain genes for the production of tumors in plants. DNA from the Ti plasmid integrates into the infected plant cell’s genome. Researchers manipulate the Ti plasmids to remove the tumor-causing genes and insert the desired DNA fragment for transfer into the plant genome. The Ti plasmids carry antibiotic resistance genes to aid selection and can be propagated in E. coli cells as well.
The Organic Insecticide Bacillus thuringiensis
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) is a bacterium that produces protein crystals during sporulation that are toxic to many insect species that affect plants. Bt toxin has to be ingested by insects for the toxin to be activated. Insects that have eaten Bt toxin stop feeding on the plants within a few hours. After the toxin is activated in the intestines of the insects, death occurs within a couple of days. Modern biotechnology has allowed plants to encode their own crystal Bt toxin that acts against insects. The crystal toxin genes have been cloned from Bt and introduced into plants. Bt toxin has been found to be safe for the environment, non-toxic to humans and other mammals, and is approved for use by organic farmers as a natural insecticide.
Flavr Savr Tomato
The first GM crop to be introduced into the market was the Flavr Savr Tomato produced in 1994. Antisense RNA technology was used to slow down the process of softening and rotting caused by fungal infections, which led to increased shelf life of the GM tomatoes. Additional genetic modification improved the flavor of this tomato. The Flavr Savr tomato did not successfully stay in the market because of problems maintaining and shipping the crop.
References
Unless otherwise noted, images on this page are licensed under CC-BY 4.0 by OpenStax.
OpenStax, Biology. OpenStax CNX. May 27, 2016 http://cnx.org/contents/s8Hh0oOc@9.10:8CA_YwJq@3/Cloning-and-Genetic-Engineerin
Moen I, Jevne C, Kalland K-H, Chekenya M, Akslen LA, Sleire L, Enger P, Reed RK, Oyan AM, Stuhr LEB. 2012. Gene expression in tumor cells and stroma in dsRed 4T1 tumors in eGFP-expressing mice with and without enhanced oxygenation. BMC Cancer. 12:21. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-12-21 PDF

