Determining Evolutionary Relationships
Scientists must collect accurate information that allows them to make evolutionary connections among organisms. Similar to detective work, scientists must use evidence to uncover the facts. In the case of phylogeny, evolutionary investigations focus on two types of evidence: morphologic (form and function) and genetic.
Two Options for Similarities
In general, organisms that share similar physical features and genomes tend to be more closely related than those that do not. Such features that overlap both morphologically (in form) and genetically are referred to as homologous structures; they stem from developmental similarities that are based on evolution. For example, the bones in the wings of bats and birds have homologous structures (Figure 1).
Notice it is not simply a single bone, but rather a grouping of several bones arranged in a similar way. The more complex the feature, the more likely any kind of overlap is due to a common evolutionary past. Imagine two people from different countries both inventing a car with all the same parts and in exactly the same arrangement without any previous or shared knowledge. That outcome would be highly improbable. However, if two people both invented a hammer, it would be reasonable to conclude that both could have the original idea without the help of the other. The same relationship between complexity and shared evolutionary history is true for homologous structures in organisms.
Misleading Appearances
Some organisms may be very closely related, even though a minor genetic change caused a major morphological difference to make them look quite different. Similarly, unrelated organisms may be distantly related, but appear very much alike. This usually happens because both organisms were in common adaptations that evolved within similar environmental conditions. When similar characteristics occur because of environmental constraints and not due to a close evolutionary relationship, it is called an analogy or homoplasy. For example, insects use wings to fly like bats and birds, but the wing structure and embryonic origin is completely different. These are called analogous structures (Figure 2).
Similar traits can be either homologous or analogous. Homologous structures share a similar embryonic origin; analogous organs have a similar function. For example, the bones in the front flipper of a whale are homologous to the bones in the human arm. These structures are not analogous. The wings of a butterfly and the wings of a bird are analogous but not homologous. Some structures are both analogous and homologous: the wings of a bird and the wings of a bat are both homologous and analogous. Scientists must determine which type of similarity a feature exhibits to decipher the phylogeny of the organisms being studied.
Molecular Comparisons
With the advancement of DNA technology, the area of molecular systematics, which describes the use of information on the molecular level including DNA analysis, has blossomed. New computer programs not only confirm many earlier classified organisms, but also uncover previously made errors. As with physical characteristics, even the DNA sequence can be tricky to read in some cases. For some situations, two very closely related organisms can appear unrelated if a mutation occurred that caused a shift in the genetic code. An insertion or deletion mutation would move each nucleotide base over one place, causing two similar codes to appear unrelated.
Sometimes two segments of DNA code in distantly related organisms randomly share a high percentage of bases in the same locations, causing these organisms to appear closely related when they are not. For both of these situations, computer technologies have been developed to help identify the actual relationships, and, ultimately, the coupled use of both morphologic and molecular information is more effective in determining phylogeny.
Why Does Phylogeny Matter?
Evolutionary biologists could list many reasons why understanding phylogeny is important to everyday life in human society. For botanists, phylogeny acts as a guide to discovering new plants that can be used to benefit people. Think of all the ways humans use plants—food, medicine, and clothing are a few examples. If a plant contains a compound that is effective in treating cancer, scientists might want to examine all of the relatives of that plant for other useful drugs.
A research team in China identified a segment of DNA thought to be common to some medicinal plants in the family Fabaceae (the legume family) and worked to identify which species had this segment (Figure 3). After testing plant species in this family, the team found a DNA marker (a known location on a chromosome that enabled them to identify the species) present. Then, using the DNA to uncover phylogenetic relationships, the team could identify whether a newly discovered plant was in this family and assess its potential medicinal properties.
Building Phylogenetic Trees
How do scientists construct phylogenetic trees? After the homologous and analogous traits are sorted, scientists often organize the homologous traits using a system called cladistics. This system sorts organisms into clades: groups of organisms that descended from a single ancestor. For example, in Figure 4, all of the organisms in the orange region evolved from a single ancestor that had amniotic eggs. Consequently, all of these organisms also have amniotic eggs and make a single clade, also called a monophyletic group. Clades must include all of the descendants from a branch point.
Which animals in this figure belong to a clade that includes animals with hair? Which evolved first, hair or the amniotic egg?
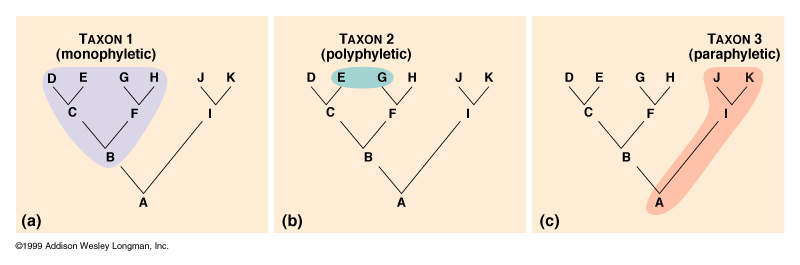
Clades can vary in size depending on which branch point is being referenced. The important factor is that all of the organisms in the clade or monophyletic group stem from a single point on the tree. This can be remembered because monophyletic breaks down into “mono,” meaning one, and “phyletic,” meaning evolutionary relationship. Figure 5 shows various examples of clades. Notice how each clade comes from a single point, whereas the non-clade groups show branches that do not share a single point.
Groups that do not include all organisms that descended from a single ancestor have different names. A paraphyletic group includes the most recent common ancestor, but not all of its descendants (Figure 6). A polyphyletic group includes unrelated organisms descended from more than one ancestor.
Shared Characteristics
Organisms evolve from common ancestors and then diversify. Scientists use the phrase “descent with modification” because even though related organisms have many of the same characteristics and genetic codes, changes occur. This pattern repeats over and over as one goes through the phylogenetic tree of life:
- A change in the genetic makeup of an organism leads to a new trait which becomes prevalent in the group.
- Many organisms descend from this point and have this trait.
- New variations continue to arise: some are adaptive and persist, leading to new traits.
- With new traits, a new branch point is determined (go back to step 1 and repeat).
If a characteristic is found in the ancestor of a group, it is considered a shared ancestral character because all of the organisms in the taxon or clade have that trait. The vertebrate in Figure 4 is a shared ancestral character. Now consider the amniotic egg characteristic in the same figure. Only some of the organisms in Figure 4 have this trait, and to those that do, it is called a shared derived character because this trait derived at some point but does not include all of the ancestors in the tree.
The tricky aspect to shared ancestral and shared derived characters is the fact that these terms are relative. The same trait can be considered one or the other depending on the particular diagram being used. Returning to Figure 4, note that the amniotic egg is a shared ancestral character for the Amniota clade, while having hair is a shared derived character for some organisms in this group. These terms help scientists distinguish between clades in the building of phylogenetic trees.
Choosing the Right Relationships
Imagine being the person responsible for organizing all of the items in a department store properly—an overwhelming task. Organizing the evolutionary relationships of all life on Earth proves much more difficult: scientists must span enormous blocks of time and work with information from long-extinct organisms. Trying to decipher the proper connections, especially given the presence of homologies and analogies, makes the task of building an accurate tree of life extraordinarily difficult. Add to that the advancement of DNA technology, which now provides large quantities of genetic sequences to be used and analyzed. Taxonomy is a subjective discipline: many organisms have more than one connection to each other, so each taxonomist will decide the order of connections.
To aid in the tremendous task of describing phylogenies accurately, scientists often use a concept called maximum parsimony, which means that events occurred in the simplest, most obvious way. For example, if a group of people entered a forest preserve to go hiking, based on the principle of maximum parsimony, one could predict that most of the people would hike on established trails rather than forge new ones.
For scientists deciphering evolutionary pathways, the same idea is used: the pathway of evolution probably includes the fewest major events that coincide with the evidence at hand. Starting with all of the homologous traits in a group of organisms, scientists look for the most obvious and simple order of evolutionary events that led to the occurrence of those traits.
These tools and concepts are only a few of the strategies scientists use to tackle the task of revealing the evolutionary history of life on Earth. Recently, newer technologies have uncovered surprising discoveries with unexpected relationships, such as the fact that people seem to be more closely related to fungi than fungi are to plants. Sound unbelievable? As the information about DNA sequences grows, scientists will become closer to mapping the evolutionary history of all life on Earth.
Summary
To build phylogenetic trees, scientists must collect accurate information that allows them to make evolutionary connections between organisms. Using morphologic and molecular data, scientists work to identify homologous characteristics and genes. Similarities between organisms can stem either from shared evolutionary history (homologies) or from separate evolutionary paths (analogies). Newer technologies can be used to help distinguish homologies from analogies. After homologous information is identified, scientists use cladistics to organize these events as a means to determine an evolutionary timeline. Scientists apply the concept of maximum parsimony, which states that the order of events probably occurred in the most obvious and simple way with the least amount of steps. For evolutionary events, this would be the path with the least number of major divergences that correlate with the evidence.
References
OpenStax, Biology. OpenStax CNX. June 25, 2020. https://cnx.org/contents/GFy_h8cu@10.137:noBcfThl@7/Understanding-Evolution.

