Levels of Organization
Living things are highly organized and structured, following a hierarchy that can be examined on a scale from small to large. The atom is the smallest and most fundamental unit of matter. It consists of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. Atoms form molecules. A molecule is a chemical structure consisting of at least two atoms held together by one or more chemical bonds. Many molecules that are biologically important are macromolecules, large molecules that are typically formed by polymerization (a polymer is a large molecule that is made by combining smaller units called monomers, which are simpler than macromolecules). An example of a macromolecule is deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) (Figure 1), which contains the instructions for the structure and functioning of all living organisms. See the section of your textbook about the chemistry of biological molecules for more information.
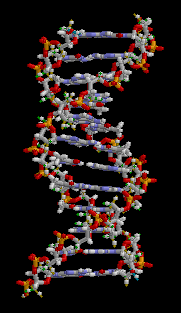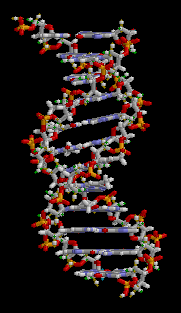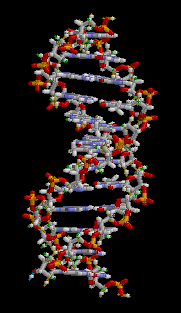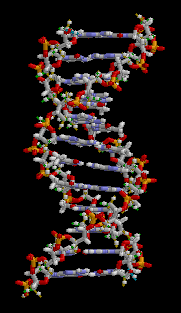
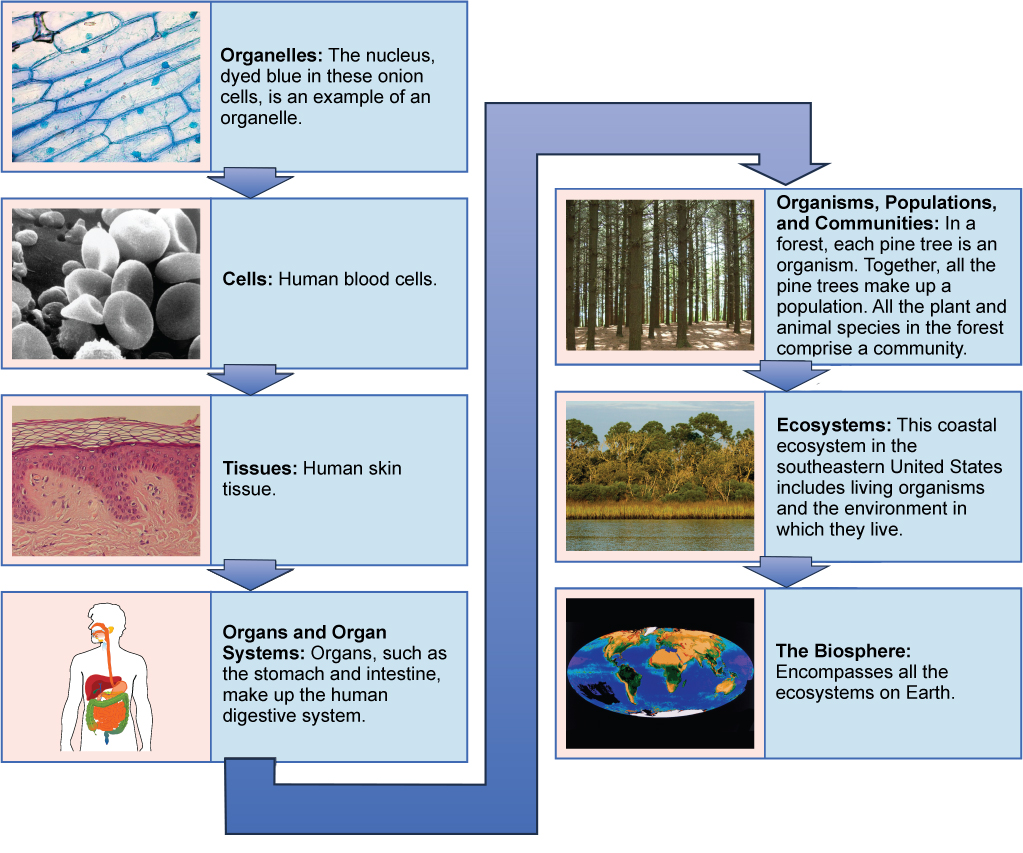
Some cells contain aggregates of macromolecules surrounded by membranes; these are called organelles. Organelles are small structures that exist within cells. Examples of organelles include mitochondria and chloroplasts, which carry out indispensable functions: mitochondria produce energy to power the cell, while chloroplasts enable green plants to utilize the energy in sunlight to make sugars. All living things are made of cells; the cell itself is the smallest fundamental unit of structure and function in living organisms. This requirement is one of the reasons why viruses are not considered living: they are not made of cells. To make new viruses, they have to invade and hijack the reproductive mechanism of a living cell; only then can they obtain the materials they need to reproduce. Some organisms consist of a single cell and others are multicellular. Cells are classified as prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Prokaryotes are single-celled or colonial organisms that do not have membrane-bound nuclei; in contrast, the cells of eukaryotes do have membrane-bound organelles and a membrane-bound nucleus.
In larger organisms, cells combine to make tissues, which are groups of similar cells carrying out similar or related functions. Organs are collections of tissues grouped together performing a common function. Organs are present not only in animals but also in plants. An organ system is a higher level of organization that consists of functionally related organs. Mammals have many organ systems. For instance, the circulatory system transports blood through the body and to and from the lungs; it includes organs such as the heart and blood vessels. Organisms are individual living entities. For example, each tree in a forest is an organism. Single-celled prokaryotes and single-celled eukaryotes are also considered organisms and are typically referred to as microorganisms.
All the individuals of a species living within a specific area are collectively called a population. For example, a forest may include many pine trees. All of these pine trees represent the population of pine trees in this forest. Different populations may live in the same specific area. For example, the forest with the pine trees includes populations of flowering plants and also insects and microbial populations. A community is the sum of populations inhabiting a particular area. For instance, all of the trees, flowers, insects, and other populations in a forest form the forest’s community. The forest itself is an ecosystem. An ecosystem consists of all the living things in a particular area together with the abiotic, non-living parts of that environment such as nitrogen in the soil or rain water. At the highest level of organization, the biosphere is the collection of all ecosystems, and it represents the zones of life on earth. It includes land, water, and even the atmosphere to a certain extent.
References
Unless otherwise noted, images on this page are licensed under CC-BY 4.0 by OpenStax.
Text adapted from: OpenStax, Concepts of Biology. OpenStax CNX. May 25, 2017 https://cnx.org/contents/GFy_h8cu@10.99:gNLp76vu@13/Themes-and-Concepts-of-Biology

