Comparing Meiosis and Mitosis
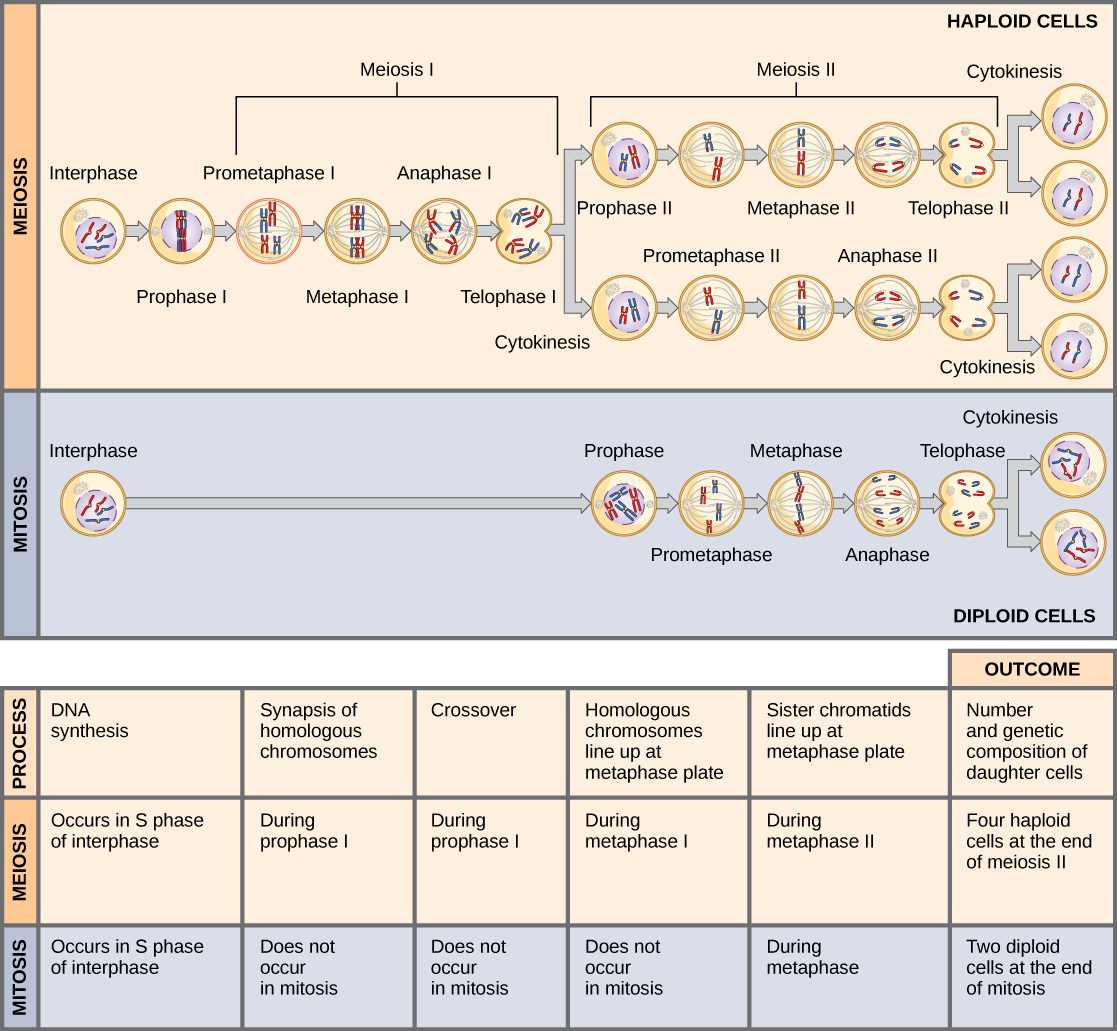
Mitosis and meiosis, which are both forms of division of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells, share some similarities, but also exhibit distinct differences that lead to their very different outcomes. Mitosis is a single nuclear division that results in two nuclei, usually partitioned into two new cells. The nuclei resulting from a mitotic division are genetically identical to the original. They have the same number of sets of chromosomes: one in the case of haploid cells, and two in the case of diploid cells. On the other hand, meiosis is two nuclear divisions that result in four nuclei, usually partitioned into four new cells. The nuclei resulting from meiosis are never genetically identical, and they contain one chromosome set only—this is half the number of the original cell, which was diploid.
The differences in the outcomes of meiosis and mitosis occur because of differences in the behavior of the chromosomes during each process. Most of these differences in the processes occur in meiosis I, which is a very different nuclear division than mitosis. In meiosis I, the homologous chromosome pairs become associated with each other, are bound together, experience chiasmata and crossover between sister chromatids, and line up along the metaphase plate in tetrads with spindle fibers from opposite spindle poles attached to each kinetochore of a homolog in a tetrad. All of these events occur only in meiosis I, never in mitosis.
Homologous chromosomes move to opposite poles during meiosis I so the number of sets of chromosomes in each nucleus-to-be is reduced from two to one. For this reason, meiosis I is referred to as a reduction division. There is no such reduction in ploidy level in mitosis.
Meiosis II is much more analogous to a mitotic division. In this case, duplicated chromosomes (only one set of them) line up at the center of the cell with divided kinetochores attached to spindle fibers from opposite poles. During anaphase II, as in mitotic anaphase, the kinetochores divide and one sister chromatid is pulled to one pole and the other sister chromatid is pulled to the other pole. If it were not for the fact that there had been crossovers, the two products of each meiosis II division would be identical as in mitosis; instead, they are different because there has always been at least one crossover per chromosome. Meiosis II is not a reduction division because, although there are fewer copies of the genome in the resulting cells, there is still one set of chromosomes, as there was at the end of meiosis I.
Cells produced by mitosis will function in different parts of the body as a part of growth or replacing dead or damaged cells. They may even be involved in asexual reproduction in some organisms. Cells produced by meiosis in a diploid-dominant organism such as an animal will only participate in sexual reproduction.
References
Unless otherwise noted, images on this page are licensed under CC-BY 4.0 by OpenStax.
OpenStax, Biology. OpenStax CNX. May 27, 2016http://cnx.org/contents/s8Hh0oOc@9.10:1Q8z96mT@4/Meiosis

